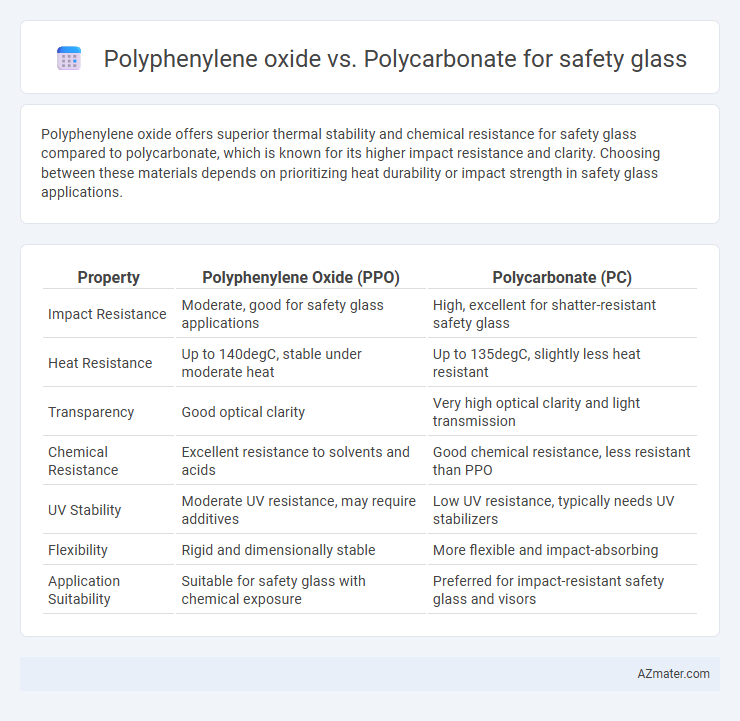
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance for safety glass compared to polycarbonate, which is known for its higher impact resistance and clarity. Choosing between these materials depends on prioritizing heat durability or impact strength in safety glass applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, good for safety glass applications | High, excellent for shatter-resistant safety glass |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 140degC, stable under moderate heat | Up to 135degC, slightly less heat resistant |
| Transparency | Good optical clarity | Very high optical clarity and light transmission |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and acids | Good chemical resistance, less resistant than PPO |
| UV Stability | Moderate UV resistance, may require additives | Low UV resistance, typically needs UV stabilizers |
| Flexibility | Rigid and dimensionally stable | More flexible and impact-absorbing |
| Application Suitability | Suitable for safety glass with chemical exposure | Preferred for impact-resistant safety glass and visors |
Introduction to Safety Glass Materials
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) and polycarbonate (PC) are essential polymers used in safety glass applications due to their exceptional impact resistance and clarity. PPO offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for environments requiring durability under high temperatures. Polycarbonate is preferred for its outstanding toughness and light weight, providing enhanced shatter resistance crucial for protective eyewear, automotive windows, and security glazing.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, impact resistance, and thermal properties, making it suitable for safety glass applications where durability and clarity are essential. PPO offers superior chemical resistance and maintains mechanical strength at elevated temperatures compared to polycarbonate, which is beneficial for environments exposed to harsh conditions. Its inherent flame retardancy and low moisture absorption contribute to the long-term reliability of safety glass components in automotive and architectural uses.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a highly durable thermoplastic polymer widely used in safety glass applications due to its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for protective barriers and glazing. It offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), ensuring enhanced shatter resistance and long-term performance under varying environmental conditions. PC also exhibits excellent UV resistance and dimensional stability, maintaining transparency and structural integrity in demanding safety glass scenarios.
Mechanical Strength: PPO vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate offers superior mechanical strength compared to polyphenylene oxide, with higher impact resistance and greater tensile strength, making it the preferred material for safety glass applications. Polycarbonate exhibits excellent durability against mechanical stress and deformation, ensuring greater protection under high-impact conditions. While PPO provides good thermal stability, its mechanical performance is inferior to polycarbonate, limiting its use in safety-critical glazing systems.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior optical clarity with high light transmission rates above 90%, making it an excellent choice for safety glass applications requiring minimal visual distortion. Polycarbonate provides robust impact resistance but tends to have slightly lower optical clarity and light transmission, typically around 88-90%, due to its inherent material properties. Selecting polyphenylene oxide enhances transparency and visual performance, while polycarbonate balances clarity with greater impact durability.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance compared to polyphenylene oxide, making it a preferred choice for safety glass applications requiring high durability and shatterproof performance. Polycarbonate can withstand impact forces up to 250 times greater than glass, whereas polyphenylene oxide offers moderate resistance but lacks the toughness essential for critical safety installations. The enhanced toughness and flexibility of polycarbonate ensure better energy absorption and crack prevention under extreme conditions.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability with a heat deflection temperature typically around 210degC, making it highly resistant to deformation under elevated temperatures compared to polycarbonate (PC), which usually withstands up to 145degC. In terms of chemical resistance, PPO offers enhanced resistance to solvents, acids, and alkalis, ensuring longer durability in harsh chemical environments, whereas polycarbonate is more prone to stress cracking and degradation when exposed to certain chemicals. These properties make PPO a preferred choice for safety glass applications requiring robust heat and chemical resistance.
Durability and Weatherability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior weatherability compared to polycarbonate, maintaining clarity and mechanical properties even after prolonged UV exposure, making it ideal for safety glass in outdoor applications. Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance but tends to yellow and degrade more rapidly under UV radiation, reducing its durability over time. PPO's excellent thermal stability and resistance to environmental stress cracking enhance the lifespan and safety performance of glazing materials.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers lower raw material costs and easier injection molding processes compared to polycarbonate, making it more economical for safety glass frames and components. Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance and thermal stability but requires higher processing temperatures and more complex tooling, increasing manufacturing expenses. Cost-efficiency analysis favors PPO for large-scale production, while polycarbonate is preferred where enhanced durability justifies the higher investment.
Applications and Recommendations for Safety Glass
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for safety glass applications in high-temperature environments such as automotive and industrial settings. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity, commonly used in protective eyewear, bulletproof glass, and windshields. For safety glass, polycarbonate is recommended when maximum impact strength and light transmission are critical, while PPO suits applications requiring enhanced thermal endurance and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polycarbonate for Safety glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com