Woodfree paper, made from chemically processed pulp, features a smooth surface with low absorbency, making it suitable for printing but less effective for absorbing ink. Blotting paper, highly porous and absorbent, is specifically designed to quickly soak up excess ink, preventing smudging on writing surfaces.
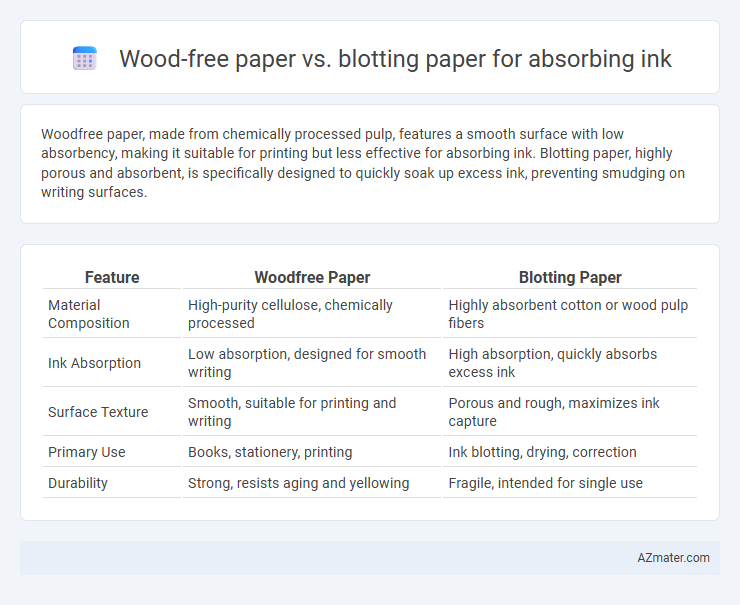
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Woodfree Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity cellulose, chemically processed | Highly absorbent cotton or wood pulp fibers |
| Ink Absorption | Low absorption, designed for smooth writing | High absorption, quickly absorbs excess ink |
| Surface Texture | Smooth, suitable for printing and writing | Porous and rough, maximizes ink capture |
| Primary Use | Books, stationery, printing | Ink blotting, drying, correction |
| Durability | Strong, resists aging and yellowing | Fragile, intended for single use |
Introduction to Ink Absorption in Paper Types
Woodfree paper, primarily composed of chemical pulp without mechanical fibers, offers a smooth surface that absorbs ink moderately, preventing excessive spreading and maintaining print clarity. Blotting paper, made from highly absorbent fibers with a rough texture, excels in rapidly soaking up excess ink, thereby minimizing smudging on writing surfaces. The difference in fiber composition and surface texture directly influences the ink absorption rate and suitability of each paper type for various ink-based applications.
What Is Woodfree Paper?
Woodfree paper is a high-quality, uncoated paper made from chemical pulp that contains minimal lignin, resulting in a smooth, durable surface ideal for printing and writing. Unlike blotting paper, which is highly absorbent and designed specifically to soak up excess ink quickly, woodfree paper has a lower absorbency to prevent ink from spreading or bleeding, ensuring sharp, clear text and images. This characteristic makes woodfree paper suitable for documents and books where precision and readability are essential.
What Is Blotting Paper?
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent type of paper specifically designed to soak up excess ink quickly without smudging, making it ideal for drying handwritten documents or artwork. Unlike woodfree paper, which contains less lignin and is primarily aimed at printing quality, blotting paper's porous texture enhances ink absorption efficiency. Its composition allows rapid moisture absorption, preventing ink from spreading or blurring on the surface.
Physical Structure and Composition Comparison
Woodfree paper, primarily composed of chemical pulp with minimal lignin, features a smoother surface and denser fiber network that limits ink absorption, making it ideal for printing but less effective at soaking ink. Blotting paper consists of loosely arranged, highly porous fibers with a high capillarity rate, allowing it to absorb excessive ink rapidly and prevent smudging on handwritten documents. The physical structure differences--dense and compact in woodfree paper versus open and fibrous in blotting paper--directly influence their distinct ink absorption capabilities.
Ink Absorption Efficiency: Woodfree vs Blotting Paper
Blotting paper exhibits superior ink absorption efficiency compared to woodfree paper due to its porous and fibrous structure, which quickly draws and traps excess ink from surfaces. Woodfree paper, commonly used for printing and writing, has a smoother, less absorbent surface that slows ink penetration and minimizes feathering, but holds less ink overall. In applications requiring rapid and high-capacity ink absorption, blotting paper remains the optimal choice.
Paper Porosity and Its Role in Absorption
Woodfree paper features lower porosity due to its tightly bonded fibers, resulting in slower ink absorption and reduced feathering effects. In contrast, blotting paper exhibits high porosity with an open fiber structure that rapidly absorbs excess ink, preventing smudging and promoting faster drying times. The degree of porosity directly influences absorption capacity, making blotting paper ideal for managing wet ink while woodfree paper suits printing where ink stability is essential.
Application Scenarios: Best Uses for Each Paper
Woodfree paper, characterized by its smooth surface and minimal absorbency, is ideal for high-quality inkjet printing, allowing precise ink placement without excessive spreading, making it suitable for documents, flyers, and brochures requiring sharp text and images. In contrast, blotting paper's high absorbency excels in scenarios such as drying freshly written ink in calligraphy, fountain pen writing, and laboratory applications where rapid ink absorption prevents smudging. For artistic and professional uses demanding ink clarity and fast absorption, choosing between woodfree and blotting paper depends on whether the priority is controlled ink distribution or quick drying and ink removal.
Durability and Handling of Absorbed Ink
Woodfree paper offers moderate ink absorption with smoother surface durability, preventing excessive ink bleeding and ensuring handling stability. Blotting paper excels in rapid ink absorption, effectively preventing smudging but tends to be more fragile and prone to tearing when saturated. For projects requiring durable handling after ink absorption, woodfree paper provides a balanced solution, whereas blotting paper is ideal for quick ink drying despite compromised durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Woodfree paper, made from chemical pulp with minimal lignin, offers smooth surfaces ideal for printing but has limited ink absorption compared to blotting paper, which is highly porous and designed to absorb excess ink efficiently. In terms of environmental impact, woodfree paper production typically consumes significant energy and chemicals, raising sustainability concerns, whereas blotting paper often uses recycled fibers and minimal processing, resulting in a lower ecological footprint. Choosing blotting paper enhances sustainability by reducing resource consumption and waste, making it a more eco-friendly option for ink absorption tasks.
Conclusion: Which Paper Is Superior for Absorbing Ink?
Woodfree paper offers smoother surfaces and minimal ink absorption, making it ideal for sharp, precise printing but less effective for absorbing excess ink. Blotting paper, designed with high porosity and superior absorbency, excels at quickly soaking up excess ink, preventing smudging and enhancing drying time. For applications prioritizing ink absorption, blotting paper is superior, while woodfree paper suits tasks requiring clarity and minimal ink spread.
Infographic: Woodfree paper vs Blotting paper for Absorbing ink
 azmater.com
azmater.com