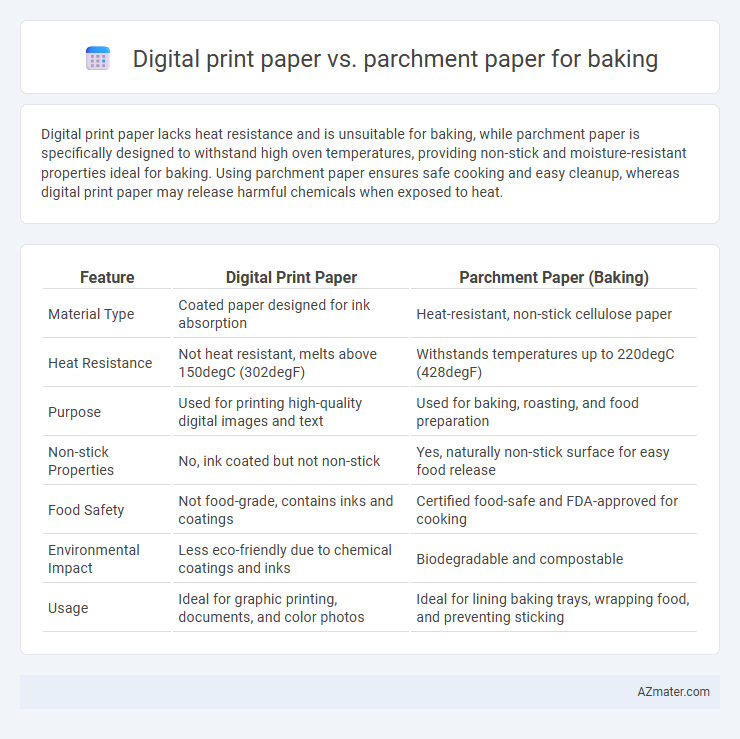
Digital print paper lacks heat resistance and is unsuitable for baking, while parchment paper is specifically designed to withstand high oven temperatures, providing non-stick and moisture-resistant properties ideal for baking. Using parchment paper ensures safe cooking and easy cleanup, whereas digital print paper may release harmful chemicals when exposed to heat.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Print Paper | Parchment Paper (Baking) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Coated paper designed for ink absorption | Heat-resistant, non-stick cellulose paper |
| Heat Resistance | Not heat resistant, melts above 150degC (302degF) | Withstands temperatures up to 220degC (428degF) |
| Purpose | Used for printing high-quality digital images and text | Used for baking, roasting, and food preparation |
| Non-stick Properties | No, ink coated but not non-stick | Yes, naturally non-stick surface for easy food release |
| Food Safety | Not food-grade, contains inks and coatings | Certified food-safe and FDA-approved for cooking |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly due to chemical coatings and inks | Biodegradable and compostable |
| Usage | Ideal for graphic printing, documents, and color photos | Ideal for lining baking trays, wrapping food, and preventing sticking |
Understanding Digital Print Paper and Parchment Paper
Digital print paper, designed primarily for high-resolution images and text reproduction, is not suitable for baking as it lacks heat resistance and can release harmful chemicals when exposed to oven temperatures. Parchment paper, made from cellulose fibers and coated with silicone, offers excellent non-stick properties and withstands high baking temperatures without emitting toxins, making it ideal for lining baking trays and preventing food from sticking. Understanding the composition and heat tolerance of both papers is crucial to ensure safe and effective baking practices.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Digital print paper for baking is typically made from thin, food-safe cardstock or lightweight paper coated with an ink-receptive surface designed for high-resolution digital printing, but it lacks heat resistance and greaseproof properties essential for baking. Parchment paper, composed of cellulose fibers treated with silicone, undergoes a coating process that creates a non-stick, heat-resistant surface preventing sticking and ensuring durability at baking temperatures up to 420degF (215degC). Manufacturing digital print paper emphasizes print quality and ink adhesion, whereas parchment paper production prioritizes chemical treatment for heat resistance, non-stick qualities, and moisture barrier performance to withstand prolonged oven exposure.
Heat Resistance and Oven Safety
Digital print paper typically lacks the heat resistance required for baking, making it unsafe for oven use due to potential melting or burning. Parchment paper is specifically designed to withstand high oven temperatures, usually up to 420-450degF (215-230degC), ensuring safety and preventing food from sticking. Choosing parchment paper over digital print paper reduces the risk of fire hazards and contamination when baking.
Non-Stick Properties Compared
Digital print paper for baking typically lacks inherent non-stick properties and may require additional greasing to prevent food from sticking, unlike parchment paper which is naturally non-stick due to its silicone coating. Parchment paper's heat-resistant silicone layer ensures easy release of baked goods, reducing the risk of tearing or sticking during baking. For consistent non-stick performance and hassle-free cleanup, parchment paper is preferred over digital print paper in baking applications.
Food Safety and Chemical Concerns
Digital print paper used in baking often contains inks and coatings that may release harmful substances when exposed to high temperatures, raising food safety concerns. Parchment paper, made from cellulose and typically coated with silicone, is heat-resistant and non-toxic, making it safer for direct contact with food during baking. Choosing parchment paper minimizes chemical exposure and ensures compliance with food safety standards, unlike many digitally printed alternatives.
Baking Performance: Evenness and Texture
Digital print paper lacks heat resistance and moisture control, often resulting in uneven baking and soggy textures when used for baking purposes. Parchment paper is specifically designed for baking, offering excellent heat resistance and non-stick properties that promote even heat distribution and a crisp, well-baked texture. Professional bakers rely on parchment paper to prevent sticking and ensure consistent results, unlike digital print paper which may compromise the quality and appearance of baked goods.
Versatility in Culinary Applications
Digital print paper offers vibrant designs suitable for food presentation but lacks heat resistance and non-stick properties essential for baking. Parchment paper ensures even heat distribution and prevents sticking, making it ideal for a wide variety of cooking methods including baking, roasting, and steaming. Versatility in culinary applications favors parchment paper due to its functional benefits over purely decorative digital print paper.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Digital print paper used in baking often contains synthetic inks and coatings that can complicate recycling and introduce chemicals harmful to the environment. Parchment paper, typically made from cellulose fibers treated with silicone, is biodegradable and more sustainable when unbleached and free from chemical additives. Choosing unbleached parchment paper reduces waste and supports eco-friendly baking practices by minimizing landfill impact and promoting compostability.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Digital print paper for baking is generally less cost-effective than parchment paper due to its specialized coatings and limited reuse potential, making parchment paper the preferred option for budget-conscious bakers. Parchment paper is widely available in most grocery stores and baking supply outlets, fostering convenience and consistent stock levels that digital print paper lacks. The broad availability and affordability of parchment paper contribute to its dominance in both home and commercial baking environments.
Which Paper is Best for Baking?
Digital print paper is not designed for baking and can release harmful chemicals when exposed to high oven temperatures, making it unsafe for food contact. Parchment paper, specifically treated for cooking, withstands heat up to 425degF (220degC) without burning or sticking, ensuring even baking and easy cleanup. For optimal safety and baking performance, parchment paper is the best choice.
Infographic: Digital print paper vs Parchment paper for Baking
 azmater.com
azmater.com