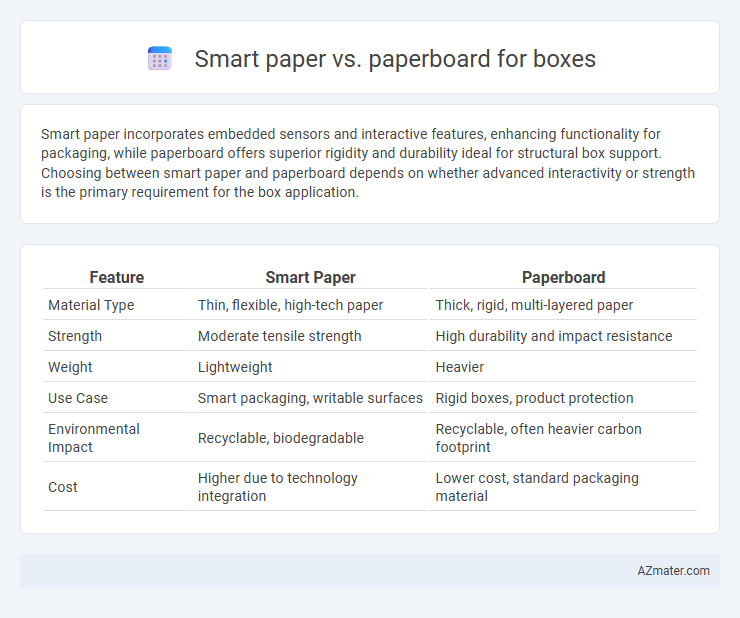
Smart paper incorporates embedded sensors and interactive features, enhancing functionality for packaging, while paperboard offers superior rigidity and durability ideal for structural box support. Choosing between smart paper and paperboard depends on whether advanced interactivity or strength is the primary requirement for the box application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Paper | Paperboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thin, flexible, high-tech paper | Thick, rigid, multi-layered paper |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High durability and impact resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Use Case | Smart packaging, writable surfaces | Rigid boxes, product protection |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, biodegradable | Recyclable, often heavier carbon footprint |
| Cost | Higher due to technology integration | Lower cost, standard packaging material |
Introduction to Smart Paper and Paperboard
Smart paper integrates electronic functionalities such as sensors and conductivity into traditional paper fibers, enabling interactive packaging solutions and enhanced consumer engagement. Paperboard, a thicker and more durable material made from multiple layers of pulp, offers superior rigidity and protection, commonly used in sturdy box construction for shipping and storage. Selecting smart paper over paperboard depends on the need for digital interactivity versus structural strength in packaging applications.
Key Differences Between Smart Paper and Paperboard
Smart paper incorporates embedded electronics such as sensors or NFC chips, enabling interactive packaging and real-time data tracking, while paperboard is a thick, durable material primarily valued for its structural strength and rigidity in box construction. The weight of paperboard typically ranges from 200 to 600 gsm, providing excellent protection for contents, whereas smart paper maintains a lighter profile, integrating technological features without significantly increasing thickness. Production costs for smart paper are higher due to advanced technology integration, contrasting with the cost-effective, widely recyclable nature of standard paperboard used in most packaging applications.
Material Composition and Properties
Smart paper typically incorporates synthetic fibers, nanomaterials, or coatings that enhance strength, flexibility, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging requiring durability and lightweight properties. Paperboard is primarily composed of multiple layers of cellulose fibers, providing stiffness, rigidity, and excellent printability, suitable for structural packaging applications. The material composition of smart paper offers superior barrier properties and adaptability, whereas paperboard excels in load-bearing capacity and recyclability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Smart paper offers enhanced tensile strength and improved tear resistance compared to traditional paperboard, making it more suitable for packaging that requires durability under stress. Paperboard, typically thicker and stiffer, provides excellent structural rigidity but may lack the flexibility and resilience of smart paper under repeated handling or impact. The integration of advanced fibers and coatings in smart paper significantly increases its resistance to moisture and wear, extending the lifespan of boxes used for shipping and storage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart paper uses advanced materials designed for recyclability and lower carbon emissions, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional paperboard. Paperboard production typically involves higher energy consumption and contributes more to deforestation, although innovations in sustainable sourcing and recycling have improved its footprint. Choosing smart paper for boxes supports circular economy principles by enhancing biodegradability and reducing landfill waste.
Cost Analysis of Smart Paper vs Paperboard
Smart paper offers a cost-efficient alternative to traditional paperboard for box manufacturing, with production expenses typically 10-20% lower due to reduced raw material and processing costs. Although paperboard provides superior durability and structural integrity, the lower weight and flexibility of smart paper reduce shipping expenses and storage requirements, contributing to overall savings. Businesses aiming to optimize packaging budgets often find that smart paper balances performance with affordability, especially for lightweight and short-term packaging needs.
Printing Quality and Customization Options
Smart paper offers superior printing quality for boxes due to its smooth surface and advanced coating technologies, enabling vibrant colors and sharp details. Paperboard provides robust customization options including various thicknesses and finishes, but often requires specialized treatments to match the print clarity of smart paper. Choosing between the two depends on whether print precision or material versatility is the priority for packaging design.
Applications in Box Packaging
Smart paper excels in flexible, lightweight box packaging for consumer electronics and food products due to its recyclable, moisture-resistant properties. Paperboard is preferred for rigid, durable packaging such as luxury goods and retail boxes, offering excellent print quality and structural strength. Both materials support sustainable packaging solutions but cater to different application needs based on durability and presentation requirements.
Future Innovations in Packaging Materials
Smart paper integrates sensors and interactive features, transforming traditional paperboard boxes into dynamic packaging solutions that enhance consumer engagement and supply chain transparency. Advanced nanotechnology and biodegradable conductive inks enable future smart packaging to offer real-time condition monitoring and anti-counterfeiting measures while maintaining eco-friendliness. Emerging innovations focus on combining sustainable materials with embedded electronics, pushing the boundaries of functionality and recyclability in packaging design.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Box
Selecting between smart paper and paperboard hinges on the specific needs of your packaging project, such as durability, print quality, and environmental impact. Smart paper offers enhanced features like moisture resistance and interactive printing capabilities, ideal for high-tech or promotional boxes, while paperboard provides robust structural strength and recyclability, making it suitable for heavy or eco-friendly packaging. Evaluating factors like box function, budget constraints, and sustainability goals helps determine the optimal material for your box design.
Infographic: Smart paper vs Paperboard for Box
 azmater.com
azmater.com