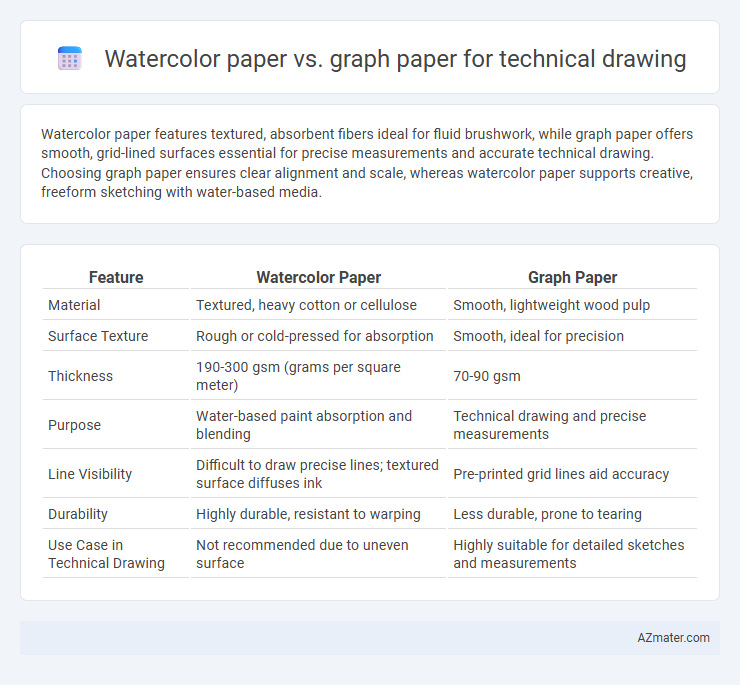
Watercolor paper features textured, absorbent fibers ideal for fluid brushwork, while graph paper offers smooth, grid-lined surfaces essential for precise measurements and accurate technical drawing. Choosing graph paper ensures clear alignment and scale, whereas watercolor paper supports creative, freeform sketching with water-based media.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Watercolor Paper | Graph Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Textured, heavy cotton or cellulose | Smooth, lightweight wood pulp |
| Surface Texture | Rough or cold-pressed for absorption | Smooth, ideal for precision |
| Thickness | 190-300 gsm (grams per square meter) | 70-90 gsm |
| Purpose | Water-based paint absorption and blending | Technical drawing and precise measurements |
| Line Visibility | Difficult to draw precise lines; textured surface diffuses ink | Pre-printed grid lines aid accuracy |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to warping | Less durable, prone to tearing |
| Use Case in Technical Drawing | Not recommended due to uneven surface | Highly suitable for detailed sketches and measurements |
Introduction to Technical Drawing Surfaces
Watercolor paper offers a textured surface ideal for artistic renderings but lacks the precision required for technical drawings, which demand accuracy and clean lines. Graph paper, with its pre-printed grid of fine lines, provides a standardized framework to guide measurements and maintain scale for technical drafts. Selecting graph paper ensures consistency and clarity crucial in engineering, architectural, and design applications.
What is Watercolor Paper?
Watercolor paper is a thick, textured paper specifically designed to absorb water and hold pigments, making it ideal for fluid art techniques but less suited for precision and clean lines in technical drawing. Its rough surface can cause lines from technical pens or pencils to bleed or appear uneven, contrasting with the smooth, grid-based structure of graph paper, which facilitates accurate measurements and detailed designs. For technical drawing, graph paper offers superior control and precision due to its uniform grid layout, while watercolor paper is better reserved for expressive or artistic renderings.
What is Graph Paper?
Graph paper is a precision-ruled paper printed with a fine grid of squares, typically used for plotting data, drawing technical diagrams, and creating accurate scale drawings essential in engineering and architecture. Unlike watercolor paper, which is textured and designed to absorb paint, graph paper offers a smooth surface that facilitates the precise placement of lines, measurements, and annotations critical for technical accuracy. The uniform grid layout on graph paper aids in maintaining consistent proportions and spatial relationships, making it indispensable in technical drawing workflows.
Surface Texture and Tooth Comparison
Watercolor paper features a textured surface with a pronounced tooth that holds pigments well, providing excellent grip for brush and ink applications in technical drawing. Graph paper has a smooth, flat surface with minimal tooth, ideal for precision and clarity when using pencils or fine pens for detailed technical sketches. The tooth on watercolor paper enhances line variation and ink absorption, while graph paper's surface ensures sharp, consistent lines without texture interference.
Durability and Longevity in Technical Drawings
Watercolor paper exhibits superior durability compared to graph paper due to its thicker, high-quality cotton or cellulose fibers, which resist tearing and warping over time, essential for preserving technical drawings. Graph paper, typically made from lightweight, less robust materials, tends to degrade faster, especially when exposed to frequent handling, erasing, or environmental factors like humidity. For longevity and maintaining the integrity of technical drawings, watercolor paper is a more reliable choice, providing archival-quality support that prevents yellowing and deterioration.
Precision and Accuracy: Line Clarity
Watercolor paper's textured surface often absorbs ink unevenly, leading to less precise and less sharp lines, which can reduce clarity in technical drawings. Graph paper's smooth, uniform grid provides consistent guidance for drafting straight, accurate lines, enhancing precision and line clarity essential for detailed technical work. For technical drawing tasks demanding high accuracy and clean, crisp lines, graph paper is the superior choice compared to watercolor paper.
Erasability and Corrections
Watercolor paper's textured surface absorbs ink and graphite, making erasing less effective and corrections challenging, which can result in smudging or paper damage. Graph paper features a smooth finish that allows for cleaner erasing and easier corrections, essential for precision in technical drawing. For workflows requiring frequent adjustments, graph paper offers better erasability and maintains line clarity over multiple revisions.
Ink and Pencil Compatibility
Watercolor paper offers a textured surface that absorbs ink differently, often causing lines to bleed and complicating fine-detail technical drawings, whereas graph paper's smooth finish provides superior control for precise ink and pencil work. Pencil marks on watercolor paper may smudge more easily due to its rough texture, but graph paper allows for clean, sharp pencil lines ideal for drafting. For technical drawings requiring accuracy with ink and pencil, graph paper is generally the preferred medium due to its enhanced compatibility and minimal absorption.
Cost and Availability
Watercolor paper typically costs more than graph paper due to its specialized texture and higher quality, making it less common for routine technical drawings. Graph paper is widely available and affordable, designed specifically to aid precision in technical and engineering drawings with its printed grid layout. The cost-effectiveness and easy accessibility of graph paper make it the preferred choice for technical drawing over watercolor paper.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Technical Drawing Needs
Watercolor paper offers a textured surface ideal for detailed, artistic technical drawings requiring varied line weights and shading, while graph paper provides a precise, grid-based layout essential for accurate measurements and scaling in engineering or architectural plans. Choosing the right paper depends on the nature of the technical drawing: use watercolor paper for creative, freehand illustration and graph paper for exact, dimension-focused drafting. Selecting paper with appropriate weight and surface quality ensures durability and clarity in technical documentation.
Infographic: Watercolor paper vs Graph paper for Technical drawing
 azmater.com
azmater.com