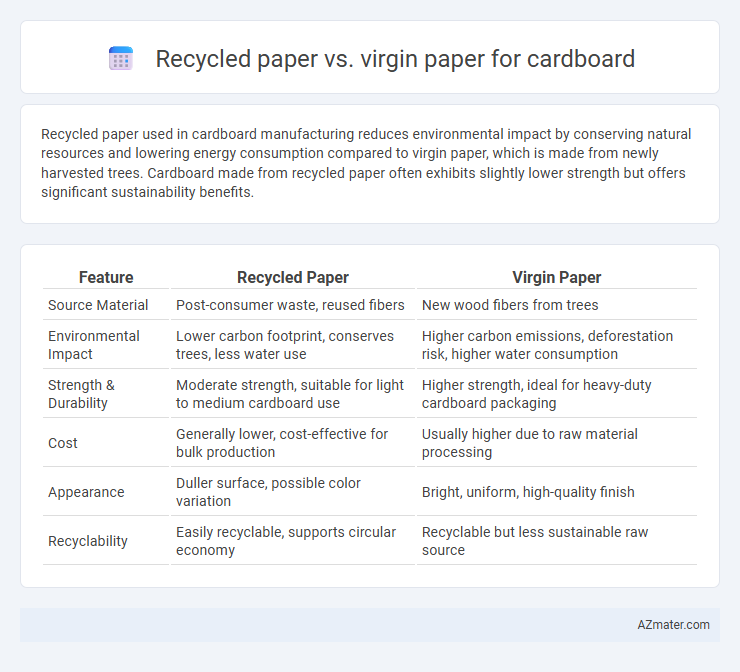
Recycled paper used in cardboard manufacturing reduces environmental impact by conserving natural resources and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin paper, which is made from newly harvested trees. Cardboard made from recycled paper often exhibits slightly lower strength but offers significant sustainability benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Paper | Virgin Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Post-consumer waste, reused fibers | New wood fibers from trees |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, conserves trees, less water use | Higher carbon emissions, deforestation risk, higher water consumption |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate strength, suitable for light to medium cardboard use | Higher strength, ideal for heavy-duty cardboard packaging |
| Cost | Generally lower, cost-effective for bulk production | Usually higher due to raw material processing |
| Appearance | Duller surface, possible color variation | Bright, uniform, high-quality finish |
| Recyclability | Easily recyclable, supports circular economy | Recyclable but less sustainable raw source |
Introduction: Understanding Recycled and Virgin Paper
Recycled paper for cardboard is made from post-consumer waste, reducing the demand for fresh pulp and conserving natural resources. Virgin paper is produced directly from newly harvested wood fibers, offering higher strength and quality for packaging durability. Choosing between recycled and virgin paper impacts sustainability, manufacturing energy consumption, and product performance in cardboard applications.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled paper significantly reduces deforestation and conserves natural resources compared to virgin paper, as it relies on post-consumer waste rather than freshly harvested wood fibers. The production of recycled cardboard consumes 40-70% less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases, lowering its carbon footprint throughout the manufacturing process. Additionally, recycled paper lessens water usage and decreases landfill waste, contributing to a more sustainable lifecycle for cardboard packaging.
Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
Recycled paper for cardboard primarily utilizes post-consumer waste, significantly reducing the demand for virgin wood pulp and preserving natural forests, which enhances sustainability. Virgin paper relies on freshly harvested timber, often contributing to deforestation, higher energy consumption, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. The use of recycled fibers reduces landfill waste and lowers water and energy usage, positioning recycled paper as a more eco-friendly and sustainable option for cardboard production.
Energy and Water Consumption
Recycled paper used in cardboard production reduces energy consumption by up to 40% compared to virgin paper, significantly lowering carbon emissions during manufacturing. Water consumption also decreases by nearly 50% when using recycled fibers, making it a more sustainable choice in resource management. Choosing recycled paper helps conserve natural resources and supports eco-friendly cardboard production processes.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Recycled paper for cardboard manufacturing involves reprocessing used paper fibers by cleaning, deinking, and reforming them, which reduces energy consumption and water usage compared to virgin paper production. Virgin paper cardboard is made directly from wood pulp, requiring more intensive mechanical and chemical treatments to break down raw timber, resulting in higher resource and emission footprints. The recycled process preserves fiber quality through advanced refining techniques, while virgin paper offers stronger fibers but demands more environmental impact due to logging and pulping stages.
Quality and Performance in Cardboard
Recycled paper used for cardboard often contains shorter fibers, which can reduce tensile strength and durability compared to virgin paper sourced from long, unprocessed fibers. Virgin paper delivers superior performance with greater rigidity, tear resistance, and moisture tolerance, essential for protective packaging applications. Advances in recycling technology have improved recycled cardboard quality, but virgin paper remains preferred for high-strength and heavy-duty cardboard requirements.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Paper
Recycled paper for cardboard production typically reduces raw material expenses by 20-30% compared to virgin paper, owing to the reuse of existing fiber stock and lower energy consumption during processing. Virgin paper, derived directly from fresh wood pulp, incurs higher costs due to extensive resource extraction and processing, with raw material prices accounting for up to 50% of overall production expenses. Companies aiming for cost efficiency often prefer recycled paper, which balances environmental benefits with significant savings in procurement and manufacturing budgets.
Recycling and End-of-Life Considerations
Recycled paper used in cardboard significantly reduces the demand for virgin fiber, conserving natural resources and lowering energy consumption during production. The recycling process for cardboard enables multiple reuses before fibers degrade, extending the material's lifecycle and minimizing landfill waste. End-of-life considerations emphasize that recycled cardboard is more environmentally sustainable due to its higher recyclability, biodegradable properties, and reduced carbon footprint compared to virgin paper-based cardboard.
Industry Trends and Consumer Preferences
The cardboard industry increasingly favors recycled paper due to rising sustainability regulations and cost-efficient production processes, with recycled fibers now accounting for over 70% of raw materials in packaging sectors. Consumer preferences strongly shift towards environmentally friendly products, driving demand for recycled cardboard that reduces deforestation and carbon footprint. Market research indicates a 45% growth in recycled packaging purchases over the last five years, reflecting heightened awareness of eco-conscious branding and corporate social responsibility.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Option for Cardboard
Selecting between recycled paper and virgin paper for cardboard depends on environmental impact, cost efficiency, and application needs. Recycled paper reduces deforestation and energy consumption, making it ideal for eco-conscious packaging, while virgin paper offers superior strength and durability for heavy-duty uses. Balancing sustainability goals with performance requirements ensures the best choice for specific cardboard production.
Infographic: Recycled paper vs Virgin paper for Cardboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com