Seed paper is an eco-friendly alternative embedded with biodegradable seeds that promote plant growth after use, whereas printing paper is typically made from processed wood pulp designed for high-quality text and image reproduction but lacks environmental benefits. Choosing seed paper reduces deforestation and waste, supporting sustainable document practices.
Table of Comparison
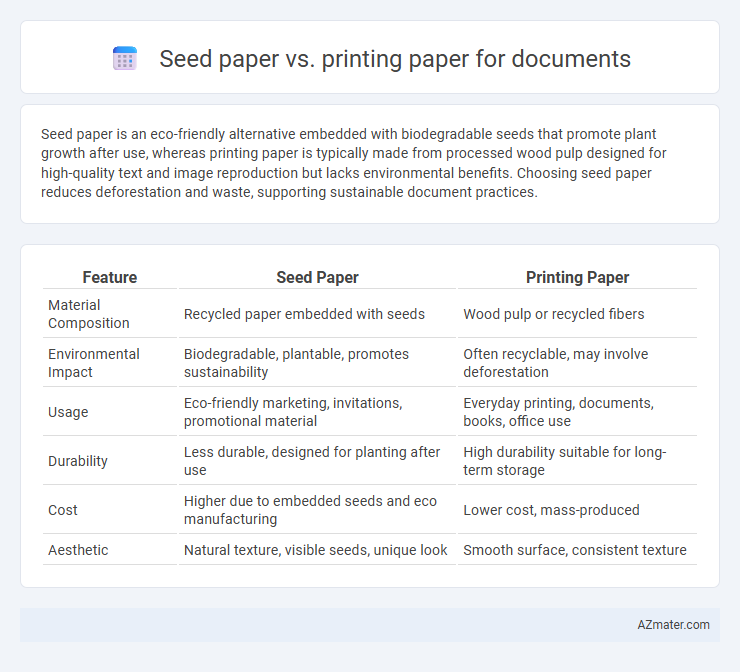
| Feature | Seed Paper | Printing Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled paper embedded with seeds | Wood pulp or recycled fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, plantable, promotes sustainability | Often recyclable, may involve deforestation |
| Usage | Eco-friendly marketing, invitations, promotional material | Everyday printing, documents, books, office use |
| Durability | Less durable, designed for planting after use | High durability suitable for long-term storage |
| Cost | Higher due to embedded seeds and eco manufacturing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Aesthetic | Natural texture, visible seeds, unique look | Smooth surface, consistent texture |
Introduction to Seed Paper and Printing Paper
Seed paper is an innovative biodegradable material embedded with seeds that can be planted to grow flowers, herbs, or vegetables, making it a sustainable choice for eco-conscious individuals. Printing paper, traditionally made from wood pulp, serves as a versatile medium for producing high-quality documents, offering smooth surfaces suitable for ink absorption and sharp text clarity. While printing paper prioritizes functionality and cost-effectiveness, seed paper integrates environmental benefits by reducing waste and promoting green initiatives.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Seed paper, embedded with biodegradable seeds, promotes environmental sustainability by enabling users to plant the paper after use, reducing waste and contributing to greener ecosystems. Conventional printing paper often relies on deforestation and chemical processing, leading to higher carbon emissions, resource depletion, and landfill accumulation. Using seed paper significantly lowers the ecological footprint compared to traditional printing paper by fostering a circular lifecycle and supporting reforestation efforts.
Material Composition and Sources
Seed paper is composed of recycled fibers embedded with plant seeds, primarily sourced from post-consumer waste and agricultural byproducts to ensure eco-friendliness and biodegradability. Printing paper, typically derived from wood pulp sourced from both virgin and recycled fibers, involves chemical and mechanical processes that focus on durability and print quality rather than sustainability. The distinct material compositions of seed paper emphasize environmental regeneration, whereas printing paper prioritizes strength and visual clarity for document reproduction.
Production Processes Explained
Seed paper production involves embedding biodegradable seeds within recycled paper pulp, requiring careful mixing to prevent damaging the seeds while ensuring they remain viable after printing. Printing paper production typically includes refining wood fibers, bleaching, and pressing into smooth, uniform sheets designed for optimal ink absorption and clarity. The key difference lies in balancing seed preservation with print quality in seed paper, contrasting with the pure fiber processing aimed at maximizing print performance in standard printing paper.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Seed paper is highly biodegradable and fully compostable, breaking down naturally within weeks and enriching soil with embedded seeds that promote plant growth. Conventional printing paper, while partially biodegradable, often contains chemical additives and coatings that slow decomposition and reduce compostability. Choosing seed paper for documents supports sustainable waste management by minimizing landfill impact and fostering beneficial environmental cycles.
Printing Quality and Usability
Seed paper offers a unique tactile experience but generally compromises printing quality due to its textured, fibrous surface, causing ink to bleed or appear uneven compared to smooth printing paper. Standard printing paper is engineered for high-resolution text and images, ensuring sharp, clear output with optimal ink absorption and drying time. Usability favors printing paper for everyday documents, as seed paper's fragility and organic composition limit its durability and versatility in typical office equipment.
Cost Analysis: Seed Paper vs Printing Paper
Seed paper typically costs 20% to 40% more than standard printing paper due to the embedded seeds and eco-friendly manufacturing process. While printing paper averages around $0.01 to $0.03 per sheet, seed paper prices range from $0.03 to $0.05 per sheet, impacting overall budget considerations for bulk orders. Businesses must weigh the premium cost of seed paper against its marketing value and environmental benefits when making purchasing decisions.
Applications and Suitable Use Cases
Seed paper is ideal for eco-friendly marketing materials, invitations, and business cards because it can be planted to grow flowers or herbs, enhancing brand sustainability efforts. Printing paper excels in high-volume document production, office printing, and detailed text or image reproduction due to its smooth texture and compatibility with various printers. Seed paper suits creative and promotional applications emphasizing environmental impact, while printing paper is preferred for everyday administrative, educational, and professional document needs.
Challenges and Limitations
Seed paper presents challenges such as higher production costs and limited durability compared to standard printing paper, reducing its suitability for everyday document use. Its textured surface can cause printing issues like smudging or misalignment, complicating high-quality text reproduction. Standard printing paper remains preferred for consistency, affordability, and compatibility with most printers despite lacking eco-friendly benefits.
Future Trends in Sustainable Paper Choices
Seed paper integrates embedded seeds that promote eco-friendly planting post-use, representing a significant innovation in sustainable paper products. Printing paper, traditionally sourced from wood pulp, is evolving with increasing adoption of recycled fibers and alternative materials such as hemp and agricultural residues to reduce environmental impact. Future trends emphasize biodegradable additives, reduced chemical usage, and circular economy principles, positioning seed paper and advanced recycled printing paper as pivotal in sustainable document management.
Infographic: Seed paper vs Printing paper for Document
 azmater.com
azmater.com