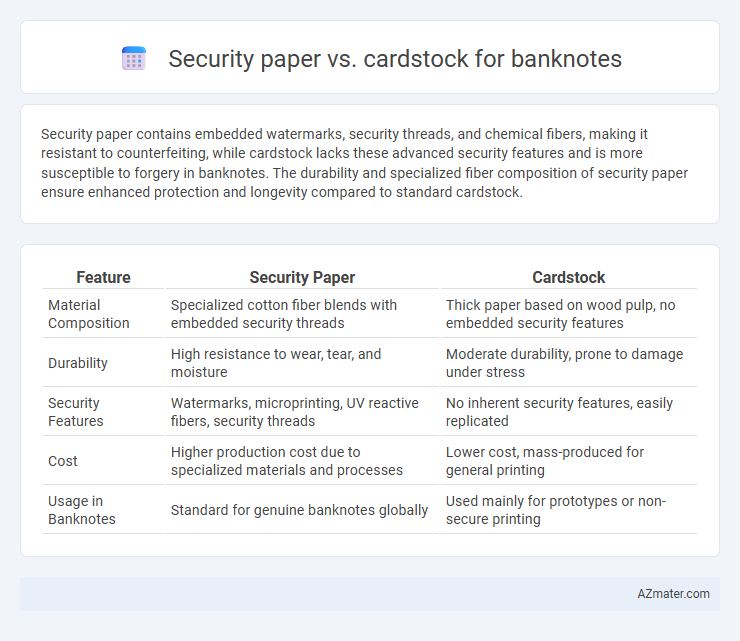
Security paper contains embedded watermarks, security threads, and chemical fibers, making it resistant to counterfeiting, while cardstock lacks these advanced security features and is more susceptible to forgery in banknotes. The durability and specialized fiber composition of security paper ensure enhanced protection and longevity compared to standard cardstock.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Security Paper | Cardstock |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Specialized cotton fiber blends with embedded security threads | Thick paper based on wood pulp, no embedded security features |
| Durability | High resistance to wear, tear, and moisture | Moderate durability, prone to damage under stress |
| Security Features | Watermarks, microprinting, UV reactive fibers, security threads | No inherent security features, easily replicated |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to specialized materials and processes | Lower cost, mass-produced for general printing |
| Usage in Banknotes | Standard for genuine banknotes globally | Used mainly for prototypes or non-secure printing |
Introduction to Banknote Paper Selection
Banknote paper selection prioritizes durability, security features, and counterfeit resistance, making security paper the preferred choice over regular cardstock. Security paper integrates specialized fibers, watermarks, and embedded security threads that are critical for authenticating currency. Unlike cardstock, security paper offers enhanced flexibility and wear resistance suitable for high-circulation environments.
Key Characteristics of Security Paper
Security paper for banknotes features embedded security elements such as watermarks, security threads, and microprinting that resist counterfeiting, unlike standard cardstock. Its fiber composition incorporates durable and unique materials ensuring longevity and tamper-evidence, critical for maintaining the integrity of currency. The paper's specialized coatings enhance durability and prevent ink smudging, supporting high-quality printing of intricate designs and security features.
Understanding Cardstock Material
Banknote security paper is engineered with embedded security features such as watermarks, security threads, and fiber inclusions to prevent counterfeiting, whereas cardstock lacks these sophisticated elements and is primarily designed for durability and rigidity. The cardstock material is usually thicker and stiffer, made from wood pulp or mixed fibers, but does not incorporate the specialized security treatments found in currency paper. Understanding cardstock material involves recognizing its role in providing structural support rather than security, as its physical properties differ significantly from security paper formulated for anti-counterfeit measures in banknotes.
Durability: Security Paper vs Cardstock
Security paper used in banknotes is engineered with watermarks, security threads, and fiber inclusions, providing superior durability against folding, tearing, and environmental wear compared to traditional cardstock. Its unique polymer or cotton fiber composition offers enhanced resistance to counterfeiting and physical deterioration, ensuring long-term circulation stability. In contrast, cardstock lacks embedded security features and has a lower tensile strength, making it more susceptible to damage and less suitable for secure currency production.
Counterfeit Prevention Features
Security paper used in banknotes incorporates advanced features such as watermarks, security threads, and embedded fibers that are difficult to replicate, significantly enhancing counterfeit prevention. Cardstock lacks these integrated security elements and is more easily duplicated using conventional printing techniques, making it less suitable for authentic currency production. Incorporating microprinting, holograms, and ultraviolet-visible features within security paper creates a multi-layered defense against forgery and ensures currency integrity.
Print Quality and Design Compatibility
Security paper offers superior print quality for banknotes due to its specialized fibers and embedded security features, ensuring sharp, vibrant images and enhanced durability. Cardstock, being thicker and less absorbent, can hinder fine detail reproduction and may not integrate well with advanced printing techniques like intaglio or microprinting. Design compatibility favors security paper as it supports complex anti-counterfeiting elements, including watermarks and security threads, which cardstock cannot reliably accommodate.
Cost Analysis: Security Paper and Cardstock
Security paper used in banknotes incorporates advanced features such as watermarks, security threads, and special fibers, resulting in higher production costs compared to standard cardstock. Cardstock, while more affordable due to simpler materials and manufacturing processes, lacks these embedded security elements, making it less suitable for anti-counterfeiting purposes. The cost analysis clearly shows that security paper demands a premium investment to ensure durability and fraud resistance essential for currency circulation.
Regulatory Standards for Banknote Materials
Security paper for banknotes is engineered to meet stringent regulatory standards involving fiber composition, durability, and embedded security features such as watermarks, security threads, and microprinting to prevent counterfeiting. Cardstock, while thicker and stiffer, generally lacks the advanced security features and specialized fibers required by central banks and regulatory authorities, making it less suitable for legitimate banknotes. Compliance with international standards like those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and central banks dictates the exclusive use of security paper to ensure authenticity and longevity in circulation.
Environmental Impact of Paper Choices
Security paper used in banknotes typically incorporates fibers and additives that enhance durability and counterfeit resistance but may complicate recycling processes and increase environmental impact compared to ordinary cardstock. Cardstock, being thicker and less specialized, generally has a simpler production process and higher recyclability, potentially reducing waste and energy consumption but lacking security features essential for currency. The environmental trade-off involves balancing the robust, tamper-resistant nature of security paper with its lifecycle emissions against the more eco-friendly but less secure cardstock alternatives.
Conclusion: Best Material for Secure Banknotes
Security paper offers advanced features like embedded watermarks, security threads, and fiber optics that significantly enhance counterfeit resistance, making it the preferred material for secure banknotes. Cardstock, while durable and cost-effective, lacks the sophisticated security elements necessary to deter modern counterfeiting techniques. Therefore, security paper represents the best material choice for banknotes requiring high-level protection and authenticity verification.
Infographic: Security paper vs Cardstock for Banknote
 azmater.com
azmater.com