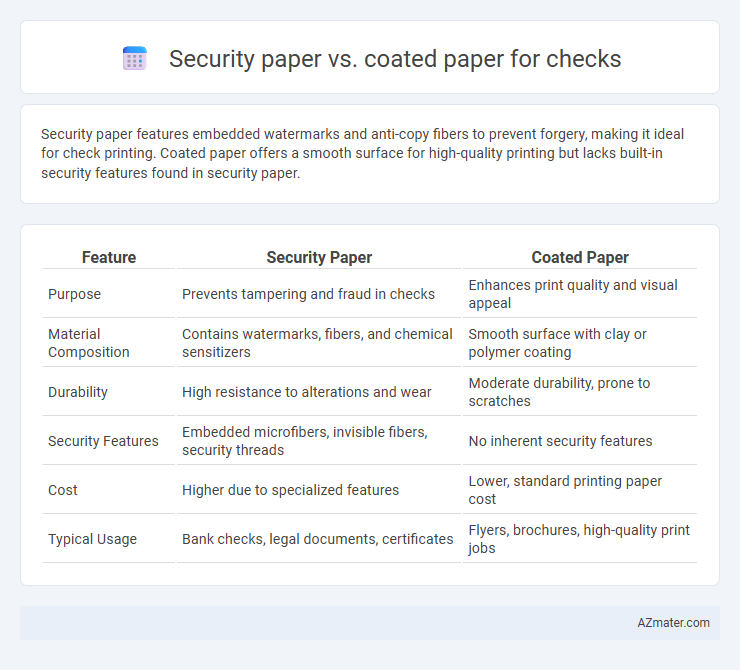
Security paper features embedded watermarks and anti-copy fibers to prevent forgery, making it ideal for check printing. Coated paper offers a smooth surface for high-quality printing but lacks built-in security features found in security paper.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Security Paper | Coated Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents tampering and fraud in checks | Enhances print quality and visual appeal |
| Material Composition | Contains watermarks, fibers, and chemical sensitizers | Smooth surface with clay or polymer coating |
| Durability | High resistance to alterations and wear | Moderate durability, prone to scratches |
| Security Features | Embedded microfibers, invisible fibers, security threads | No inherent security features |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized features | Lower, standard printing paper cost |
| Typical Usage | Bank checks, legal documents, certificates | Flyers, brochures, high-quality print jobs |
Introduction to Security Paper and Coated Paper
Security paper incorporates embedded features such as watermarks, security fibers, and chemical sensitivity to prevent forgery and unauthorized alterations, making it essential for checks and sensitive documents. Coated paper features a smooth, sealed surface created by applying a layer of coating material, enhancing print quality and durability but lacking intrinsic anti-counterfeit measures. The choice between security and coated paper for checks hinges on the need for advanced fraud prevention versus high-quality print aesthetics.
Key Differences Between Security Paper and Coated Paper
Security paper features embedded watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitizers to prevent forgery and tampering, making it ideal for checks requiring high fraud protection. Coated paper, typically finished with a smooth, glossy or matte surface, enhances print quality and appearance but lacks inherent anti-counterfeiting measures. While security paper prioritizes authentication and fraud deterrence, coated paper focuses on print clarity and aesthetic presentation.
Essential Features of Security Paper for Checks
Security paper for checks features embedded security fibers, watermarks, and chemical sensitivity to prevent tampering and forgery, which distinguishes it from coated paper that primarily offers surface smoothness and print quality. These essential security features enable verification of authenticity and protect against alterations, ensuring the integrity of financial documents. Unlike coated paper, security paper often incorporates microprinting and embedded threads that are visible under UV light, enhancing anti-counterfeiting measures.
Coated Paper: Properties and Uses in Printing
Coated paper features a smooth finish achieved by applying a surface coating for enhanced brightness, opacity, and print quality, making it ideal for high-resolution images and sharp text in check printing. Its properties include improved ink adherence, reduced ink absorption, and resistance to smudging, which ensures better durability and legibility in security documents. Coated paper is widely used in commercial printing of checks, vouchers, and certificates where clarity and security are critical.
Security Measures in Check Printing
Security paper used in check printing integrates advanced anti-counterfeiting features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity to prevent forgery and alteration. Coated paper, while offering a smooth surface for high-quality printing, lacks these embedded security elements, making it less effective in deterring fraudulent activities. The implementation of security paper significantly enhances the integrity of checks by providing multiple layers of security measures essential for financial documents.
Durability Comparison: Security Paper vs. Coated Paper
Security paper offers superior durability compared to coated paper due to embedded fibers, watermarks, and chemical treatments that resist tampering, tearing, and wear, making it highly reliable for checks. Coated paper, while smoother and glossy due to its surface finish, is more susceptible to damage from handling, moisture, and erasure attempts, reducing its lifespan in transactional documents. The enhanced resilience of security paper ensures long-term integrity and authenticity, critical for preventing fraud in financial instruments like checks.
Cost Implications: Security Paper vs. Coated Paper
Security paper typically incurs higher costs than coated paper due to specialized features such as watermarks, microprinting, and embedded security threads that prevent counterfeiting and fraud. Coated paper, often used for standard check printing, offers a smoother surface and lower production expenses but lacks advanced anti-fraud measures, potentially increasing risks and indirect costs related to check fraud. Organizations prioritizing fraud prevention may find the initial investment in security paper justified by reduced financial losses and enhanced check authenticity.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Security paper for checks incorporates embedded features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity to prevent alteration and counterfeiting, ensuring strong compliance with financial regulations and legal standards. Coated paper lacks these advanced security elements, making it less suitable for checks that require strict adherence to anti-fraud laws and banking compliance protocols. Financial institutions and businesses prioritize security paper to meet legal requirements and reduce the risk of fraudulent transactions.
Best Practices for Choosing Paper for Checks
Security paper for checks incorporates embedded features like watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity to prevent fraud, making it a superior choice for safeguarding financial transactions. Coated paper, while providing a smooth surface and high-quality print output, lacks anti-counterfeiting elements essential for check security. Best practices for choosing check paper emphasize selecting security paper certified to industry standards such as ANSI X9.100-140, ensuring compatibility with MICR printers and enhancing fraud deterrence.
Final Recommendation: Security Paper vs. Coated Paper for Check Printing
Security paper offers advanced anti-fraud features such as watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity that significantly reduce the risk of check tampering and counterfeiting. Coated paper, while providing a smooth surface for high-quality printing, lacks intrinsic security elements, making it less suitable for checks requiring fraud prevention. For check printing, security paper is the recommended choice due to its enhanced protective properties and compliance with banking standards.
Infographic: Security paper vs Coated paper for Check
 azmater.com
azmater.com