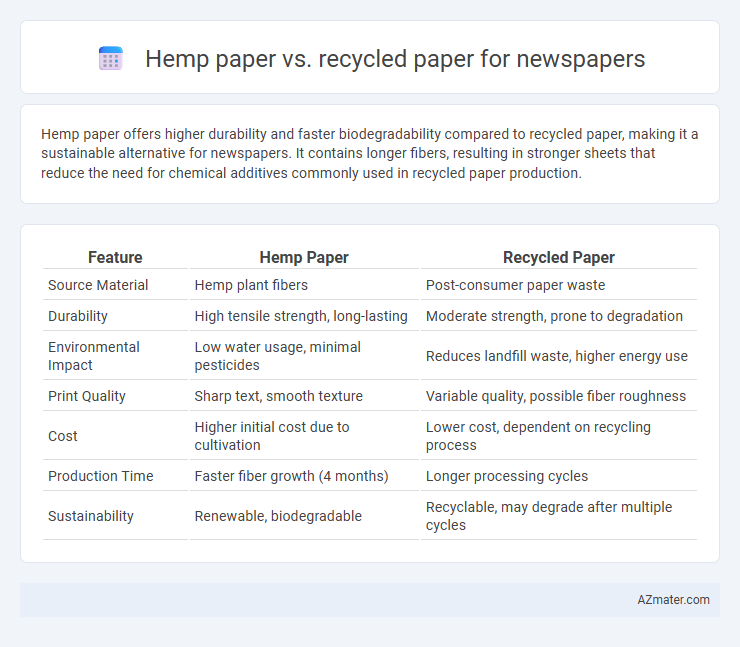
Hemp paper offers higher durability and faster biodegradability compared to recycled paper, making it a sustainable alternative for newspapers. It contains longer fibers, resulting in stronger sheets that reduce the need for chemical additives commonly used in recycled paper production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Recycled Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Hemp plant fibers | Post-consumer paper waste |
| Durability | High tensile strength, long-lasting | Moderate strength, prone to degradation |
| Environmental Impact | Low water usage, minimal pesticides | Reduces landfill waste, higher energy use |
| Print Quality | Sharp text, smooth texture | Variable quality, possible fiber roughness |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to cultivation | Lower cost, dependent on recycling process |
| Production Time | Faster fiber growth (4 months) | Longer processing cycles |
| Sustainability | Renewable, biodegradable | Recyclable, may degrade after multiple cycles |
Introduction to Hemp Paper and Recycled Paper
Hemp paper is made from the fibers of the hemp plant, known for its durability, brightness, and sustainability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional paper sources. Recycled paper for newspapers is produced by reprocessing used paper, reducing waste and conserving natural resources, but often results in lower brightness and strength compared to virgin fibers. Both materials offer environmental benefits, yet hemp paper stands out for its faster growth rate and lower chemical usage in production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp paper offers a significant environmental advantage over recycled paper for newspaper production due to its faster growth rate and higher yield per acre, reducing deforestation and land use. Hemp requires fewer pesticides and less water compared to traditional timber sources used in recycled paper, lowering chemical runoff and water consumption. The biodegradability of hemp paper also enhances its environmental sustainability by decomposing more efficiently in natural settings.
Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
Hemp paper is derived from fast-growing hemp plants that require minimal pesticides and water, offering a renewable raw material source compared to recycled paper, which relies on the collection and reprocessing of post-consumer or post-industrial waste. The cultivation of hemp results in higher biomass yield per acre, enhancing sustainability by reducing deforestation associated with traditional wood pulp sourcing. Recycled paper reduces landfill waste and energy consumption but is limited by the availability and quality of recovered fibers, making hemp paper a more consistent and eco-friendly option for newspaper production.
Production Process Differences
Hemp paper production involves processing bast fibers from the hemp stalk, which are retted, decorticated, and chemically pulped to create long, durable fibers ideal for high-quality newspaper print. Recycled paper production begins with waste paper collection, which is sorted, deinked, and mechanically pulped to remove contaminants and print residues, often resulting in shorter fibers and slightly lower tensile strength. The chemical pulping in hemp paper yields stronger, more sustainable sheets, while recycled paper's mechanical pulping emphasizes resource reuse but can lead to fiber degradation over multiple cycles.
Print Quality and Durability
Hemp paper offers superior print quality for newspapers due to its longer fibers, resulting in sharper text and more vibrant images compared to recycled paper. Its durability surpasses that of recycled paper, resisting tearing and yellowing over time, which extends the lifespan of printed materials. Recycled paper often contains shorter fibers that can cause print fading and reduced structural integrity, making it less ideal for high-quality newspaper production.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Paper vs Recycled Paper
Hemp paper generally incurs higher production costs than recycled paper due to its raw material processing and limited industrial scale, leading to a steeper price point for newspaper manufacturing. Recycled paper benefits from established recycling infrastructure, lowering expenses and making it more economically viable for large-scale newspaper production. Despite hemp paper's durability and sustainability advantages, its current cost disadvantage limits widespread adoption in the newspaper industry compared to recycled paper.
Availability and Scalability for Newspapers
Hemp paper, derived from the rapid-growing hemp plant, offers exceptional durability but faces limited availability and higher production costs compared to recycled paper. Recycled paper dominates the newspaper industry due to widespread access, established processing infrastructure, and cost-effective scalability across mass production facilities. Newspapers prioritize recycled paper for large-scale distribution, while hemp paper remains niche, constrained by raw material supply and manufacturing capacity.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Hemp paper degrades faster and more completely in natural environments compared to recycled newspaper paper, which often contains residual chemicals and inks that slow biodegradation. The cellulose fibers in hemp paper break down efficiently, resulting in less environmental impact during composting or landfill disposal. End-of-life management favors hemp paper due to its cleaner composition and higher biodegradability, reducing long-term pollution associated with traditional recycled newspaper materials.
Industry Adoption and Case Studies
Hemp paper demonstrates superior durability and environmental benefits compared to recycled paper, leading to increasing industry adoption in newspaper production by companies like The Times and The Guardian. Case studies reveal that hemp paper reduces reliance on wood pulp by up to 80% and lowers carbon footprint by 60%, driving sustainability goals in print media. Despite higher initial costs, long-term savings and regulatory incentives have encouraged publishers to transition towards hemp-based newsprint for enhanced recyclability and print quality.
Future Prospects for Eco-Friendly Newsprint
Hemp paper offers superior durability and faster growth cycles compared to traditional wood-based recycled paper, making it a promising sustainable raw material for eco-friendly newsprint. Innovations in hemp cultivation and processing are reducing costs and enhancing fiber quality, positioning hemp as a viable alternative to recycled paper in large-scale newspaper production. The integration of hemp paper can significantly reduce deforestation and carbon emissions, aligning with global environmental goals for sustainable publishing.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Recycled paper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com