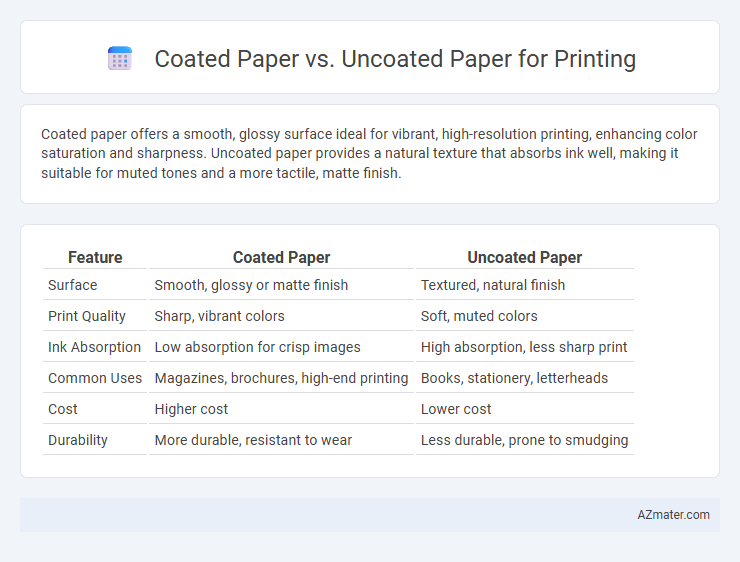
Coated paper offers a smooth, glossy surface ideal for vibrant, high-resolution printing, enhancing color saturation and sharpness. Uncoated paper provides a natural texture that absorbs ink well, making it suitable for muted tones and a more tactile, matte finish.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coated Paper | Uncoated Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Surface | Smooth, glossy or matte finish | Textured, natural finish |
| Print Quality | Sharp, vibrant colors | Soft, muted colors |
| Ink Absorption | Low absorption for crisp images | High absorption, less sharp print |
| Common Uses | Magazines, brochures, high-end printing | Books, stationery, letterheads |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Durability | More durable, resistant to wear | Less durable, prone to smudging |
Introduction to Coated and Uncoated Paper
Coated paper features a smooth finish achieved by applying a surface sealant, enhancing ink hold and color vibrancy for high-quality printing results, especially in magazines and brochures. Uncoated paper lacks this surface layer, offering a more porous texture that absorbs ink differently, making it preferable for stationery and books requiring a natural feel. Understanding the differences in surface texture, ink absorption, and visual appeal is crucial for selecting the appropriate paper type for specific printing needs.
What is Coated Paper?
Coated paper is a type of paper that has a surface treated with a layer of coating, usually made from materials like clay, calcium carbonate, or latex, to create a smooth and glossy finish. This coating enhances the paper's ability to hold ink, resulting in sharper, more vibrant images and text, making it ideal for high-quality printing such as magazines, brochures, and product packaging. In comparison to uncoated paper, coated paper offers better durability, reduced ink absorption, and improved color contrast, but tends to be less porous and less suitable for writing or note-taking.
What is Uncoated Paper?
Uncoated paper is a type of paper that has no additional surface coating, resulting in a more porous and absorbent finish ideal for writing and printing. It typically offers a natural look and feel, providing excellent ink absorption that enhances readability and vibrant color reproduction in printing processes. Used commonly in books, notepads, and stationery, uncoated paper is favored for its versatility and eco-friendly properties compared to coated paper.
Differences Between Coated and Uncoated Paper
Coated paper features a smooth, glossy or matte finish due to a layer of coating applied, enhancing color vibrancy and sharpness in printing, making it ideal for high-quality images and detailed graphics. Uncoated paper lacks this surface treatment, resulting in a more porous texture that absorbs ink differently, offering a natural, tactile feel preferred for text-heavy documents and stationery. The choice between coated and uncoated paper impacts ink absorption, print clarity, and the overall visual and tactile experience of the printed material.
Print Quality Comparison: Coated vs Uncoated
Coated paper offers superior print quality due to its smooth surface, allowing for sharper images and more vibrant colors in printing. Uncoated paper absorbs more ink, resulting in softer edges and duller colors, which may be desirable for a natural or textured look. The choice between coated and uncoated paper directly affects print clarity, color saturation, and overall visual impact of printed materials.
Applications and Uses of Coated Paper
Coated paper is primarily used in high-quality print applications such as magazines, brochures, and product packaging due to its smooth surface that enhances color vibrancy and sharpness. It is ideal for photographic prints and promotional materials where a glossy or matte finish is desired to improve visual appeal and durability. This type of paper is also preferred for marketing collateral, labels, and catalogs requiring crisp images and professional presentation.
Applications and Uses of Uncoated Paper
Uncoated paper is widely used for applications requiring excellent ink absorption and a natural feel, such as letterheads, business forms, notebooks, and newspapers. Its porous surface enhances write-ability and is ideal for printing materials like flyers, brochures, and textbooks where tactile quality and readability are prioritized over gloss. Unlike coated paper, uncoated paper supports eco-friendly printing projects due to its recyclability and lower chemical processing.
Cost Considerations: Coated vs Uncoated Paper
Coated paper generally incurs higher production costs due to the additional coating process, which enhances print quality and visual appeal, making it more expensive than uncoated paper. Uncoated paper offers a cost-effective option ideal for bulk printing tasks where texture and absorbency are prioritized over sheen or sharpness. Businesses weigh these cost differences against specific project requirements, balancing budget constraints with desired print outcomes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coated paper features a layer of clay or polymer that enhances print quality but involves more energy-intensive production and chemical use, resulting in higher environmental impact compared to uncoated paper. Uncoated paper, often made from recycled fibers and processed with fewer chemicals, generally offers better biodegradability and recyclability, making it more sustainable for eco-conscious printing projects. Selecting uncoated paper supports reduced carbon emissions and waste, aligning with green printing practices and sustainability goals.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Printing Project
Choosing the right paper for your printing project depends on the desired visual impact and tactile experience. Coated paper offers a smooth finish with enhanced color vibrancy and sharpness, making it ideal for high-quality photos and graphics, while uncoated paper provides a natural texture and better ink absorption, suitable for text-heavy documents and a more subdued look. Consider factors such as finish, weight, and printing method to ensure optimal print quality and durability tailored to your specific project needs.
Infographic: Coated paper vs Uncoated paper for Printing
 azmater.com
azmater.com