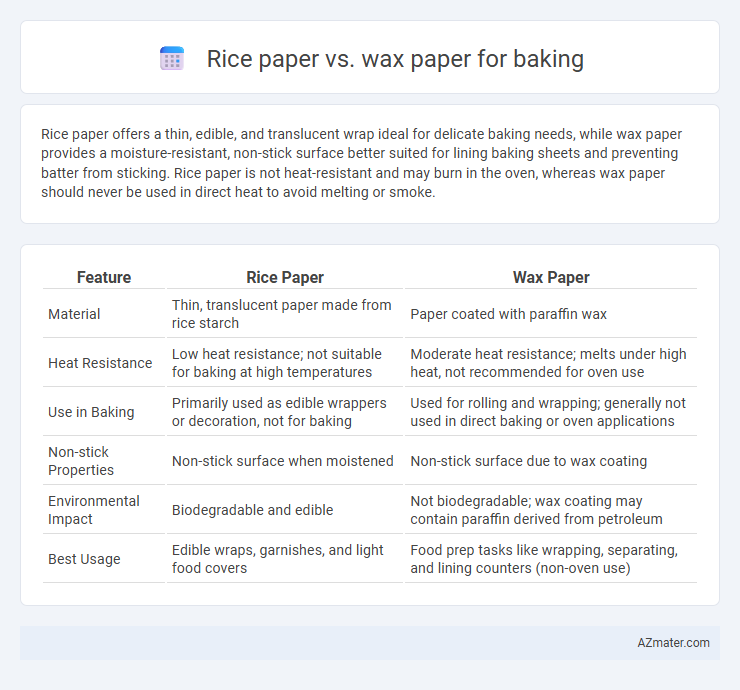
Rice paper offers a thin, edible, and translucent wrap ideal for delicate baking needs, while wax paper provides a moisture-resistant, non-stick surface better suited for lining baking sheets and preventing batter from sticking. Rice paper is not heat-resistant and may burn in the oven, whereas wax paper should never be used in direct heat to avoid melting or smoke.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rice Paper | Wax Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thin, translucent paper made from rice starch | Paper coated with paraffin wax |
| Heat Resistance | Low heat resistance; not suitable for baking at high temperatures | Moderate heat resistance; melts under high heat, not recommended for oven use |
| Use in Baking | Primarily used as edible wrappers or decoration, not for baking | Used for rolling and wrapping; generally not used in direct baking or oven applications |
| Non-stick Properties | Non-stick surface when moistened | Non-stick surface due to wax coating |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and edible | Not biodegradable; wax coating may contain paraffin derived from petroleum |
| Best Usage | Edible wraps, garnishes, and light food covers | Food prep tasks like wrapping, separating, and lining counters (non-oven use) |
Introduction: Rice Paper vs Wax Paper for Baking
Rice paper, made from rice flour and water, offers a thin, translucent texture ideal for wrapping delicate foods and crisp baking results without added oils. Wax paper, coated with a layer of paraffin wax, excels at non-stick baking applications but is unsuitable for high-temperature oven use due to its low melting point. Understanding the distinct properties of rice paper and wax paper helps bakers choose the appropriate material for tasks like rolling, wrapping, or lining baking sheets.
What is Rice Paper?
Rice paper is a thin, translucent edible sheet made primarily from rice flour, water, and salt, commonly used in Asian cuisine for wrapping spring rolls and other delicate foods. Unlike wax paper, which is coated with a thin layer of paraffin wax to provide non-stick and moisture-resistant properties but is not edible, rice paper is safe for consumption and can be baked or steamed without losing its texture. Its natural composition allows rice paper to become pliable when moistened, making it ideal for creating light, crispy textures in baking applications.
What is Wax Paper?
Wax paper is a moisture-resistant, non-stick paper coated with a thin layer of paraffin wax, commonly used in baking to prevent food from sticking and to wrap items for storage. It is not heat-resistant and should not be used in the oven, as the wax coating can melt or ignite at high temperatures. Unlike parchment or rice paper, wax paper is best suited for tasks like rolling out dough or lining countertops rather than direct baking applications.
Heat Resistance: Can Rice Paper or Wax Paper Withstand Baking?
Rice paper offers moderate heat resistance, making it suitable for light baking tasks such as wrapping ingredients or creating delicate layers in baked goods. Wax paper is coated with a thin layer of wax that melts at relatively low temperatures, causing it to smoke or even catch fire when exposed to direct heat in the oven. For baking, parchment paper is recommended over both since it can withstand high temperatures without melting, burning, or sticking.
Non-Stick Properties: Which is Better for Baking?
Rice paper is not ideal for baking due to its brittle texture and tendency to stick to baked goods, lacking effective non-stick properties. Wax paper features a coating of paraffin wax, providing better non-stick performance but is unsuitable for oven use as the wax can melt or ignite at high temperatures. For optimal non-stick results and safety in baking, parchment paper remains superior, as it combines heat resistance with excellent non-stick qualities.
Edibility and Food Safety Considerations
Rice paper is edible and safe to consume, making it suitable for wrapping and baking applications where the wrapper is intended to be eaten, while wax paper is coated with paraffin wax and not meant for consumption, posing potential safety risks if ingested. In baking, rice paper offers a non-toxic alternative that can withstand oven temperatures without melting or releasing harmful chemicals, unlike wax paper, which can smoke, catch fire, or contaminate food when exposed to high heat. Food safety guidelines recommend using rice paper for edible wraps and relying on parchment paper or silicone mats for baking to avoid the hazards associated with wax paper.
Common Baking Applications for Rice Paper
Rice paper is commonly used in baking for delicate, gluten-free treats like spring rolls, wrappers for desserts, and edible cups due to its thin, pliable texture that crisps nicely when baked. It provides a neutral taste and enhances presentation by forming a translucent, crunchy layer without adding moisture or grease, making it ideal for light, crispy snacks. Unlike wax paper, rice paper withstands oven heat without melting, ensuring clean, stable results in baked goods and creative applications.
Common Baking Applications for Wax Paper
Wax paper is commonly used in baking for tasks like lining cake pans, rolling out dough, and wrapping food for storage, thanks to its non-stick surface and moisture resistance. It prevents sticking and protects countertops but is not suitable for oven use as the wax coating can melt or ignite at high temperatures. For heat applications such as baking cookies or roasting, parchment paper is preferred over wax paper to ensure safety and proper cooking.
Environmental Impact: Rice Paper vs Wax Paper
Rice paper is biodegradable and compostable, making it an environmentally friendly choice compared to wax paper, which often contains paraffin wax derived from petroleum. Wax paper is less eco-friendly due to its slower decomposition and the potential release of microplastics during disposal. Choosing rice paper for baking reduces plastic waste and supports sustainable practices by minimizing environmental pollution.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Paper for Your Baking Needs
Rice paper provides a non-stick, heat-resistant option ideal for delicate baking tasks requiring moisture control, while wax paper offers a cost-effective, moisture-resistant surface better suited for cold food preparation and light baking. Understanding the specific heat tolerance--rice paper withstands oven temperatures up to 450degF, unlike wax paper which can melt around 200degF--is crucial in selecting the appropriate product. For optimal baking results, prioritize rice paper for high-heat applications and wax paper for low-heat or non-heat uses.
Infographic: Rice paper vs Wax paper for Baking
 azmater.com
azmater.com