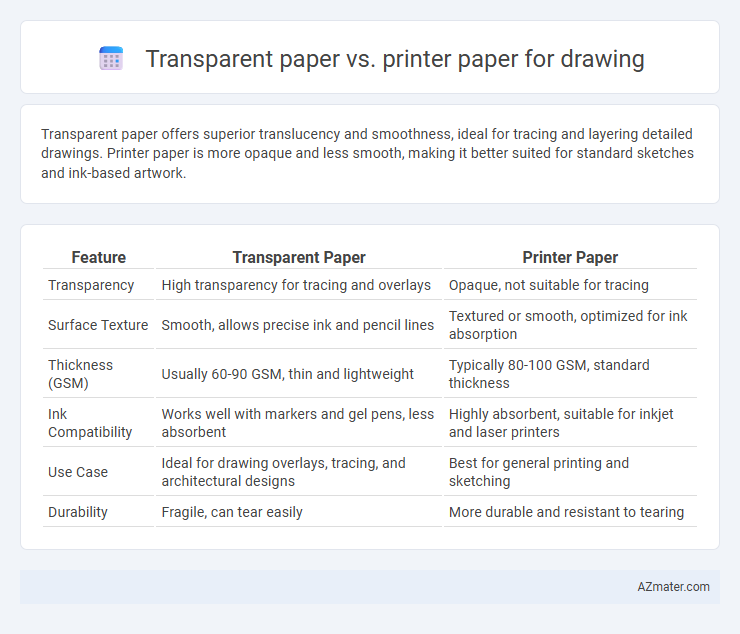
Transparent paper offers superior translucency and smoothness, ideal for tracing and layering detailed drawings. Printer paper is more opaque and less smooth, making it better suited for standard sketches and ink-based artwork.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Paper | Printer Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High transparency for tracing and overlays | Opaque, not suitable for tracing |
| Surface Texture | Smooth, allows precise ink and pencil lines | Textured or smooth, optimized for ink absorption |
| Thickness (GSM) | Usually 60-90 GSM, thin and lightweight | Typically 80-100 GSM, standard thickness |
| Ink Compatibility | Works well with markers and gel pens, less absorbent | Highly absorbent, suitable for inkjet and laser printers |
| Use Case | Ideal for drawing overlays, tracing, and architectural designs | Best for general printing and sketching |
| Durability | Fragile, can tear easily | More durable and resistant to tearing |
Introduction: Understanding Drawing Paper Types
Transparent paper, often known as tracing paper, features a smooth, semi-translucent surface ideal for transferring and refining sketches in drawing. Printer paper, typically made from standard wood pulp with a matte finish, is less durable and absorbs ink differently, making it less suitable for precision art techniques. Artists prefer transparent paper for layering and corrections, while printer paper suits quick sketches and practice drawings.
What is Transparent Paper?
Transparent paper, also known as tracing paper, is a semi-translucent material designed to allow light to pass through, enabling artists to trace images with precision. Unlike standard printer paper, which is opaque and primarily intended for inkjet or laser printing, transparent paper is crafted from cellulose fibers processed to achieve clarity and smoothness, making it ideal for detailed drawing work. This specialized paper facilitates layering and refining sketches, essential for technical drawings, animations, and artistic projects requiring exact replication.
What is Printer Paper?
Printer paper, typically made from wood pulp, is designed for smooth ink absorption and crisp text output, making it ideal for everyday printing tasks. It usually has a weight of 20 pounds per ream and a brightness rating around 92-96, offering a smooth, white surface suitable for detailed pencil or ink drawings. Unlike transparent paper, printer paper is opaque and provides a sturdy base for various drawing media without bleeding or see-through.
Surface Texture: Transparent vs Printer Paper
Transparent paper features a smooth, non-absorbent surface that allows precise ink flow without feathering, making it ideal for detailed line work and overlays in drawing. Printer paper has a slightly rougher texture designed to absorb ink quickly, which can cause minor bleeding but enhances shading effects with pencils and charcoal. Choosing between the two depends on the desired effect: transparency and sharp lines versus texture-enhanced shading and blending.
Compatibility with Drawing Tools
Transparent paper, often called tracing paper, offers excellent compatibility with pencils, pens, and markers due to its smooth, non-absorbent surface, allowing for precise lines and easy corrections. Printer paper tends to absorb ink and graphite more readily, which can cause smudging and less control when using fine drawing tools. Artists who require layering or transferring sketches find transparent paper superior, while printer paper suits basic sketches and practice work with standard pencils.
Tracing and Layering Capabilities
Transparent paper, such as tracing paper or vellum, offers superior translucency essential for precise tracing and layering in detailed drawings, enabling artists to overlay multiple sheets without losing clarity. Printer paper lacks this level of transparency, making it less effective for tracing while often absorbing ink too much, which can blur finer details. For artists prioritizing accurate replication and multi-layer compositions, transparent paper significantly enhances the drawing process compared to standard printer paper.
Durability and Erasability
Transparent paper offers superior erasability due to its smooth surface, allowing artists to easily correct mistakes without damaging the material. Printer paper, while more affordable, tends to be less durable under repeated erasing, often tearing or warping during extensive drawing sessions. For sketches requiring frequent adjustments and long-lasting quality, transparent paper provides a more resilient and forgiving medium compared to standard printer paper.
Color Reproduction and Vibrancy
Transparent paper enhances color reproduction and vibrancy by allowing light to pass through, making colors appear more luminous and vivid, which benefits tracing and layered artwork. Printer paper often absorbs ink, resulting in colors that may appear muted or less saturated, affecting the overall vibrancy of the drawing. Artists seeking bright, richly colored results often prefer transparent paper for its superior color clarity and depth.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Transparent paper, commonly known as tracing paper, tends to be more expensive than standard printer paper due to its specialized manufacturing process and material quality, making it less cost-effective for large-scale drawing projects. Printer paper is widely available in various weights and finishes at lower prices, providing a more budget-friendly option for everyday sketching and conceptual drawings. Availability of transparent paper is often limited to art supply stores or specialty retailers, whereas printer paper can be easily found in supermarkets, office supply stores, and online platforms.
Which Paper Should You Choose for Drawing?
Transparent paper, often known as tracing paper, offers a smooth surface ideal for detailed line work, allowing artists to trace and refine sketches effortlessly. Printer paper, typically made from lower-quality pulp, absorbs ink quickly but may cause smudging or feathering, making it less suitable for precision drawing or layering techniques. Choose transparent paper for clarity and accuracy in drafts or overlays, while printer paper works best for rough sketches or practice due to its affordability.
Infographic: Transparent paper vs Printer paper for Drawing
 azmater.com
azmater.com