Kraft paper has a coarse texture and low absorbency, making it unsuitable for ink absorption, while blotting paper features a highly porous surface designed specifically to quickly absorb and diffuse ink. Blotting paper excels in preventing smudging and drying ink rapidly, unlike Kraft paper, which tends to cause ink pooling and smearing.
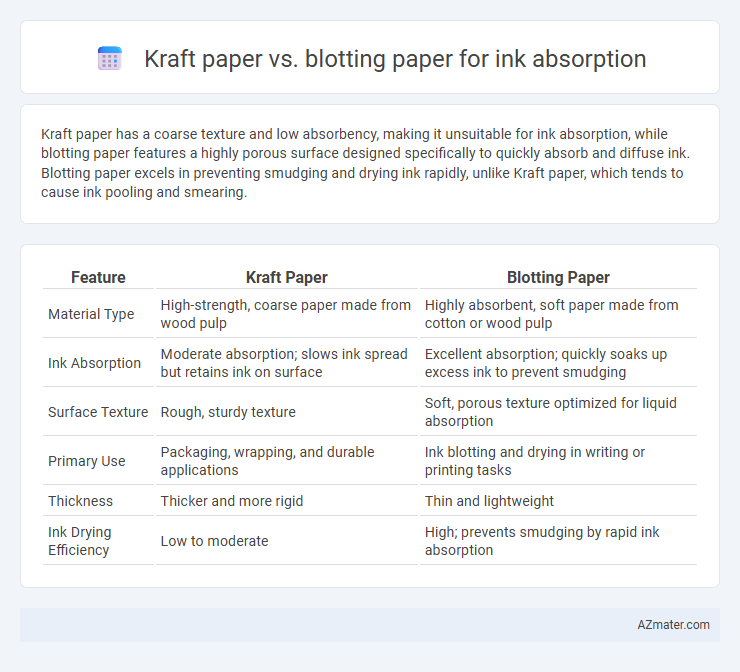
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kraft Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-strength, coarse paper made from wood pulp | Highly absorbent, soft paper made from cotton or wood pulp |
| Ink Absorption | Moderate absorption; slows ink spread but retains ink on surface | Excellent absorption; quickly soaks up excess ink to prevent smudging |
| Surface Texture | Rough, sturdy texture | Soft, porous texture optimized for liquid absorption |
| Primary Use | Packaging, wrapping, and durable applications | Ink blotting and drying in writing or printing tasks |
| Thickness | Thicker and more rigid | Thin and lightweight |
| Ink Drying Efficiency | Low to moderate | High; prevents smudging by rapid ink absorption |
Introduction to Kraft Paper and Blotting Paper
Kraft paper is a sturdy, coarse paper made from wood pulp, known for its high durability and moderate ink absorption, making it ideal for packaging and wrapping. Blotting paper, produced from highly absorbent cellulose fibers, is specifically designed for rapid ink absorption, preventing smudging and ensuring dry surfaces in writing or art applications. The key difference lies in blotting paper's superior porosity and absorbency compared to the denser, less permeable structure of kraft paper.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Kraft paper is made from wood pulp through the kraft process, resulting in strong, coarse fibers ideal for packaging but less absorbent for ink. Blotting paper is manufactured from highly processed cellulose fibers, creating a porous, soft texture designed specifically to absorb excess ink quickly. The distinct fiber treatments and production methods cause kraft paper to resist ink penetration, while blotting paper excels in rapid ink absorption.
Physical Properties Comparison
Kraft paper exhibits a coarse texture with high tensile strength and moderate porosity, allowing it to absorb ink steadily but less rapidly than blotting paper. Blotting paper, characterized by its ultra-porous and fibrous structure, maximizes ink absorption by quickly pulling excess liquid away from surfaces. The denser fiber network of blotting paper ensures superior ink absorption efficiency, while kraft paper offers durability and controlled ink spread.
Ink Absorption Capabilities
Kraft paper exhibits moderate ink absorption, making it suitable for packaging and crafting where ink bleed control is not critical. Blotting paper possesses superior ink absorption capabilities due to its high porosity and fibrous structure, effectively preventing smudging and drying ink quickly. For applications requiring precise ink control and fast drying, blotting paper outperforms kraft paper significantly.
Surface Texture and Smoothness
Kraft paper exhibits a coarse and fibrous surface texture that provides moderate ink absorption but can cause slight feathering due to its roughness. Blotting paper features an ultra-porous and smooth surface specifically designed for rapid ink absorption, minimizing smudging and promoting clean lines. The inherent smoothness of blotting paper makes it superior for controlling excess ink compared to the rough texture of kraft paper.
Suitability for Writing and Drawing
Kraft paper offers moderate ink absorption with a rough texture, making it suitable for bold, textured writing and sketching but less ideal for fine detail or smooth ink flow. Blotting paper excels at rapid ink absorption without smudging, providing superior performance for pen and ink drawings or calligraphy that require clean, crisp lines and quick drying. For artists and writers prioritizing precision and ink control, blotting paper is the preferred choice, while kraft paper suits more rustic, expressive styles.
Durability and Strength in Practice
Kraft paper exhibits superior durability and strength in practical applications, making it ideal for handling ink absorption where resistance to tearing or deterioration is essential. Blotting paper, designed for rapid ink absorption, lacks the structural integrity of kraft paper and may weaken or disintegrate under heavy ink loads. The dense fiber composition of kraft paper maintains its form while absorbing inks, whereas the porous, fragile nature of blotting paper prioritizes quick ink uptake over physical robustness.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Kraft paper typically offers lower cost and widespread availability compared to blotting paper, making it a budget-friendly option for general ink absorption needs. Blotting paper, designed specifically for rapid ink absorption, is usually more expensive and less commonly stocked in standard paper suppliers. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the superior absorption efficiency of blotting paper against the affordability and easy access of kraft paper.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kraft paper, made from chemical pulp, offers moderate ink absorption and is highly valued for its biodegradability and recyclability, contributing positively to environmental sustainability. Blotting paper excels in rapid ink absorption due to its high porosity but often involves intensive chemical processing, raising concerns about its environmental footprint. Choosing kraft paper supports reduced deforestation and lower chemical usage, making it a more eco-friendly option compared to traditional blotting paper for sustainable ink absorption needs.
Choosing the Right Paper for Ink Applications
Kraft paper offers moderate ink absorption suitable for packaging and crafts requiring durability, while blotting paper excels in rapid ink absorption, preventing smudging in writing or printing applications. Choosing the right paper depends on the ink type and desired drying time; blotting paper is ideal for fountain pens and calligraphy, whereas kraft paper suits ink applications where absorption with minimal bleed-through is necessary. Assessing factors like ink viscosity and project purpose ensures optimal performance in ink absorption tasks.
Infographic: Kraft paper vs Blotting paper for Ink Absorption
 azmater.com
azmater.com