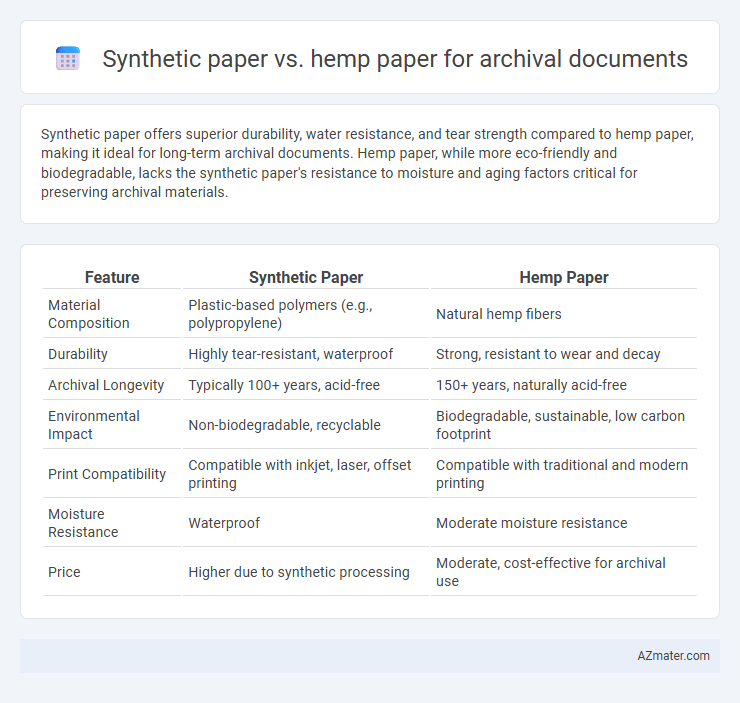
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear strength compared to hemp paper, making it ideal for long-term archival documents. Hemp paper, while more eco-friendly and biodegradable, lacks the synthetic paper's resistance to moisture and aging factors critical for preserving archival materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Paper | Hemp Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic-based polymers (e.g., polypropylene) | Natural hemp fibers |
| Durability | Highly tear-resistant, waterproof | Strong, resistant to wear and decay |
| Archival Longevity | Typically 100+ years, acid-free | 150+ years, naturally acid-free |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Biodegradable, sustainable, low carbon footprint |
| Print Compatibility | Compatible with inkjet, laser, offset printing | Compatible with traditional and modern printing |
| Moisture Resistance | Waterproof | Moderate moisture resistance |
| Price | Higher due to synthetic processing | Moderate, cost-effective for archival use |
Introduction to Synthetic Paper and Hemp Paper
Synthetic paper, made from polypropylene or polyethylene, offers waterproof, tear-resistant, and chemical-resistant properties ideal for long-lasting archival documents. Hemp paper, derived from the durable fibers of the hemp plant, provides natural acid-free qualities that prevent yellowing and deterioration over time. Comparing their archival benefits reveals synthetic paper's superior durability, while hemp paper excels in environmental sustainability and biodegradability.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Hemp Papers
Synthetic paper offers superior water resistance, tear strength, and longevity, making it ideal for archival documents requiring durability and protection from environmental damage. Hemp paper, derived from natural fibers, provides excellent biodegradability and acid-free properties, which contribute to its archival stability but with less resistance to moisture and physical wear compared to synthetic paper. Both papers exhibit archival quality, yet synthetic paper is favored for its enhanced durability while hemp paper supports sustainability through its organic composition.
Durability and Longevity for Archival Purposes
Synthetic paper offers superior durability and resistance to water, tearing, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for archival documents requiring long-term preservation. Hemp paper provides excellent longevity due to its high cellulose content and natural resistance to degradation, often outlasting traditional wood-pulp paper in archival conditions. Both materials enhance archival quality, but synthetic paper excels in physical durability while hemp paper ensures natural aging resistance for extended document preservation.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Synthetic paper exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, making it highly suitable for archival documents requiring long-term preservation. Hemp paper offers natural durability and biodegradability but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to humidity and light compared to synthetic alternatives. For archival purposes demanding resistance to mold, water damage, and chemical degradation, synthetic paper provides enhanced protection and longevity.
Chemical Composition and Safety Concerns
Synthetic paper, often made from polypropylene or polyethylene, offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to hemp paper, which is primarily composed of cellulose fibers. Hemp paper, being organic and biodegradable, can degrade over time when exposed to acidic environments, while synthetic paper resists moisture, acids, and UV exposure, ensuring safer long-term archival storage. Safety concerns around synthetic paper include potential off-gassing of additives and limited recyclability, whereas hemp paper carries risks of microbial growth but is free from harmful synthetic chemicals.
Printability and Ink Absorption
Synthetic paper offers superior printability due to its smooth, consistent surface that enhances ink adhesion and color vibrancy, making it ideal for high-quality archival document reproduction. Hemp paper, while eco-friendly and durable, tends to have a rougher texture that may lead to uneven ink absorption and potential smudging over time. For long-term archival purposes, synthetic paper ensures sharper, more stable prints with better resistance to fading and ink bleed.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic paper offers durability and water resistance but relies on petrochemical-based polymers, contributing to higher carbon emissions and limited biodegradability compared to hemp paper. Hemp paper, made from fast-growing, renewable plants, provides superior biodegradability and requires less water and pesticides, reducing its overall environmental footprint. The sustainable cultivation of hemp enhances soil health and carbon sequestration, making it a more eco-friendly choice for archival documents aiming for long-term preservation with minimal ecological impact.
Cost Comparison for Archival Applications
Synthetic paper for archival documents offers higher durability and water resistance but typically comes at a 30-50% higher cost compared to hemp paper. Hemp paper, valued for its natural lignin-free fibers, provides excellent longevity at a lower price, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale archival preservation. Budget-conscious archival projects often prefer hemp paper due to its balance of affordability and archival-quality performance.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Synthetic paper, often made from polypropylene, meets ISO 9706 standards for permanence and is resistant to water, tears, and chemicals, making it ideal for archival documents requiring long-term durability. Hemp paper, certified by the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and often compliant with ANSI/NISO Z39.48 standards, offers exceptional biodegradability and lignin-free composition, ensuring resistance to yellowing and acid degradation over time. Industry preferences hinge on specific archival needs, with synthetic paper favored for physical durability and hemp paper preferred for environmentally sustainable, acid-free document preservation.
Choosing the Best Paper for Archival Document Preservation
Synthetic paper offers superior durability, water resistance, and tear-proof qualities, making it an excellent choice for long-term archival document preservation. Hemp paper, known for its natural fibers and high lignin content, provides strong durability but may be more susceptible to environmental degradation compared to synthetic alternatives. Selecting the best paper involves balancing synthetic paper's longevity and resilience against hemp paper's biodegradability and traditional archival appeal.
Infographic: Synthetic paper vs Hemp paper for Archival document
 azmater.com
azmater.com