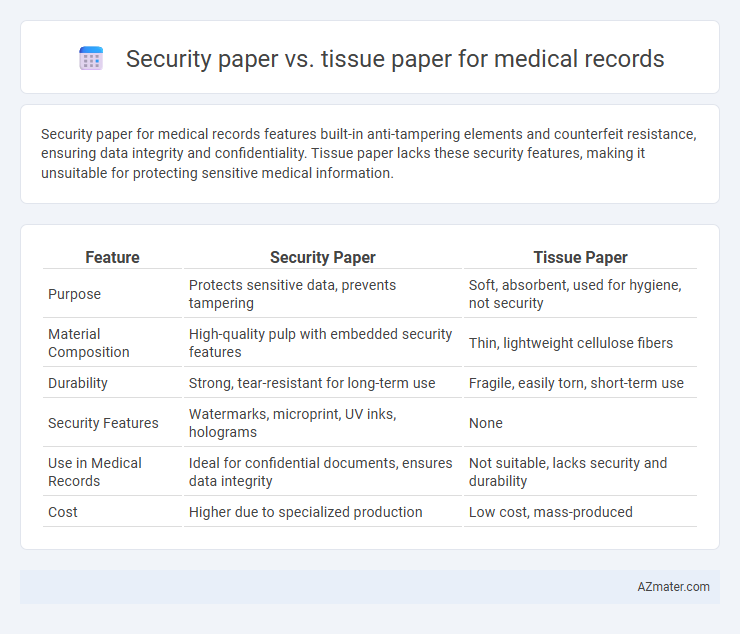
Security paper for medical records features built-in anti-tampering elements and counterfeit resistance, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. Tissue paper lacks these security features, making it unsuitable for protecting sensitive medical information.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Security Paper | Tissue Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects sensitive data, prevents tampering | Soft, absorbent, used for hygiene, not security |
| Material Composition | High-quality pulp with embedded security features | Thin, lightweight cellulose fibers |
| Durability | Strong, tear-resistant for long-term use | Fragile, easily torn, short-term use |
| Security Features | Watermarks, microprint, UV inks, holograms | None |
| Use in Medical Records | Ideal for confidential documents, ensures data integrity | Not suitable, lacks security and durability |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized production | Low cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Paper Types in Medical Records
Security paper used in medical records incorporates features like watermarks, microprinting, and chemical sensitivity to prevent tampering and unauthorized copying, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. Tissue paper, typically thin and fragile, lacks security attributes and is unsuitable for preserving sensitive patient information or maintaining record durability. Choosing security paper is critical for compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and safeguarding medical documentation against fraud.
What is Security Paper?
Security paper is a specialized type of paper designed with embedded features such as watermarks, microprinting, and invisible fibers to prevent forgery and unauthorized copying of sensitive documents, including medical records. Unlike standard tissue paper, security paper provides physical and chemical protections that enhance document integrity and confidentiality. These security elements help ensure that medical records remain authentic and compliant with regulatory standards.
What is Tissue Paper?
Tissue paper is a lightweight, thin material primarily made from cellulose fibers, widely used for hygiene purposes such as facial tissues or toilet paper. In medical settings, tissue paper lacks the durability and security features required for protecting sensitive medical records, making it unsuitable for document preservation or confidentiality. Security paper, in contrast, incorporates watermarks, chemical sensitivity, and tamper-evident designs specifically engineered to safeguard medical information from unauthorized access or reproduction.
Key Features of Security Paper
Security paper for medical records is specifically designed to prevent unauthorized copying and tampering, featuring watermarks, microprinting, and chemical-sensitive fibers that react to erasure attempts. Unlike tissue paper, which is thin, fragile, and intended for hygienic use, security paper offers durability and enhanced protection against fraud or data breaches. The key features include secure fiber technology, invisible ink, and embedded holograms that ensure the authenticity and integrity of sensitive medical documentation.
Properties of Tissue Paper
Tissue paper for medical records offers superior softness, absorbency, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for delicate handling and minimizing damage during frequent use. Its breathable and flexible nature allows for easy folding and secure storage without compromising the integrity of the records. However, tissue paper lacks the durability and tamper-evident security features found in security paper, which is designed to protect sensitive information from forgery and unauthorized access.
Role of Security Paper in Preventing Fraud
Security paper plays a crucial role in preventing fraud in medical records by incorporating advanced features such as watermarks, microprint, and tamper-evident overlays that ensure document authenticity and integrity. Unlike tissue paper, which lacks any security elements and can be easily copied or altered, security paper helps maintain the confidentiality and trustworthiness of sensitive patient information. The use of security paper significantly reduces the risk of forgery, unauthorized alterations, and counterfeit records within healthcare institutions.
Suitability of Tissue Paper for Medical Documentation
Tissue paper lacks the durability and opacity required for secure medical documentation, making security paper the preferred choice for safeguarding sensitive patient information. Security paper incorporates features like watermarks, micro-text, and tamper-evident coatings that prevent unauthorized copying and alteration, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of medical records. While tissue paper is lightweight and soft, its susceptibility to tearing, smudging, and transparency limits its suitability for legally binding and long-term medical documentation.
Durability and Longevity in Medical Record Keeping
Security paper offers enhanced durability and longevity compared to tissue paper for medical record keeping, as it is designed to resist wear, moisture, and tampering, ensuring the integrity of sensitive information. Its robust fibers and special coatings protect against fading and physical damage over time, making it ideal for long-term archival purposes. Tissue paper lacks these protective features, leading to faster deterioration, increased risk of data loss, and compromised record preservation.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Security paper used for medical records ensures compliance with healthcare regulations by providing tamper-evident features, watermarks, and microprint patterns that prevent unauthorized alterations and counterfeiting. Tissue paper lacks these security elements, making it unsuitable for preserving the integrity and confidentiality required by HIPAA and other healthcare standards. Employing security paper significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and supports audit trails mandated for medical documentation.
Choosing the Right Paper for Medical Records
Security paper offers advanced protection against tampering and unauthorized copying, making it ideal for sensitive medical records requiring confidentiality. Tissue paper lacks security features and durability, increasing the risk of damage and data breach in medical documentation. Choosing security paper ensures compliance with healthcare regulations and preserves the integrity of patient information.
Infographic: Security paper vs Tissue paper for Medical record
 azmater.com
azmater.com