Recycled paper for newspapers reduces deforestation and energy consumption by up to 40% compared to virgin paper. Virgin paper offers higher print quality but contributes significantly more to environmental degradation and carbon emissions.
Table of Comparison
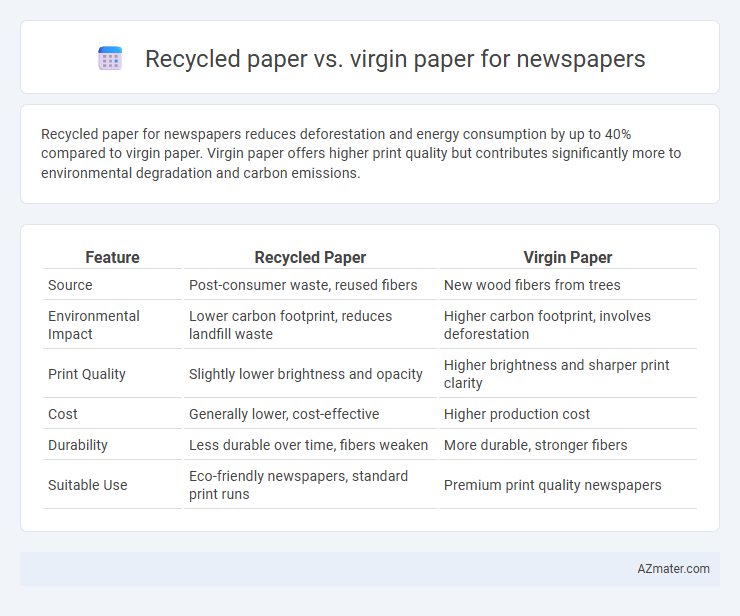
| Feature | Recycled Paper | Virgin Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer waste, reused fibers | New wood fibers from trees |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon footprint, involves deforestation |
| Print Quality | Slightly lower brightness and opacity | Higher brightness and sharper print clarity |
| Cost | Generally lower, cost-effective | Higher production cost |
| Durability | Less durable over time, fibers weaken | More durable, stronger fibers |
| Suitable Use | Eco-friendly newspapers, standard print runs | Premium print quality newspapers |
Introduction to Recycled and Virgin Paper
Recycled paper for newspapers is made from post-consumer waste, reducing deforestation and lowering energy consumption during production. Virgin paper, derived directly from fresh wood pulp, offers higher strength and brightness, making it a preferred choice for print clarity and durability. Choosing between recycled and virgin paper impacts environmental sustainability and print quality in newspaper production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled paper significantly reduces deforestation and lowers energy consumption by up to 60% compared to virgin paper used in newspapers, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Virgin paper production demands extensive use of fresh wood fibers and chemicals, resulting in higher water pollution and carbon footprint. Choosing recycled paper for newspapers supports sustainable forestry and waste reduction, contributing to a smaller environmental impact.
Production Processes: Recycled vs Virgin Paper
Recycled paper for newspapers is produced by collecting post-consumer waste, which is then cleaned and de-inked to remove contaminants before being pulped, significantly reducing the need for raw wood fibers. Virgin paper production involves harvesting fresh timber, followed by mechanical or chemical pulping processes that extract cellulose fibers directly from wood, resulting in higher fiber strength and brightness. The recycled paper process consumes less energy and water, emitting fewer pollutants, while virgin paper requires more intensive processing and raw material extraction, impacting environmental sustainability.
Resource Consumption and Sustainability
Recycled paper for newspapers significantly reduces resource consumption by reusing fibers, lowering the demand for fresh wood pulp and conserving natural forests. Virgin paper production requires more water, energy, and chemicals, increasing environmental impact through deforestation and higher greenhouse gas emissions. Prioritizing recycled paper enhances sustainability by minimizing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices in the print media industry.
Quality and Printability Differences
Recycled paper for newspapers typically has a lower brightness and can exhibit more fiber variability, affecting print sharpness and color vibrancy compared to virgin paper made from fresh wood pulp which offers a smoother, more uniform surface. Virgin paper generally provides superior printability with consistent ink absorption and less dust generation during high-speed printing, resulting in clearer images and text. The trade-off often involves balancing environmental benefits with the need for optimal quality and print performance in newspaper production.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Paper
Recycled paper generally offers a lower production cost compared to virgin paper due to reduced raw material expenses and energy consumption in the pulping process. Virgin paper requires fresh wood fibers, leading to higher costs related to logging, transportation, and chemical treatments. Newspapers opting for recycled paper benefit from cost savings while supporting environmental sustainability, though slight quality differences may influence printing efficiency and ink absorption.
Availability and Supply Chain Considerations
Recycled paper for newspapers relies heavily on the collection and processing of post-consumer fibers, which can fluctuate based on local recycling rates and infrastructure efficiency, making availability region-dependent. Virgin paper supply chains benefit from established forestry operations and integrated pulp mills, ensuring a more consistent and scalable resource flow, though they face increasing scrutiny over sustainability. Disruptions in recycled material streams due to contamination or logistical challenges often lead publishers to balance cost and environmental impact when selecting between recycled and virgin paper options.
Impact on Newspaper Readership and Perception
Recycled paper for newspapers often enhances public perception by aligning with growing environmental awareness, potentially increasing reader loyalty and trust in the publication's social responsibility. Virgin paper, known for its superior brightness and print quality, can improve readability and visual appeal, which may attract a broader readership. However, the trade-off between environmental impact and print clarity influences consumer preferences, shaping newspaper readership through sustainability values or aesthetic expectations.
Regulatory Requirements and Industry Standards
Recycled paper for newspapers must comply with EPA regulations such as the Comprehensive Procurement Guidelines, ensuring minimum recycled content to reduce environmental impact, while virgin paper adheres to forestry certification standards like FSC or PEFC for sustainable sourcing. Industry standards, such as the PRINTING INK COUNCIL (PIC) guidelines, mandate the use of non-toxic inks compatible with both paper types to maintain recyclability and print quality. Compliance with these regulatory requirements and standards ensures newspapers meet environmental policies and maintain product safety across the production and recycling lifecycle.
Future Trends in Newspaper Paper Choices
Future trends in newspaper paper choices indicate a strong shift towards recycled paper due to rising environmental concerns and regulatory pressures promoting sustainability. Innovations in recycling technology are enhancing the quality and printability of recycled paper, making it a more viable option compared to traditional virgin paper derived from deforestation. Market forecasts suggest increasing adoption of eco-friendly newspaper paper supported by consumer demand for green products and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Infographic: Recycled paper vs Virgin paper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com