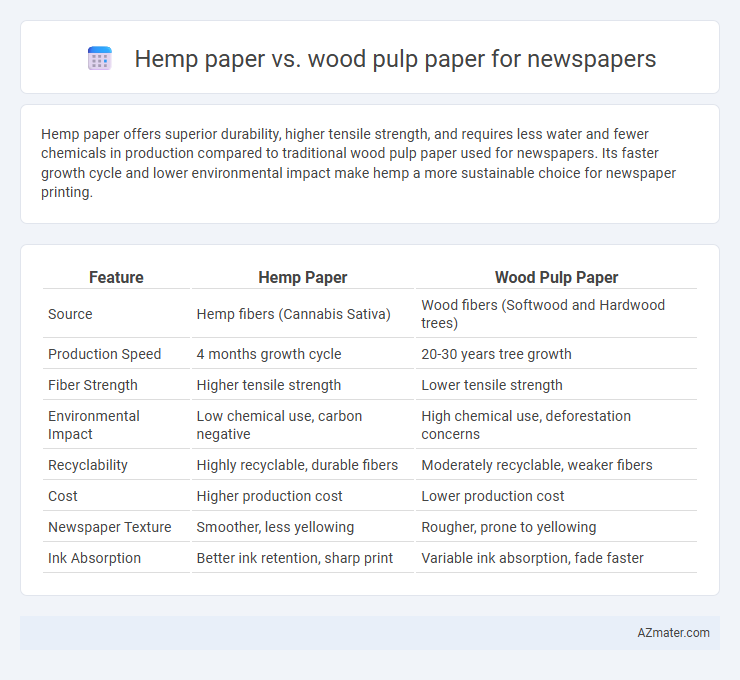
Hemp paper offers superior durability, higher tensile strength, and requires less water and fewer chemicals in production compared to traditional wood pulp paper used for newspapers. Its faster growth cycle and lower environmental impact make hemp a more sustainable choice for newspaper printing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Wood Pulp Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp fibers (Cannabis Sativa) | Wood fibers (Softwood and Hardwood trees) |
| Production Speed | 4 months growth cycle | 20-30 years tree growth |
| Fiber Strength | Higher tensile strength | Lower tensile strength |
| Environmental Impact | Low chemical use, carbon negative | High chemical use, deforestation concerns |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable, durable fibers | Moderately recyclable, weaker fibers |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Newspaper Texture | Smoother, less yellowing | Rougher, prone to yellowing |
| Ink Absorption | Better ink retention, sharp print | Variable ink absorption, fade faster |
Introduction to Hemp Paper and Wood Pulp Paper
Hemp paper, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers higher tensile strength and durability compared to wood pulp paper, making it an eco-friendly alternative in newspaper production. Wood pulp paper, traditionally sourced from softwood and hardwood trees, dominates the newspaper industry due to its lower cost and established manufacturing processes despite its environmental impact. Innovations in hemp paper processing emphasize reduced chemical use and faster growth cycles, positioning it as a sustainable substitute for conventional wood pulp paper in printing newspapers.
Historical Overview of Paper Materials
Hemp paper dates back to ancient China, where it was prized for its durability and resistance to yellowing compared to wood pulp paper, which became dominant during the Industrial Revolution due to the rapid availability of timber resources. Wood pulp paper revolutionized newspaper production in the 19th century, enabling mass circulation but often sacrificing longevity and environmental sustainability. Recent interest in hemp paper resurfaces as a sustainable alternative, offering higher fiber strength and requiring fewer chemicals in processing than traditional wood pulp sources.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Hemp paper, derived from the fast-growing stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, provides a highly renewable raw material with a growth cycle of just 3-4 months, compared to the 20-80 years required for wood pulp from trees like pine and spruce. Hemp fibers yield 3-4 times more pulp per acre than wood, significantly reducing deforestation and land use. The minimal pesticide and water requirements of hemp cultivation enhance its sustainability, making hemp paper a more eco-friendly alternative in newspaper production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp paper production generates significantly lower carbon emissions compared to wood pulp paper due to faster growth cycles and reduced need for chemical processing. Hemp cultivation demands less water and pesticides, contributing to decreased soil degradation and biodiversity loss relative to traditional wood-based paper. Recycling rates and biodegradability of hemp paper also enhance its environmental sustainability over wood pulp alternatives.
Production Processes: Hemp vs Wood Pulp
Hemp paper production involves harvesting hemp fibers, retting to separate fibers, and mechanical or chemical processing to create pulp with higher cellulose content and less lignin compared to wood pulp. Wood pulp paper manufacturing requires debarking, chipping, and chemical pulping processes such as kraft or sulfite methods, which are energy-intensive and produce more pollutants due to lignin removal. Hemp's faster growth cycle and lower chemical input result in a more sustainable and efficient production process for newspaper paper compared to conventional wood pulp.
Paper Quality and Printability
Hemp paper offers superior paper quality for newspapers due to its longer fibers, resulting in increased tear strength, durability, and resistance to yellowing compared to wood pulp paper. The printability of hemp paper excels with its smoother surface and better ink absorption, enhancing image sharpness and color vibrancy. Wood pulp newspapers often suffer from quicker degradation and lower print clarity, impacting overall readability and lifespan.
Cost Analysis for Newspaper Publishers
Hemp paper production involves higher initial costs due to specialized processing equipment and limited large-scale supply compared to traditional wood pulp paper, which benefits from established infrastructure and abundant raw materials. However, hemp yields significantly more fiber per acre annually, potentially reducing long-term raw material expenses and offering greater sustainability. Newspaper publishers must weigh the upfront investment against hemp's environmental advantages and possible cost savings as production scales and demand for eco-friendly printing materials increases.
Lifespan and Archival Properties
Hemp paper exhibits superior lifespan and archival qualities compared to wood pulp paper used in newspapers, lasting up to 300 years due to its high cellulose content and resistance to oxidation. Wood pulp paper typically deteriorates within 30 to 50 years as lignin causes yellowing and brittleness over time. Archival properties of hemp paper make it ideal for preserving historical documents, while wood pulp newspapers require chemical treatments to enhance durability.
Market Availability and Industry Adoption
Hemp paper, praised for its durability and eco-friendliness, faces limited market availability compared to wood pulp paper, which dominates the newspaper industry due to its established supply chains and cost efficiency. Newspaper publishers largely prefer wood pulp paper because of widespread industry adoption and infrastructure supporting mass production. Despite hemp paper's potential for sustainability, scaling its production remains a challenge, slowing its mainstream use in newspaper printing.
The Future of Newspaper Printing Materials
Hemp paper offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp paper for newspaper printing, providing higher durability and faster ink absorption that enhances print clarity. The future of newspaper printing materials increasingly favors hemp due to its rapid growth cycle, requiring significantly fewer chemicals and less water compared to wood pulp production. As environmental regulations tighten, the shift towards hemp-based paper supports eco-friendly practices and reduces deforestation associated with wood pulp sourcing.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Wood pulp paper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com