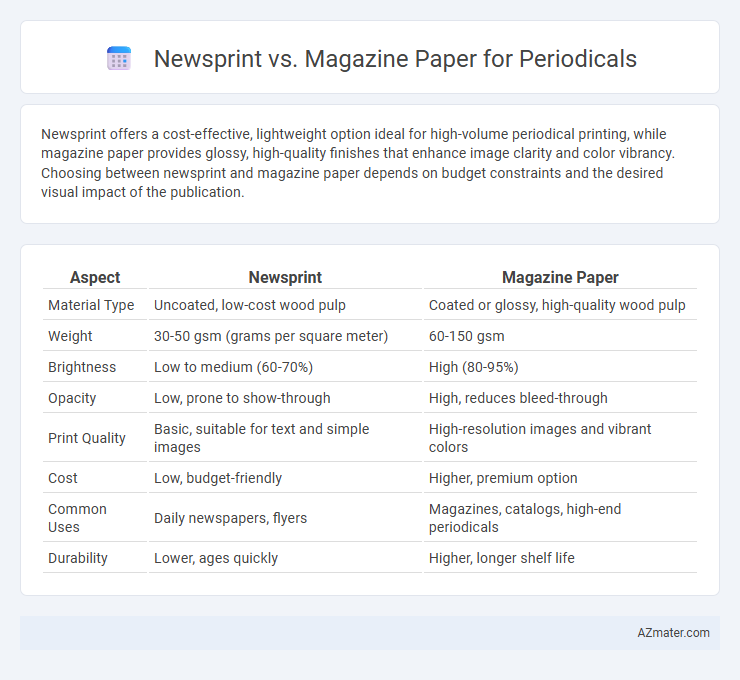
Newsprint offers a cost-effective, lightweight option ideal for high-volume periodical printing, while magazine paper provides glossy, high-quality finishes that enhance image clarity and color vibrancy. Choosing between newsprint and magazine paper depends on budget constraints and the desired visual impact of the publication.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Newsprint | Magazine Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Uncoated, low-cost wood pulp | Coated or glossy, high-quality wood pulp |
| Weight | 30-50 gsm (grams per square meter) | 60-150 gsm |
| Brightness | Low to medium (60-70%) | High (80-95%) |
| Opacity | Low, prone to show-through | High, reduces bleed-through |
| Print Quality | Basic, suitable for text and simple images | High-resolution images and vibrant colors |
| Cost | Low, budget-friendly | Higher, premium option |
| Common Uses | Daily newspapers, flyers | Magazines, catalogs, high-end periodicals |
| Durability | Lower, ages quickly | Higher, longer shelf life |
Introduction to Periodical Paper Types
Periodical paper types primarily include newsprint and magazine paper, each serving distinct purposes in publishing. Newsprint is a lightweight, inexpensive paper with high opacity, ideal for daily newspapers due to its affordability and ability to handle fast printing processes. Magazine paper, often coated and glossy, offers superior image reproduction and durability, making it suitable for high-quality prints with vibrant colors in monthly or weekly magazines.
Defining Newsprint: Key Characteristics
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper primarily made from wood pulp, featuring a lightweight, thin, and highly porous structure ideal for high-speed printing presses used in periodicals. Its brightness level ranges between 40-60% ISO, providing moderate print contrast that accommodates bold text and photos but limits color vibrancy compared to coated magazine paper. Newsprint's high absorbency allows fast drying of ink but results in lower durability and increased susceptibility to yellowing and tearing over time, making it suited for short-term, mass-distribution publications like daily newspapers and certain periodicals.
Understanding Magazine Paper: Features and Benefits
Magazine paper offers a smoother, glossier finish compared to newsprint, enhancing image clarity and color vibrancy essential for high-quality periodicals. Its higher brightness and weight contribute to a premium tactile experience, improving reader engagement and perceived value. Durable and less prone to yellowing, magazine paper extends the longevity of printed materials, making it ideal for upscale magazines and promotional publications.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Newsprint, commonly used for newspapers, offers lower durability and a shorter lifespan due to its inexpensive, lightweight, and highly absorbent nature, making it prone to yellowing and tearing over time. Magazine paper, typically coated and produced from higher-quality pulp, provides superior durability with enhanced resistance to aging, moisture, and fading, resulting in a longer-lasting and visually appealing finish. For periodicals requiring extended preservation and vibrant imagery, magazine paper is the preferred choice, while newsprint suits short-term, cost-effective distribution.
Print Quality and Visual Appeal
Newsprint offers a cost-effective option for periodicals but features lower print quality due to its absorbent, rough texture that can cause ink bleed and less sharp images. Magazine paper, often coated and smoother, enhances print resolution and color vibrancy, providing superior visual appeal and crisp graphics ideal for high-impact visuals. Choosing magazine paper elevates the overall reader experience with richer tones and glossy finishes, whereas newsprint suits high-volume, budget-conscious publications with primarily text-based content.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Recycling
Newsprint typically has a lower environmental impact than magazine paper due to its higher recyclability and use of uncoated, wood-based fibers that decompose more easily. Magazine paper, often coated with glossy finishes and containing chemical additives, presents challenges in recycling processes and increases pollution risks. Sustainable choices favor newsprint for periodicals to reduce carbon footprint and support circular paper production systems.
Cost Considerations for Publishers
Newsprint offers publishers a significantly lower raw material cost compared to magazine paper, making it ideal for large circulation periodicals with tight budgets. Magazine paper, often coated and higher quality, incurs greater expenses due to superior brightness and print resolution, thus increasing overall production costs. Publishers must balance these costs against audience expectations and the periodicity of distribution to optimize profitability.
Reader Experience and Perception
Newsprint offers a lightweight, inexpensive option for periodicals, often resulting in a rougher texture and lower print quality that can affect readability and image vibrancy. Magazine paper, typically glossy and coated, enhances color saturation and sharpness, providing a premium tactile experience that positively influences reader perception and engagement. The choice between newsprint and magazine paper directly impacts the overall aesthetic appeal, durability, and perceived value of the publication.
Common Uses and Industry Trends
Newsprint is widely utilized for daily newspapers and mass-distributed periodicals due to its cost-efficiency and quick print turnaround. Magazine paper, characterized by higher brightness and coated finishes, caters to premium periodicals emphasizing vibrant visuals and durability. Industry trends show a shift towards eco-friendly, recycled newsprint and digitally optimized magazine papers reflecting evolving consumer preferences and sustainability mandates.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Periodical
Selecting the ideal paper for your periodical impacts print quality, cost, and reader experience. Newsprint offers affordability and recyclability, making it suitable for high-volume, short-lived publications with less emphasis on color vibrancy. Magazine paper, typically coated and brighter, enhances image sharpness and durability, ideal for premium periodicals aiming to attract advertisers and retain readers through superior visual appeal.
Infographic: Newsprint vs Magazine Paper for Periodical
 azmater.com
azmater.com