Hemp paper offers superior durability and eco-friendliness with higher tensile strength and faster growth cycles compared to sugarcane paper, which utilizes bagasse waste and supports circular economy by reducing agricultural residue. Both materials provide sustainable alternatives to traditional wood pulp paper, but hemp paper excels in longevity and recycling potential.
Table of Comparison
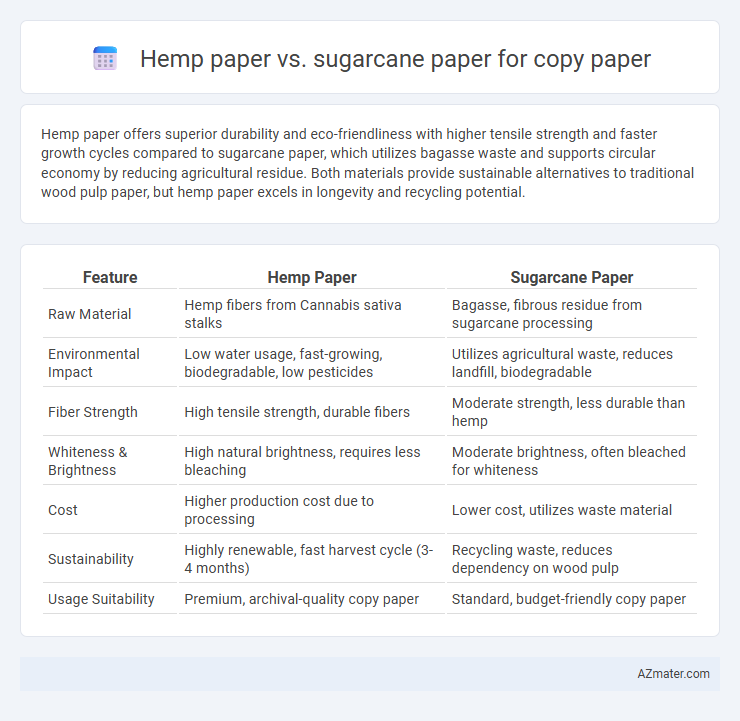
| Feature | Hemp Paper | Sugarcane Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp fibers from Cannabis sativa stalks | Bagasse, fibrous residue from sugarcane processing |
| Environmental Impact | Low water usage, fast-growing, biodegradable, low pesticides | Utilizes agricultural waste, reduces landfill, biodegradable |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength, durable fibers | Moderate strength, less durable than hemp |
| Whiteness & Brightness | High natural brightness, requires less bleaching | Moderate brightness, often bleached for whiteness |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to processing | Lower cost, utilizes waste material |
| Sustainability | Highly renewable, fast harvest cycle (3-4 months) | Recycling waste, reduces dependency on wood pulp |
| Usage Suitability | Premium, archival-quality copy paper | Standard, budget-friendly copy paper |
Introduction to Hemp Paper and Sugarcane Paper
Hemp paper, derived from the bast fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers high durability, longevity, and sustainability due to its fast growth rate and minimal pesticide requirements. Sugarcane paper, produced from bagasse--the fibrous residue remaining after juice extraction--provides an eco-friendly alternative by utilizing agricultural waste, reducing deforestation and water consumption. Both materials serve as promising raw sources for copy paper, each contributing unique environmental benefits and performance characteristics.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Hemp paper is sourced from the fast-growing fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, requiring less water and pesticides compared to traditional wood pulp, making it a highly sustainable raw material. Sugarcane paper utilizes bagasse, the fibrous residue left after extracting juice, which repurposes agricultural waste and reduces dependency on trees. Both options offer eco-friendly alternatives to conventional paper, but hemp's higher fiber yield per acre and shorter cultivation cycle provide superior environmental benefits for copy paper production.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Hemp paper manufacturing involves extracting fibers through retting and mechanical processing, resulting in a durable pulp with minimal chemical additives, while sugarcane paper production utilizes bagasse, the fibrous residue from sugar extraction, which is chemically pulped to create a softer, less resilient material. Hemp fibers require less bleaching and fewer harsh chemicals due to their natural strength and fiber length, reducing the environmental impact compared to sugarcane paper, which often demands more intensive chemical treatments. The energy consumption in hemp paper production is generally lower because of its reduced need for refining processes, making it a more sustainable option for copy paper manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
Hemp paper for copy paper significantly reduces environmental impact due to its rapid growth cycle and minimal pesticide use, contributing to a lower carbon footprint compared to sugarcane paper. Sugarcane paper, while utilizing agricultural waste like bagasse, often requires more energy-intensive processing and results in higher greenhouse gas emissions. Lifecycle assessments show hemp paper's carbon sequestration during cultivation offsets emissions, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly office supplies.
Paper Quality and Performance
Hemp paper offers superior durability and tear resistance compared to sugarcane paper, making it ideal for high-quality copy paper. Sugarcane paper, derived from bagasse, provides a smooth finish and excellent print clarity but tends to be less resilient under frequent handling. Both papers are eco-friendly, yet hemp paper generally outperforms sugarcane paper in longevity and overall performance in office environments.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp paper generally incurs higher production costs due to the labor-intensive extraction process and limited large-scale cultivation, resulting in a higher market price compared to sugarcane paper. Sugarcane paper benefits from the abundant availability of bagasse, a byproduct of sugar production, which reduces raw material costs and enhances its market presence as an affordable, eco-friendly alternative. Market availability of sugarcane paper is significantly broader, supported by established supply chains and increasing demand for sustainable copy paper options in commercial sectors.
Biodegradability and Recycling
Hemp paper exhibits superior biodegradability due to its natural fiber composition, breaking down faster in composting environments compared to sugarcane paper, which contains residual bagasse fibers with slower decomposition rates. Recycling hemp paper is more efficient because its longer fibers produce stronger recycled pulp, reducing the need for chemical treatments and energy-intensive processing seen in sugarcane paper recycling. Both materials support sustainable copy paper alternatives, but hemp's enhanced biodegradability and recycling qualities position it as a more environmentally friendly option.
Applications in Copy Paper Uses
Hemp paper offers superior durability and higher tear resistance compared to sugarcane paper, making it ideal for high-traffic copy paper applications in offices and educational institutions. Sugarcane paper provides a sustainable alternative with a smoother finish, enhancing print quality for everyday printing and photocopying tasks. Both materials support eco-friendly initiatives, but hemp excels in longevity and recyclability for long-term document preservation.
Challenges and Limitations
Hemp paper offers superior durability and sustainability compared to sugarcane paper, yet its higher production costs and limited supply chain infrastructure pose significant challenges for widespread copy paper use. Sugarcane paper benefits from abundant agricultural waste availability, but its lower fiber strength and bleaching requirements can reduce print quality and increase environmental impact. Both options face scalability issues due to current industrial processes tailored primarily for wood pulp, limiting their competitive adoption in the copy paper market.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Hemp paper exhibits superior durability and sustainability due to its fast growth cycle and minimal pesticide use, making it a promising alternative for eco-friendly copy paper production. Innovations in enzymatic pulping and fiber refinement are enhancing hemp paper's print quality and cost-effectiveness, driving future adoption in commercial printing. Sugarcane paper leverages agricultural waste, reducing landfill impact and offering biodegradable options, with ongoing advancements in processing technology improving its texture and strength for competitive use in copy paper markets.
Infographic: Hemp paper vs Sugarcane paper for Copy paper
 azmater.com
azmater.com