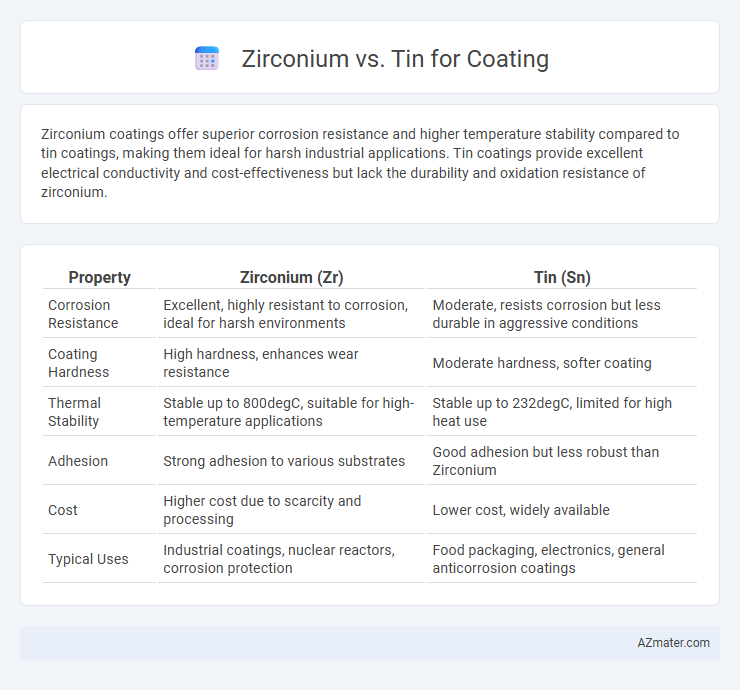
Zirconium coatings offer superior corrosion resistance and higher temperature stability compared to tin coatings, making them ideal for harsh industrial applications. Tin coatings provide excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but lack the durability and oxidation resistance of zirconium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium (Zr) | Tin (Sn) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to corrosion, ideal for harsh environments | Moderate, resists corrosion but less durable in aggressive conditions |
| Coating Hardness | High hardness, enhances wear resistance | Moderate hardness, softer coating |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 800degC, suitable for high-temperature applications | Stable up to 232degC, limited for high heat use |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion to various substrates | Good adhesion but less robust than Zirconium |
| Cost | Higher cost due to scarcity and processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Uses | Industrial coatings, nuclear reactors, corrosion protection | Food packaging, electronics, general anticorrosion coatings |
Introduction to Zirconium and Tin Coatings
Zirconium coatings provide exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring durable protective layers. Tin coatings offer excellent solderability and electrical conductivity, commonly used in electronics and food packaging to prevent oxidation. Both materials enhance surface properties, but zirconium excels in harsh chemical environments while tin is preferred for lightweight, cost-effective protection.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Zirconium exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to its stable oxide layer (ZrO2), making it ideal for protective coatings in harsh chemical environments. Tin, with its softer metallic nature and lower melting point, forms a less durable oxide layer (SnO2), resulting in moderate chemical stability and limited corrosion protection. The chemical inertness of zirconium's oxide significantly outperforms tin's, enhancing longevity and resistance against acids and alkalis in coating applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Zirconium vs Tin
Zirconium coating provides superior corrosion resistance compared to tin due to its chemical inertness and ability to form a stable, protective oxide layer that prevents metal degradation in harsh environments. Tin coatings offer moderate corrosion resistance but are more prone to oxidation and wear, especially in acidic or saline conditions. Therefore, zirconium is preferred in applications requiring long-term durability and resistance to aggressive corrosive agents.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Zirconium coatings exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to tin due to their higher hardness and resistance to wear and corrosion, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. Zirconium forms a robust oxide layer that enhances abrasion resistance and extends service life under harsh conditions, whereas tin coatings are softer and more prone to deformation and wear. As a result, zirconium-coated surfaces maintain structural integrity longer, providing better protection for substrates exposed to mechanical stress and corrosive environments.
Thermal Stability of Each Coating
Zirconium coatings exhibit superior thermal stability due to their high melting point of approximately 1855degC, making them ideal for high-temperature applications and resistance to oxidation. Tin coatings, with a lower melting point around 232degC, offer limited thermal stability and tend to degrade or deform under prolonged heat exposure. The enhanced thermal resistance of zirconium ensures longer-lasting protective performance in extreme thermal environments compared to tin coatings.
Application Methods and Techniques
Zirconium coatings are commonly applied using techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and physical vapor deposition (PVD), offering excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability in aerospace and nuclear industries. Tin coatings are typically applied via electroplating or hot-dip methods, providing superior solderability and corrosion protection mainly in electronics and automotive sectors. Both materials require surface preparation procedures like cleaning and etching to enhance adhesion and coating uniformity, but zirconium's application methods generally demand more controlled environments due to its reactivity and process complexity.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Zirconium coatings demonstrate superior environmental safety due to their corrosion resistance and non-toxic properties, reducing hazardous waste and exposure risks compared to tin coatings. Tin, while commonly used, can pose environmental concerns through potential tin dust inhalation and bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems, raising toxicity issues. Selecting zirconium over tin enhances sustainability by minimizing ecological contamination and promoting safer workplace conditions during application and disposal.
Cost Considerations and Economic Viability
Zirconium coatings typically incur higher initial costs due to expensive raw materials and complex processing techniques compared to tin, which is more affordable and widely available. Despite the higher price, zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating economic viability requires balancing upfront investment against lifetime performance benefits, especially in applications demanding enhanced wear resistance.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Zirconium coatings are widely used in industrial applications requiring exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, particularly in chemical processing, nuclear reactors, and aerospace components. Tin coatings offer excellent solderability, electrical conductivity, and corrosion protection, making them ideal for electronics manufacturing, food packaging, and automotive parts. While zirconium excels in harsh environments due to its robust oxide layer, tin provides cost-effective protection suitable for moderate industrial conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Zirconium and Tin
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher thermal stability compared to tin, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Tin, being cost-effective and providing excellent solderability, suits electronic and food-grade coatings where affordability and non-toxicity are priorities. Selecting between zirconium and tin depends on balancing performance needs with budget constraints, with zirconium preferred for heavy-duty protection and tin favored for economical, safe coatings.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Tin for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com