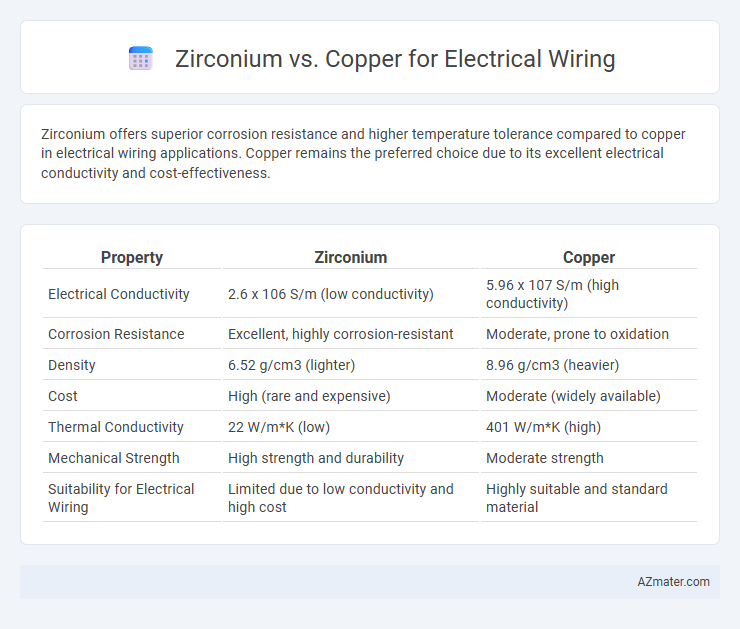
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to copper in electrical wiring applications. Copper remains the preferred choice due to its excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 2.6 x 106 S/m (low conductivity) | 5.96 x 107 S/m (high conductivity) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly corrosion-resistant | Moderate, prone to oxidation |
| Density | 6.52 g/cm3 (lighter) | 8.96 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Cost | High (rare and expensive) | Moderate (widely available) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 22 W/m*K (low) | 401 W/m*K (high) |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and durability | Moderate strength |
| Suitability for Electrical Wiring | Limited due to low conductivity and high cost | Highly suitable and standard material |
Introduction to Electrical Wiring Materials
Zirconium and copper are materials used for electrical wiring, with copper being the industry standard due to its excellent electrical conductivity of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m and superior malleability. Zirconium, known for its corrosion resistance and strength, offers lower conductivity around 1.4 x 10^7 S/m, making it less efficient for conducting electricity compared to copper. Copper's balance of cost, durability, and high electrical performance establishes it as the preferred choice in most electrical wiring applications.
Overview of Zirconium and Copper
Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance and high thermal stability, making it suitable for specialized electrical wiring applications in harsh environments. Copper remains the industry standard for electrical wiring due to its superior electrical conductivity, ductility, and cost-effectiveness. While copper provides efficient energy transmission, zirconium's unique properties can enhance performance in niche applications demanding durability and resistance to extreme conditions.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Zirconium exhibits significantly lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, with copper boasting a conductivity of approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m versus zirconium's 2.6 x 10^6 S/m. This substantial difference makes copper the preferred material for electrical wiring due to its superior ability to efficiently conduct electric current. While zirconium offers advantages like corrosion resistance, its limited conductivity restricts its use in standard electrical wiring applications.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Zirconium offers superior thermal performance compared to copper due to its higher melting point of approximately 1855degC, enabling better heat resistance in high-temperature electrical wiring applications. Copper, with a melting point of 1085degC, exhibits excellent electrical conductivity but is more susceptible to heat-induced degradation and thermal expansion. Zirconium's stability at elevated temperatures makes it ideal for specialized wiring environments requiring enhanced durability and safety under thermal stress.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Zirconium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in harsh and high-temperature environments, outperforming copper by forming a stable oxide layer that protects against oxidation and chemical degradation. Copper, while highly conductive, is more susceptible to corrosion from moisture and chemicals, which can compromise its durability over time. Zirconium's superior durability and resistance to environmental factors make it a more reliable choice for electrical wiring in demanding industrial applications.
Cost and Availability
Copper remains the preferred choice for electrical wiring due to its widespread availability and relatively lower cost compared to zirconium. Zirconium, although offering good corrosion resistance and conductivity, is significantly more expensive and less readily available, limiting its use in standard wiring applications. The high price and scarcity of zirconium make copper the more cost-effective and practical option for residential and commercial electrical installations.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Zirconium offers superior mechanical strength and corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Copper remains more flexible than zirconium, allowing easier bending and installation in complex wiring configurations. The choice between zirconium and copper depends on the balance needed between strength and flexibility for specific electrical wiring needs.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability compared to copper, enhancing safety by minimizing oxidation-related failures in electrical wiring. Copper's high electrical conductivity and well-established usage ensure reliable energy transmission, but it is more prone to corrosion and mechanical wear under harsh conditions. Choosing zirconium over copper can improve long-term reliability in environments with extreme temperatures or corrosive elements, reducing maintenance and failure risks.
Typical Applications in Industry
Zirconium is rarely used for electrical wiring due to its high cost and specialty applications, whereas copper remains the industry standard for electrical wiring because of its excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and affordability. Copper wiring is extensively deployed in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, including power generation, transmission, and distribution systems. Zirconium alloys find niche roles in nuclear reactors and aerospace, where their superior resistance to high temperatures and corrosion is critical but do not replace copper in typical electrical wiring applications.
Final Considerations: Which is Better for Electrical Wiring?
Zirconium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher thermal stability compared to copper, making it ideal for specialized electrical applications in harsh environments. Copper remains the preferred choice for standard electrical wiring due to its excellent electrical conductivity, flexibility, and widespread availability. Considering cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and electrical performance, copper generally provides the best overall solution for most wiring needs.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Copper for Electrical wiring
 azmater.com
azmater.com