Zinc plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and is cost-effective, making it ideal for automotive and construction applications. Nickel plating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and a lustrous finish, commonly used in electronics and decorative coatings.
Table of Comparison
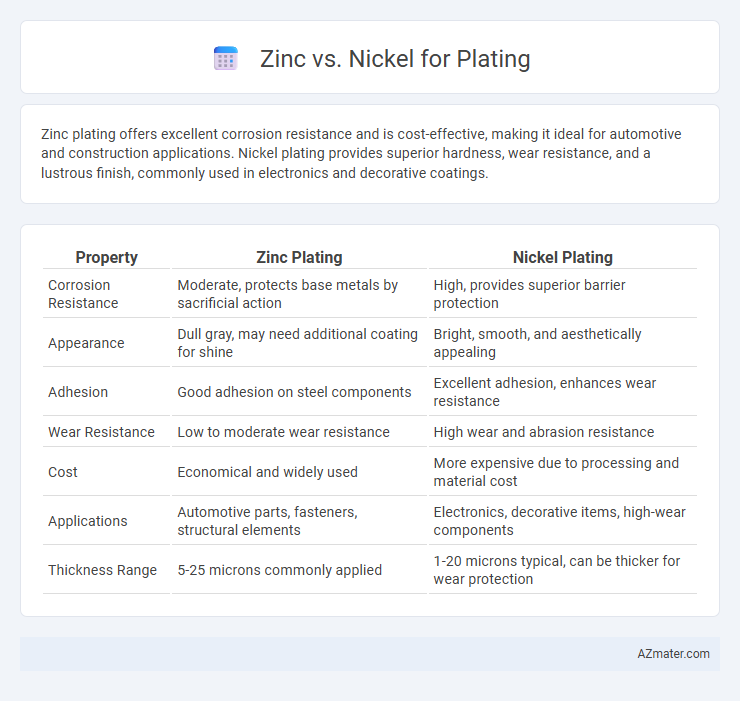
| Property | Zinc Plating | Nickel Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, protects base metals by sacrificial action | High, provides superior barrier protection |
| Appearance | Dull gray, may need additional coating for shine | Bright, smooth, and aesthetically appealing |
| Adhesion | Good adhesion on steel components | Excellent adhesion, enhances wear resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Low to moderate wear resistance | High wear and abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Economical and widely used | More expensive due to processing and material cost |
| Applications | Automotive parts, fasteners, structural elements | Electronics, decorative items, high-wear components |
| Thickness Range | 5-25 microns commonly applied | 1-20 microns typical, can be thicker for wear protection |
Introduction to Metal Plating
Metal plating enhances corrosion resistance, wear durability, and aesthetic appeal by depositing a thin layer of metal onto a substrate. Zinc plating offers excellent rust protection through sacrificial anodic behavior, making it ideal for automotive and construction applications. Nickel plating provides superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and a smooth finish frequently used in electronics, decorative items, and industrial components.
Overview of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is a corrosion-resistant coating widely used in automotive, construction, and electronics industries for protecting steel and iron components. It forms a barrier against rust by providing sacrificial protection, where zinc corrodes preferentially to the underlying metal, enhancing durability and longevity. Compared to nickel plating, zinc plating is more cost-effective and offers excellent resistance to oxidation but generally provides a thinner, less decorative finish.
Overview of Nickel Plating
Nickel plating involves depositing a thin layer of nickel onto a metal surface to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. This electrochemical process creates a durable, smooth, and oxidation-resistant coating widely used in automotive, electronics, and hardware industries. Nickel plating offers superior hardness and a brighter finish compared to zinc plating, making it ideal for applications requiring increased durability and decorative qualities.
Corrosion Resistance: Zinc vs Nickel
Zinc plating offers excellent corrosion resistance by forming a protective zinc oxide layer that prevents rust, making it ideal for outdoor and marine environments. Nickel plating provides superior corrosion resistance in harsh chemical and high-temperature conditions due to its dense, non-porous surface. Choosing between zinc and nickel depends on the specific environmental exposure and durability requirements of the plated component.
Cost Comparison: Zinc and Nickel Plating
Zinc plating generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to nickel plating due to lower raw material and processing expenses, making it suitable for large-scale, budget-conscious applications. Nickel plating provides superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal but at a higher price point, which increases production costs. The choice between zinc and nickel plating often hinges on balancing performance requirements against cost constraints in industrial and decorative uses.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Zinc plating offers a bright, reflective surface with a typically light bluish-silver finish, enhancing corrosion resistance and providing a smooth, aesthetically pleasing look ideal for automotive and hardware applications. Nickel plating delivers a harder, more durable surface characterized by a warm, gold to silver tone that resists wear and tarnishing, making it preferred for decorative items and electronic components. The choice between zinc and nickel plating hinges on the desired balance between surface hardness, corrosion protection, and visual appeal for specific industrial uses.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Zinc plating offers moderate durability and corrosion resistance, suitable for protecting steel from rust but prone to wear under heavy friction. Nickel plating provides superior wear resistance and hardness, making it ideal for applications exposed to frequent abrasion or mechanical stress. The choice between zinc and nickel plating depends on the required balance of corrosion protection and surface durability for the specific application.
Typical Applications of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is commonly used in automotive, construction, and electronics industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Typical applications include fasteners, hardware, and automotive parts where a protective, non-decorative coating is required to prevent rust. Nickel plating, while offering superior hardness and wear resistance, is generally reserved for decorative and high-wear components rather than broad corrosion protection.
Typical Applications of Nickel Plating
Nickel plating is commonly used in automotive parts, electronics, and aerospace components due to its superior corrosion resistance, hardness, and excellent wear protection. It provides a smooth, bright finish that enhances both the aesthetic appeal and durability of metal surfaces, making it ideal for decorative and functional applications. Compared to zinc plating, nickel plating performs better in high-temperature and corrosive environments, extending the lifespan of precision-engineered parts.
Choosing the Best Plating Option
Zinc plating offers superior corrosion resistance and affordability, making it ideal for automotive and fastener applications exposed to moisture. Nickel plating provides excellent wear resistance, enhanced hardness, and an attractive, smooth finish, suitable for decorative and high-performance industrial parts. Selecting between zinc and nickel plating depends on environmental exposure, desired aesthetic, and mechanical durability requirements.
Infographic: Zinc vs Nickel for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com