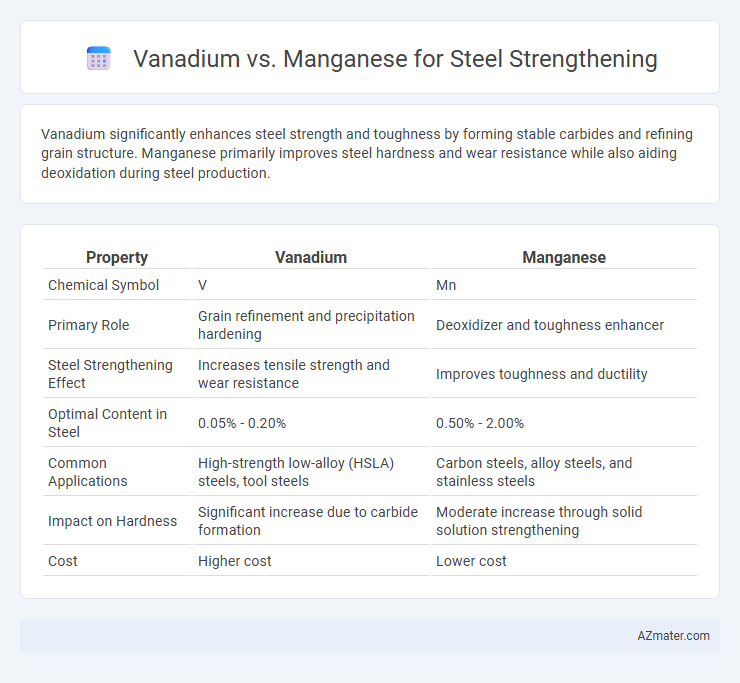
Vanadium significantly enhances steel strength and toughness by forming stable carbides and refining grain structure. Manganese primarily improves steel hardness and wear resistance while also aiding deoxidation during steel production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Vanadium | Manganese |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Symbol | V | Mn |
| Primary Role | Grain refinement and precipitation hardening | Deoxidizer and toughness enhancer |
| Steel Strengthening Effect | Increases tensile strength and wear resistance | Improves toughness and ductility |
| Optimal Content in Steel | 0.05% - 0.20% | 0.50% - 2.00% |
| Common Applications | High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, tool steels | Carbon steels, alloy steels, and stainless steels |
| Impact on Hardness | Significant increase due to carbide formation | Moderate increase through solid solution strengthening |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Steel Strengtheners
Vanadium and manganese are critical alloying elements used to enhance steel strength through different metallurgical mechanisms. Vanadium forms fine vanadium carbides and nitrides, refining grain structure and increasing toughness and wear resistance in high-strength low-alloy steels. Manganese primarily improves hardenability and tensile strength by stabilizing austenite and reducing brittleness, making it essential for construction-grade and automotive steels.
Overview of Vanadium in Steel
Vanadium is a critical microalloying element in steel production, known for significantly enhancing strength and toughness through grain refinement and precipitation hardening. Its ability to form stable carbides and nitrides improves wear resistance and fatigue strength, making vanadium steels ideal for high-performance applications like automotive components and structural tools. Compared to manganese, vanadium delivers superior strength-to-weight ratios and better thermal stability under extreme conditions.
Role of Manganese in Steel Alloys
Manganese plays a crucial role in steel alloys by improving toughness, wear resistance, and tensile strength through its ability to remove oxygen and sulfur impurities during production. It acts as a deoxidizer and contributes to the formation of austenite, enhancing the hardenability of steel and promoting finer grain structures. Compared to vanadium, which primarily increases strength through carbide formation, manganese offers more balanced improvements in ductility and impact resistance in steel.
Chemical Properties: Vanadium vs Manganese
Vanadium enhances steel strength by forming stable carbides and nitrides, improving hardness and wear resistance through grain refinement and precipitation strengthening. Manganese acts as a deoxidizer and sulfur scavenger, increasing toughness and hardenability by stabilizing austenite and forming manganese sulfides that prevent brittleness. The distinct chemical properties of vanadium and manganese offer complementary roles in steel alloy composition, optimizing overall mechanical performance.
Impact on Steel Strength and Hardness
Vanadium significantly enhances steel strength and hardness by promoting fine grain structure and forming stable carbides, resulting in improved wear resistance and toughness. Manganese increases steel hardness primarily through solid solution strengthening and improves tensile strength by reducing brittleness and enhancing hardenability. Comparing both, vanadium offers superior grain refinement and higher hardness levels, while manganese provides cost-effective hardness improvements with better ductility and impact resistance.
Effects on Ductility and Toughness
Vanadium enhances steel's strength primarily through grain refinement and the formation of vanadium carbides, significantly improving toughness while maintaining good ductility. Manganese acts as a deoxidizer and alloying element, increasing hardness and strength but can reduce ductility if added in excessive amounts. The balance of vanadium provides superior toughness and ductility, whereas manganese optimizes strength with a moderate impact on flexibility.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Vanadium-enhanced steel demonstrates superior corrosion resistance compared to manganese due to the formation of stable vanadium carbides that refine grain structure and reduce micro-galvanic corrosion sites. Manganese primarily improves toughness and hardness but offers less protection against environmental degradation, making vanadium alloys more suitable for applications demanding enhanced resistance to rust and chemical wear. Studies reveal that vanadium's higher resistance to oxidation and pitting significantly extends the lifespan of structural steel in harsh environments.
Cost and Availability of Vanadium and Manganese
Vanadium and manganese are critical alloying elements used to enhance steel strength, with vanadium typically offering higher strength improvements but at a greater cost. Manganese is more widely available and significantly less expensive, making it a preferred choice in large-volume steel production where cost efficiency is paramount. The price volatility of vanadium due to limited global reserves contrasts with the abundant and stable supply of manganese, impacting their selection based on budget constraints and project scale.
Environmental Considerations
Vanadium enhances steel strength by promoting fine grain structures, enabling lower alloy contents and reducing overall material use, which decreases carbon emissions in production. Manganese also improves toughness and wear resistance but often requires higher quantities, leading to increased energy consumption and environmental impact during mining and processing. Choosing vanadium as a steel strengthener supports sustainability goals by minimizing resource extraction and lowering the ecological footprint of steel manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Alloying Element for Steel
Vanadium enhances steel strength by refining grain size and increasing toughness through the formation of stable carbides, making it ideal for high-strength, wear-resistant applications. Manganese improves steel's hardenability and tensile strength by acting as a deoxidizer and sulfur fixer, which is essential for structural steel and weldability. Choosing between vanadium and manganese depends on the specific mechanical properties required, such as toughness versus ductility, and the intended application environment of the steel.
Infographic: Vanadium vs Manganese for Steel Strengthener
 azmater.com
azmater.com