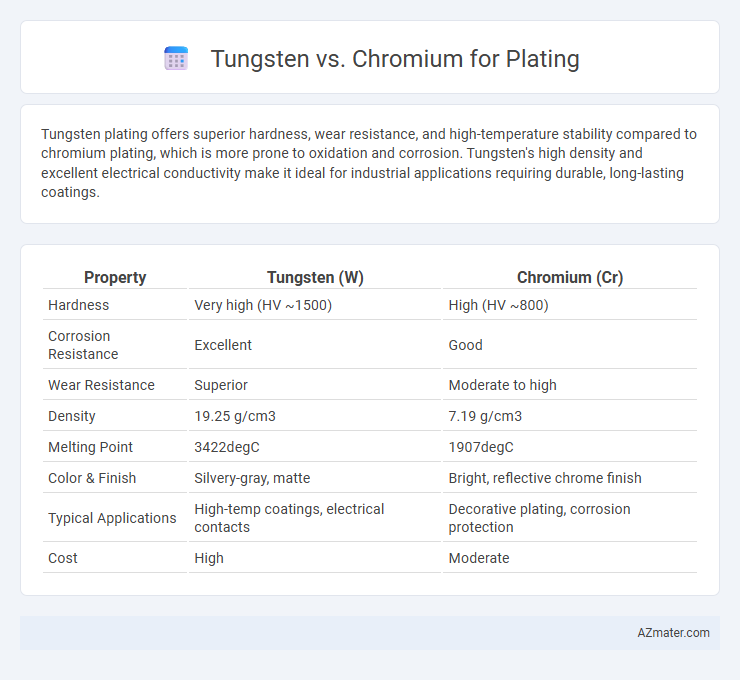
Tungsten plating offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature stability compared to chromium plating, which is more prone to oxidation and corrosion. Tungsten's high density and excellent electrical conductivity make it ideal for industrial applications requiring durable, long-lasting coatings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tungsten (W) | Chromium (Cr) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Very high (HV ~1500) | High (HV ~800) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Wear Resistance | Superior | Moderate to high |
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 | 7.19 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 3422degC | 1907degC |
| Color & Finish | Silvery-gray, matte | Bright, reflective chrome finish |
| Typical Applications | High-temp coatings, electrical contacts | Decorative plating, corrosion protection |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Tungsten vs Chromium
Tungsten and chromium are widely used metals in plating due to their distinct properties enhancing surface durability and corrosion resistance. Tungsten offers superior hardness and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for applications requiring extreme wear resistance. Chromium plating provides excellent corrosion protection and a brilliant, reflective finish commonly utilized in automotive and decorative industries.
Chemical and Physical Properties Compared
Tungsten exhibits a higher melting point of 3422degC and exceptional hardness, making it ideal for wear-resistant plating, while chromium melts at 1907degC and provides excellent corrosion resistance and a bright, decorative finish. Chemically, tungsten is highly inert with excellent oxidation resistance at high temperatures, whereas chromium forms a stable oxide layer that protects against rust and tarnishing in various environments. Physically, tungsten's density is around 19.3 g/cm3, contributing to durability, whereas chromium's lower density of 7.19 g/cm3 offers lighter plating solutions without compromising toughness.
Plating Processes: Techniques and Requirements
Tungsten plating typically involves chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and electroplating, requiring high temperatures and precise control of deposition parameters to achieve uniform coatings with excellent hardness and corrosion resistance. Chromium plating utilizes electroplating processes with acidic chromium baths, demanding strict control of pH, temperature, and current density to produce thin, decorative, and wear-resistant layers. Both metals require surface preparation such as cleaning and activation steps to ensure adhesion and coating quality, but tungsten plating mandates more specialized equipment due to its higher melting point and complex chemistry.
Durability and Hardness Analysis
Tungsten plating offers exceptional hardness with a Mohs scale rating close to 7.5, significantly enhancing wear resistance and durability in high-stress applications. Chromium plating provides excellent hardness as well, around 8.5 on the Mohs scale, and superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial components. While chromium excels in hardness and corrosion protection, tungsten's superior thermal stability and impact resistance make it more suitable for extreme environments requiring prolonged durability.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Tungsten plating offers superior corrosion resistance in highly aggressive environments, such as acidic or alkaline solutions, due to its dense and stable oxide layer formation. Chromium plating is widely favored for corrosion resistance in industrial applications because of its ability to form a hard, protective chromium oxide surface that withstands oxidation and wear. Both metals provide robust protection, but tungsten excels in extreme chemical exposure while chromium delivers reliable, cost-effective corrosion resistance in less severe conditions.
Aesthetic Finishes and Color Differences
Tungsten plating offers a darker, matte finish with excellent resistance to scratches and wear, making it ideal for modern, industrial aesthetics. Chromium plating provides a bright, reflective silver sheen that enhances visual appeal with a polished, high-gloss surface commonly used in automotive and decorative applications. The color difference significantly impacts design choices, as tungsten's subtle gray tones suit minimalist styles, while chromium's shiny, mirror-like quality appeals to classic and vibrant finishes.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Tungsten plating offers superior hardness and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring wear and corrosion protection, such as aerospace components and cutting tools. Chromium plating is favored in commercial applications for its excellent corrosion resistance, bright finish, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in automotive parts and decorative surfaces. Both metals provide distinct benefits: tungsten excels in durability under extreme conditions, while chromium delivers aesthetic appeal and moderate protection at a lower cost.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Tungsten plating offers superior corrosion resistance and lower toxicity compared to chromium plating, which commonly involves hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen with significant environmental hazards. The waste generated from chromium plating requires specialized treatment due to its high toxicity and potential for soil and water contamination, whereas tungsten plating produces fewer hazardous byproducts, resulting in a reduced environmental footprint. Safety protocols for tungsten plating are less stringent, minimizing respiratory and dermal exposure risks commonly associated with chromium plating processes.
Cost Considerations and Economic Feasibility
Tungsten plating incurs higher costs due to its complex deposition processes and the need for specialized equipment, making it less economically feasible for large-scale applications compared to chromium. Chromium plating offers a cost-effective solution with lower material and operational expenses, benefitting industries focused on decorative and corrosion-resistant finishes. Economic feasibility analysis often favors chromium plating for mass production, while tungsten plating is reserved for niche applications requiring superior hardness and wear resistance despite elevated costs.
Choosing the Right Metal: Key Factors to Consider
Tungsten offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance compared to chromium, making it ideal for high-wear, high-temperature applications in aerospace and industrial machinery. Chromium plating provides excellent aesthetic appeal and moderate corrosion protection, commonly used in automotive and decorative finishes. When choosing between tungsten and chromium, consider factors such as desired durability, environmental conditions, cost, and specific application requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com