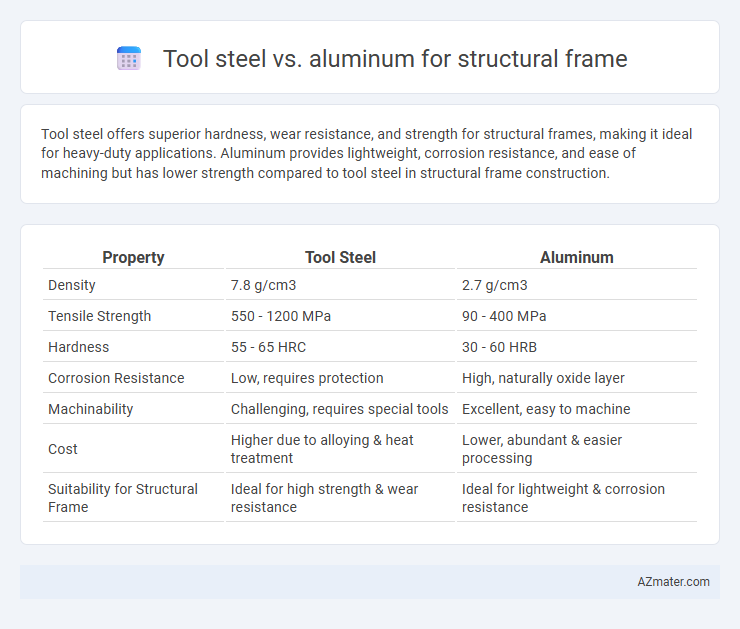
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and strength for structural frames, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Aluminum provides lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of machining but has lower strength compared to tool steel in structural frame construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.8 g/cm3 | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 550 - 1200 MPa | 90 - 400 MPa |
| Hardness | 55 - 65 HRC | 30 - 60 HRB |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, requires protection | High, naturally oxide layer |
| Machinability | Challenging, requires special tools | Excellent, easy to machine |
| Cost | Higher due to alloying & heat treatment | Lower, abundant & easier processing |
| Suitability for Structural Frame | Ideal for high strength & wear resistance | Ideal for lightweight & corrosion resistance |
Introduction to Structural Frame Materials
Tool steel offers superior strength, hardness, and wear resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for heavy-duty structural frames subjected to high stress and impact. Aluminum, with its lightweight and excellent corrosion resistance, is preferred for applications requiring reduced weight and enhanced corrosion protection. Selecting between tool steel and aluminum depends on balancing load-bearing capacity, durability, and environmental conditions in structural frame design.
Overview of Tool Steel
Tool steel exhibits exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and high tensile strength, making it an ideal material for structural frames that demand durability under heavy loads. Its ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures and resist deformation ensures longevity in demanding industrial applications. Compared to aluminum, tool steel offers superior toughness and fatigue resistance, albeit at a higher density and weight.
Key Properties of Aluminum
Aluminum offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for structural frames requiring lightweight materials without compromising durability. Its excellent corrosion resistance ensures longevity in various environments, reducing maintenance costs compared to tool steel. Aluminum also provides superior thermal conductivity and ease of fabrication, enhancing design flexibility and performance in structural applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tool steel exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and hardness compared to aluminum, making it ideal for structural frames requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity and wear resistance. Aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance and lightweight properties but tends to have lower strength and durability under heavy mechanical stress. In applications demanding long-term structural integrity and resistance to deformation, tool steel outperforms aluminum despite its higher weight.
Weight Considerations in Structural Frames
Tool steel is significantly denser than aluminum, resulting in a heavier structural frame when used in construction. Aluminum's low density--approximately one-third that of steel--makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical without compromising strength. Choosing aluminum for structural frames enhances portability and reduces load on foundations, improving overall design efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance: Tool Steel vs Aluminum
Tool steel offers high strength and durability but generally has lower corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, which naturally forms a protective oxide layer that shields it from many environmental factors. Aluminum's resistance to rust and oxidation makes it ideal for structural frames exposed to moisture or corrosive environments, whereas tool steel typically requires protective coatings or treatments to prevent rust. Choosing between these materials depends on the balance between mechanical strength needs and the environmental conditions impacting corrosion vulnerability.
Fabrication and Machinability Differences
Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance for structural frames but presents challenges in fabrication due to its high strength and low thermal conductivity, requiring specialized cutting tools and slower machining speeds. Aluminum provides excellent machinability with faster cutting rates and easier shaping, attributed to its lower density and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for rapid fabrication processes. In terms of structural frame applications, aluminum allows greater design flexibility and reduced weight, while tool steel ensures higher durability and load-bearing capacity, though with increased machining complexity and cost.
Cost Factors and Availability
Tool steel offers superior strength and durability for structural frames but comes at a higher cost due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes. Aluminum provides a more cost-effective option with widespread availability and easier fabrication, though it sacrifices some load-bearing capacity and wear resistance. The choice between tool steel and aluminum hinges on budget constraints and project requirements for longevity versus affordability.
Typical Applications in Structural Frames
Tool steel is commonly used in structural frames requiring exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and load-bearing capacity, such as in heavy machinery and precision equipment frameworks. Aluminum is favored in structural frames for applications demanding lightweight construction and corrosion resistance, including aerospace, automotive, and architectural structures. The choice between tool steel and aluminum depends on factors like strength-to-weight ratio, environmental exposure, and specific mechanical performance requirements in structural design.
Choosing the Right Material: Decision Criteria
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and tensile strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty structural frames subjected to high stress and abrasive environments. Aluminum provides excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and ease of fabrication, suitable for applications demanding weight reduction and moderate strength. Key decision criteria include load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, fabrication complexity, and cost-efficiency, guiding the selection between durability of tool steel and the lightweight versatility of aluminum.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Aluminum for Structural frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com