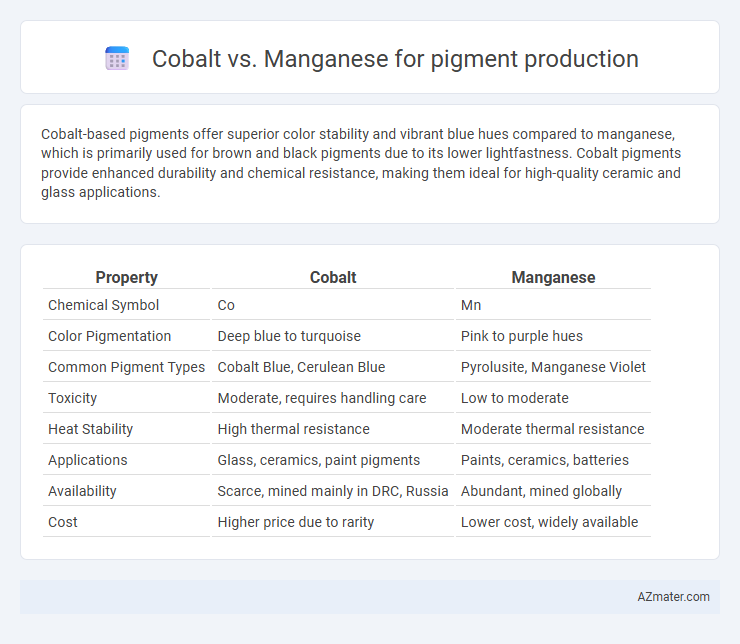
Cobalt-based pigments offer superior color stability and vibrant blue hues compared to manganese, which is primarily used for brown and black pigments due to its lower lightfastness. Cobalt pigments provide enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-quality ceramic and glass applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cobalt | Manganese |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Symbol | Co | Mn |
| Color Pigmentation | Deep blue to turquoise | Pink to purple hues |
| Common Pigment Types | Cobalt Blue, Cerulean Blue | Pyrolusite, Manganese Violet |
| Toxicity | Moderate, requires handling care | Low to moderate |
| Heat Stability | High thermal resistance | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Applications | Glass, ceramics, paint pigments | Paints, ceramics, batteries |
| Availability | Scarce, mined mainly in DRC, Russia | Abundant, mined globally |
| Cost | Higher price due to rarity | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Cobalt and Manganese Pigments
Cobalt pigments, renowned for their intense blue hues and high stability, are extensively used in ceramics, glass, and paints due to their excellent heat resistance and vibrant color retention. Manganese pigments, often appearing in purple, brown, or black shades, offer versatility in coloration and are valued for their cost-effectiveness and ability to enhance durability in coatings and ceramics. Both cobalt and manganese pigments contribute significantly to the color industry, with cobalt favored for brightness and long-lasting performance, while manganese provides diverse tonal options and economic advantages.
Historical Use of Cobalt vs Manganese in Pigment Production
Cobalt has been historically dominant in pigment production due to its vibrant blue hues, with the use of cobalt blue pigments dating back to ancient Egypt and gaining prominence during the Renaissance for ceramics and glass. Manganese pigments, primarily in the form of manganese dioxide, have been used since prehistoric times for black and purple colors, often in cave paintings and pottery. The development of synthetic cobalt blue in the 18th century marked a shift towards more stable and intense blue pigments, while manganese remained essential for darker pigments and as a decolorizing agent in glassmaking.
Chemical Properties and Pigment Color Range
Cobalt compounds, primarily cobalt blue (CoAl2O4), offer excellent chemical stability, high heat resistance, and vibrant deep blue hues ideal for ceramic and glass pigments. Manganese pigments, such as manganese violet (MnNH4P2O7), provide a broader color range from violet to pink and earth tones, with notable oxidation states (II, III, IV) influencing color variations and chemical reactivity. Both metals deliver unique pigment properties, but cobalt's superior lightfastness and chemical inertness contrast with manganese's versatility in producing more variegated color spectrums.
Extraction and Processing Methods
Cobalt extraction primarily involves mining from ores like cobaltite and processing through hydrometallurgical techniques including acid leaching and solvent extraction to obtain high-purity cobalt suitable for pigment production. Manganese is extracted chiefly from minerals such as pyrolusite using pyrometallurgical methods like roasting and reduction, followed by electrolytic refining to produce manganese dioxide pigments. Both metals require tailored processing to optimize pigment quality, with cobalt offering vibrant blue hues and manganese providing a range of black to purple pigments.
Pigment Performance: Lightfastness and Durability
Cobalt pigments exhibit superior lightfastness and durability compared to manganese pigments, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term color stability under exposure to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. Manganese pigments, while cost-effective, typically show lower resistance to UV degradation and can fade or alter color over time when exposed to light. The enhanced chemical stability and robust oxidative resistance of cobalt-based pigments significantly enhance their performance in high-demand pigment applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Concerns
Cobalt and manganese differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for pigment production; cobalt mining often leads to severe ecological degradation, high carbon emissions, and ethical issues related to labor practices, while manganese extraction tends to have lower toxicity and less environmental disruption. Sustainable pigment manufacture increasingly favors manganese due to its abundance, lower energy demands during processing, and reduced risk of toxic byproducts compared to cobalt-based pigments, which pose challenges in waste management and pollutant containment. Efforts to develop eco-friendly alternatives highlight manganese as a promising material for sustainable pigment production with minimized environmental footprint.
Health and Safety Aspects in Manufacturing
Cobalt pigments are associated with respiratory sensitization and dermatitis risks due to cobalt dust exposure, necessitating strict industrial hygiene and personal protective equipment (PPE) protocols. Manganese pigments, while less allergenic, pose neurotoxic hazards with prolonged inhalation of manganese dust or fumes, requiring effective ventilation and exposure monitoring in manufacturing environments. Both metals demand rigorous safety measures to minimize airborne particulates, ensuring worker health and regulatory compliance in pigment production facilities.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Cobalt pigments are generally more expensive due to the higher cost of cobalt, which is a scarcer and more geopolitically sensitive metal compared to manganese. Manganese pigments offer a cost-effective alternative with more abundant supply, resulting in greater market availability and stable pricing. The choice between cobalt and manganese pigments often hinges on budget constraints and the specific color intensity requirements in industrial applications.
Applications in Art, Industry, and Coatings
Cobalt pigments offer vibrant blue and green hues extensively used in fine art painting and high-quality ceramic glazes due to their excellent lightfastness and stability. Manganese pigments provide purples, browns, and blacks with strong UV resistance and are favored in industrial coatings and concrete coloring for their durability and economic efficiency. Both metals contribute uniquely to coatings, where cobalt acts as a drying agent in paints and manganese compounds improve corrosion resistance and colorfastness in protective industrial finishes.
Future Trends in Pigment Innovation
Cobalt and manganese are critical elements driving future trends in pigment innovation due to their distinct chemical properties and environmental impact profiles. Cobalt pigments offer intense blue and green hues with superior stability, making them ideal for high-performance applications, while manganese-based pigments are gaining traction for their cost-effectiveness and eco-friendly characteristics in sustainable manufacturing. Advances in nanotechnology and eco-conscious synthesis methods are expanding the use of both metals to create vibrant, durable, and non-toxic pigments for automotive, coatings, and plastics industries.
Infographic: Cobalt vs Manganese for Pigment production
 azmater.com
azmater.com