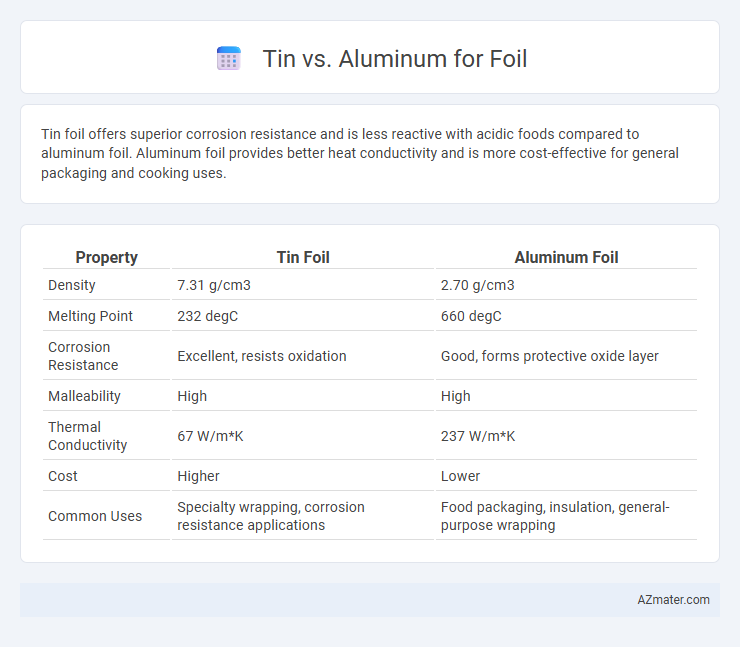
Tin foil offers superior corrosion resistance and is less reactive with acidic foods compared to aluminum foil. Aluminum foil provides better heat conductivity and is more cost-effective for general packaging and cooking uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin Foil | Aluminum Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 232 degC | 660 degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists oxidation | Good, forms protective oxide layer |
| Malleability | High | High |
| Thermal Conductivity | 67 W/m*K | 237 W/m*K |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses | Specialty wrapping, corrosion resistance applications | Food packaging, insulation, general-purpose wrapping |
Introduction: Understanding Tin and Aluminum Foil
Tin foil, made from pure tin, offers superior resistance to corrosion and enhances food preservation by preventing metallic taste transfer. Aluminum foil, crafted from rolled aluminum sheets, provides excellent heat conductivity and flexibility, making it widely used for cooking and packaging. Both materials reflect heat and light effectively, but aluminum foil is more cost-efficient and abundant compared to the less common, though more environmentally friendly, tin foil.
Historical Background of Tin and Aluminum Foil
Tin foil was widely used in the late 19th and early 20th centuries due to tin's malleability and resistance to corrosion, becoming common for packaging and food storage. Aluminum foil emerged in the early 20th century after advancements in aluminum production, offering a lighter, more flexible, and cost-effective alternative that quickly replaced tin foil in most applications. The transition from tin to aluminum foil revolutionized food preservation and packaging industries by providing improved barrier properties and easier manufacturability.
Material Composition: Tin vs Aluminum
Tin foil is primarily composed of pure tin, offering greater flexibility and resistance to corrosion, while aluminum foil consists mainly of aluminum metal, which provides higher strength and excellent heat conductivity. Aluminum's atomic structure allows for better barrier properties against light, moisture, and contaminants compared to tin foil. The distinct material composition affects their suitability for different food packaging and preservation applications due to differences in durability, reactivity, and thermal performance.
Physical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Tin foil exhibits moderate strength and flexibility, making it suitable for light wrapping tasks, but it is generally softer and more prone to tearing compared to aluminum foil. Aluminum foil offers superior tensile strength and greater flexibility, allowing it to withstand folding, crimping, and shaping without easily breaking or tearing. The higher durability and resilience of aluminum foil make it the preferred choice for heavy-duty packaging and insulation purposes.
Heat Conductivity and Resistance Comparison
Tin foil has lower heat conductivity compared to aluminum foil, making aluminum more efficient for rapid heat transfer in cooking or packaging applications. Aluminum foil demonstrates superior heat resistance, enduring higher temperatures without melting or degradation, unlike tin foil, which has a lower melting point around 232degC (450degF). The thermal conductivity of aluminum is approximately 237 W/m*K, significantly higher than tin's 67 W/m*K, enhancing aluminum foil's performance in heat-sensitive tasks.
Food Safety and Reactivity Differences
Tin foil, historically used before aluminum foil became widespread, offers better resistance to acidic foods, reducing the risk of chemical reactions that can alter food taste or safety. Aluminum foil is more reactive, especially with acidic or salty foods, potentially causing aluminum to leach into the food, which may raise health concerns with prolonged exposure. Food safety experts recommend using tin foil or aluminum foil with a non-reactive coating when wrapping acidic or highly seasoned foods to minimize reactivity and maintain food quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tin foil, traditionally used before aluminum became widespread, has a heavier environmental footprint due to less efficient extraction and limited recycling processes compared to aluminum. Aluminum foil offers greater sustainability because it is highly recyclable, reducing mining waste and energy consumption when recycled, which accounts for up to 75% less energy than primary production. The environmental impact of aluminum production remains significant, but advancements in recycling technologies and the material's lightweight nature contribute to its overall lower carbon footprint in foil applications.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Tin foil, historically popular, is significantly more expensive than aluminum foil due to limited supply and higher production costs. Aluminum foil dominates the market with widespread availability and lower price points, driven by abundant bauxite resources and advanced manufacturing technologies. Cost-efficiency and accessibility make aluminum foil the preferred choice for packaging, cooking, and insulation applications worldwide.
Common Uses: Tin Foil vs Aluminum Foil
Aluminum foil is widely used for food packaging, cooking, and insulation due to its lightweight, flexibility, and excellent barrier properties against moisture, light, and bacteria. Tin foil, made from pure tin, was historically used for food wrapping but has largely been replaced by aluminum because it is less durable and more expensive. Common uses for tin foil today include specialized industrial applications and artistic crafts, while aluminum foil remains the go-to choice for everyday household and commercial food-related uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foil for Your Needs
Tin foil offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking and long-term food storage. Aluminum foil provides better flexibility, affordability, and light-weight properties suited for everyday kitchen use and wrapping delicate items. Selecting the right foil depends on specific requirements such as temperature tolerance, budget, and usage frequency.
Infographic: Tin vs Aluminum for Foil
 azmater.com
azmater.com