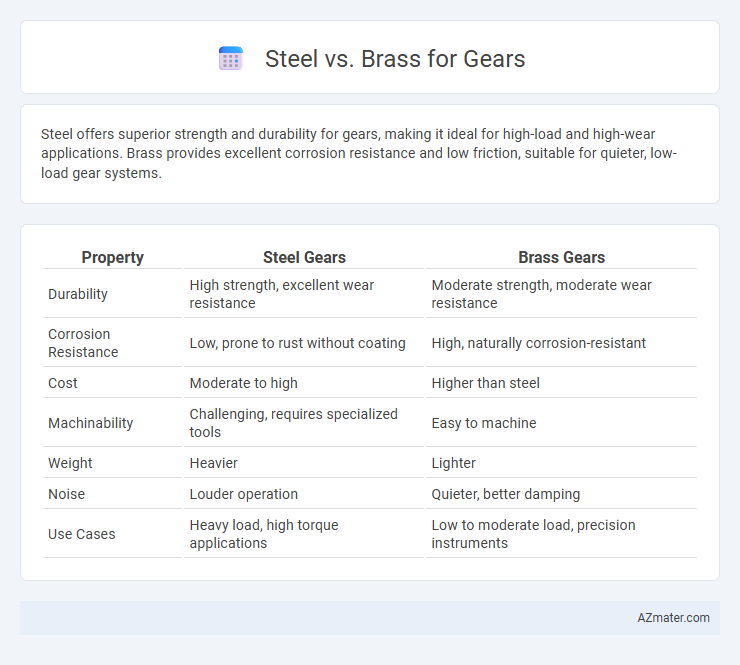
Steel offers superior strength and durability for gears, making it ideal for high-load and high-wear applications. Brass provides excellent corrosion resistance and low friction, suitable for quieter, low-load gear systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Steel Gears | Brass Gears |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High strength, excellent wear resistance | Moderate strength, moderate wear resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, prone to rust without coating | High, naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Higher than steel |
| Machinability | Challenging, requires specialized tools | Easy to machine |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Noise | Louder operation | Quieter, better damping |
| Use Cases | Heavy load, high torque applications | Low to moderate load, precision instruments |
Introduction to Steel and Brass Gears
Steel gears offer exceptional strength, durability, and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-load and high-speed applications. Brass gears provide excellent corrosion resistance, low friction, and quiet operation, which are suited for low-load, precision mechanisms. The choice between steel and brass gears depends on the specific performance requirements and environmental conditions of the gear system.
Material Properties: Steel vs Brass
Steel offers superior strength and durability compared to brass, making it ideal for high-load gear applications requiring resistance to wear and deformation. Brass features excellent corrosion resistance and machinability, suitable for gears operating in low-load or decorative settings where noise reduction and ease of fabrication are priorities. The choice between steel and brass gears depends on balancing mechanical strength needs with environmental exposure and manufacturing considerations.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Steel gears exhibit superior durability and wear resistance compared to brass gears due to their higher hardness and tensile strength, making them ideal for high-load and high-speed applications. Brass gears offer good corrosion resistance and quieter operation but tend to wear faster under heavy stress and abrasive conditions. For industrial settings requiring longevity and minimal maintenance, steel gears are the preferred choice, while brass gears suit low-load, low-noise environments.
Strength and Load Capacity Differences
Steel gears offer superior strength and higher load capacity compared to brass gears due to their dense crystal structure and alloy composition, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Brass gears, while more corrosion resistant and quieter in operation, typically have lower tensile strength and are better suited for light to moderate load environments. The choice between steel and brass gears largely depends on the specific mechanical demands and longevity requirements of the gear system.
Machinability and Manufacturing Considerations
Steel gears offer high strength and durability but generally present challenges in machinability due to their hardness and the need for specialized tooling and cooling during manufacturing. Brass gears provide excellent machinability with easier cutting, shaping, and finishing processes, reducing manufacturing time and costs while ensuring good wear resistance for moderate-load applications. Selecting between steel and brass gears depends heavily on balancing required mechanical performance against machining efficiency and production scale.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Steel gears offer excellent strength but are more prone to rust and corrosion without proper protective coatings, reducing their lifespan in humid or wet environments. Brass gears naturally resist corrosion due to their copper-zinc alloy composition, making them ideal for applications exposed to moisture and chemicals. Brass typically lasts longer in corrosive settings, while steel requires additional treatments like plating or galvanizing to achieve comparable durability.
Noise and Vibration Performance
Steel gears offer superior noise reduction and vibration damping compared to brass gears due to their higher stiffness and better dimensional stability under load. Brass gears tend to produce higher noise levels and more vibration because of their softer material properties and lower modulus of elasticity. Choosing steel gears enhances overall gear system performance by minimizing operational noise and reducing vibration-induced wear.
Cost Analysis: Steel vs Brass Gears
Steel gears offer higher strength and durability compared to brass, often resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs despite a higher initial price. Brass gears are generally less expensive upfront and provide good corrosion resistance and quieter operation, making them suitable for lighter-load applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors steel in heavy-duty environments, while brass is cost-effective for low-stress, precision gear requirements.
Typical Applications for Steel and Brass Gears
Steel gears are predominantly used in heavy-duty applications such as automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and robotics due to their high strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Brass gears are favored in precision instruments, clocks, and low-load electrical devices where corrosion resistance, machinability, and noise reduction are critical. Both materials serve distinct roles based on load requirements and environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Gear Needs
Steel gears offer superior strength, durability, and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-load and high-speed applications where longevity is critical. Brass gears provide excellent corrosion resistance, quieter operation, and better machinability, suited for low to moderate load scenarios with precision and noise reduction priorities. Selecting the right gear material depends on application requirements such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and the importance of noise control versus mechanical strength.
Infographic: Steel vs Brass for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com