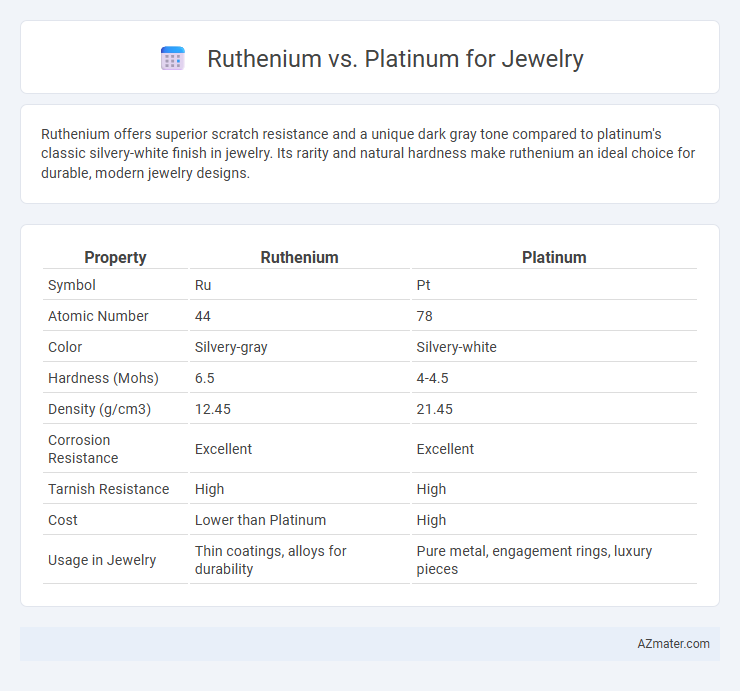
Ruthenium offers superior scratch resistance and a unique dark gray tone compared to platinum's classic silvery-white finish in jewelry. Its rarity and natural hardness make ruthenium an ideal choice for durable, modern jewelry designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium | Platinum |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Ru | Pt |
| Atomic Number | 44 | 78 |
| Color | Silvery-gray | Silvery-white |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.5 | 4-4.5 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 12.45 | 21.45 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Tarnish Resistance | High | High |
| Cost | Lower than Platinum | High |
| Usage in Jewelry | Thin coatings, alloys for durability | Pure metal, engagement rings, luxury pieces |
Introduction to Ruthenium and Platinum
Ruthenium and platinum both belong to the platinum group metals, prized for their durability and rarity in high-end jewelry. Ruthenium is a hard, corrosion-resistant metal often used as a plating material to enhance the scratch resistance and color of jewelry, while platinum is a naturally white, dense metal favored for its hypoallergenic properties and luxurious luster. Platinum's higher density and weight give jewelry a substantial feel, whereas ruthenium's use as an alloy or coating improves wear resistance without significantly increasing weight.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ruthenium and platinum differ significantly in physical properties relevant to jewelry making; ruthenium is a hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a high melting point of 2334degC, whereas platinum is a dense, malleable metal with a melting point of 1768degC. Ruthenium's hardness rates around 6.5 on the Mohs scale, offering superior scratch resistance compared to platinum's softer rating of about 4 to 4.5. Despite its hardness, ruthenium is less commonly used alone due to brittleness, while platinum's ductility and weight provide a luxurious, durable finish ideal for fine jewelry designs.
Appearance and Color Differences
Ruthenium exhibits a unique dark gray to blackish hue, offering a modern and edgy aesthetic in jewelry, while platinum is prized for its naturally bright, silvery-white luster that remains untarnished over time. Platinum's high reflectivity gives it a brilliant and classic shine preferred for traditional fine jewelry, whereas ruthenium's matte or glossy finishes provide more contemporary and contrasting accents, especially when used as a plating or alloy element. Jewelry designers often select platinum for its timeless elegance and hypoallergenic properties, whereas ruthenium's distinctive darker tone creates striking, innovative pieces, making the choice dependent on desired visual impact and style.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Ruthenium exhibits exceptional durability and wear resistance, making it highly effective as a protective coating over softer metals in jewelry. Platinum, known for its dense and tough nature, offers superior resistance to scratches and tarnish, maintaining its lustrous appearance over time. Both metals provide long-lasting strength, but ruthenium's hardness often surpasses platinum, ideal for enhancing the longevity of fine jewelry pieces.
Hypoallergenic Qualities
Ruthenium and platinum are both valued metals in jewelry for their hypoallergenic properties, making them suitable for sensitive skin. Platinum is naturally hypoallergenic due to its purity and resistance to tarnishing, while ruthenium, a rare member of the platinum group metals, is often used as a coating to enhance jewelry's durability and reduce allergic reactions. Jewelry coated or alloyed with ruthenium offers an extra layer of protection against skin irritation compared to pure platinum, especially for those with metal sensitivities.
Cost and Market Value
Ruthenium offers a more affordable alternative to platinum in jewelry, with a lower market price driven by its scarcity and industrial demand rather than extensive use in luxury items. While platinum maintains a higher market value due to its established prestige, durability, and demand in fine jewelry, ruthenium's unique properties make it a cost-effective choice for accentuating designs without significantly increasing overall expense. The cost difference reflects platinum's rarity and consumer perception, with ruthenium positioned as a niche metal increasingly recognized for its affordability and modern appeal in the jewelry market.
Common Jewelry Uses
Ruthenium is commonly used as a durable alloy in jewelry, often mixed with platinum or palladium to enhance hardness and scratch resistance, making it ideal for rings and bracelets. Platinum is prized for its natural white luster, hypoallergenic properties, and strength, frequently used in engagement rings, wedding bands, and high-end watches. Both metals provide excellent corrosion resistance, but platinum's popularity in fine jewelry is higher due to its prestigious appeal and malleability for intricate designs.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Ruthenium jewelry requires minimal maintenance due to its exceptional hardness and resistance to tarnish, making it highly durable for everyday wear. Platinum, while also durable, demands regular polishing to maintain its shine and may accumulate scratches over time. Both metals benefit from gentle cleaning with mild soap and water, but platinum requires more frequent professional care to preserve its lustrous appearance.
Environmental Impact and Sourcing
Ruthenium offers a more sustainable alternative to platinum due to its lower extraction intensity and higher abundance in the Earth's crust, reducing environmental degradation during mining. Platinum mining involves significant energy consumption and habitat disruption, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to ruthenium. Sourcing ruthenium, often obtained as a byproduct of nickel and platinum refining, leverages existing mining operations, minimizing additional environmental impact in contrast to the standalone extraction required for pure platinum.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Jewelry
Ruthenium offers exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for durable and long-lasting jewelry pieces. Platinum, known for its natural white luster and hypoallergenic properties, remains a classic option favored for engagement rings and fine jewelry. Consider factors like budget, metal weight, and skin sensitivity when choosing between ruthenium and platinum to ensure your jewelry combines both comfort and longevity.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Platinum for Jewelry
 azmater.com
azmater.com