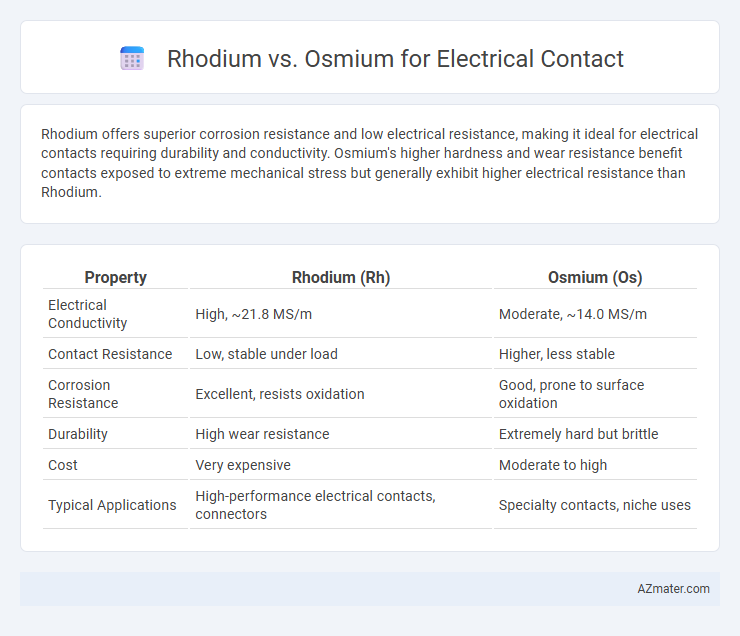
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and low electrical resistance, making it ideal for electrical contacts requiring durability and conductivity. Osmium's higher hardness and wear resistance benefit contacts exposed to extreme mechanical stress but generally exhibit higher electrical resistance than Rhodium.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium (Rh) | Osmium (Os) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, ~21.8 MS/m | Moderate, ~14.0 MS/m |
| Contact Resistance | Low, stable under load | Higher, less stable |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists oxidation | Good, prone to surface oxidation |
| Durability | High wear resistance | Extremely hard but brittle |
| Cost | Very expensive | Moderate to high |
| Typical Applications | High-performance electrical contacts, connectors | Specialty contacts, niche uses |
Introduction to Rhodium and Osmium in Electrical Contacts
Rhodium and osmium are both part of the platinum group metals, prized for their exceptional electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance in electrical contacts. Rhodium offers superior reflectivity and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for high-reliability contact points in harsh environments. Osmium, noted for its hardness and durability, provides long-lasting performance in electrical applications but is less commonly used due to its brittleness and higher cost.
Physical and Chemical Properties: Rhodium vs Osmium
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Osmium, with its exceptionally high melting point and hardness, provides durability but has lower conductivity and tends to form toxic oxides during oxidation. The choice between rhodium and osmium hinges on balancing rhodium's chemical stability and conductivity against osmium's mechanical strength.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Rhodium exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to osmium, making it more efficient for electrical contact applications where low resistance is essential. With a conductivity of approximately 22.3 million Siemens per meter, rhodium ensures minimal power loss and excellent signal transmission. Osmium, while highly durable, offers lower electrical conductivity around 16 million Siemens per meter, limiting its effectiveness in high-performance electrical contacts.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Rhodium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to osmium, making it highly reliable for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Osmium tends to oxidize more readily at elevated temperatures, which can degrade electrical performance over time. The enhanced stability of rhodium ensures consistent conductivity and longevity in contacts exposed to moisture and corrosive agents.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Rhodium exhibits a hardness of approximately 6.0 on the Mohs scale, offering excellent wear resistance that ensures durable electrical contacts in high-load applications. Osmium, with a Mohs hardness around 7.0, provides superior wear resistance but is less commonly used due to its brittleness and higher cost. For electrical contacts, rhodium's combination of hardness and exceptional oxidation resistance makes it the preferred choice for maintaining low contact resistance and long service life.
Cost and Market Availability
Rhodium offers excellent corrosion resistance and conductivity, making it a preferred choice for high-performance electrical contacts, but its high cost and limited market availability can be a constraint for large-scale applications. Osmium, while having slightly lower conductivity, is more abundant and generally less expensive, providing a cost-effective alternative for electrical contacts in less demanding environments. Market fluctuations of rhodium, driven by its rarity and platinum group status, often lead manufacturers to consider osmium or other platinum-group metals to balance performance and affordability.
Applications in Electrical and Electronic Devices
Rhodium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and low electrical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts in connectors and switches within telecommunications and aerospace industries. Osmium, though less commonly used, provides superior hardness and wear resistance, which benefits applications requiring durable contacts in harsh environments. Both metals enhance reliability and conductivity in electronic devices, with rhodium favored for precision contacts and osmium for heavy-duty, high-wear applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Rhodium offers excellent corrosion resistance and low electrical resistance, making it a preferred choice for electrical contacts with minimal environmental impact due to its high recyclability and lower toxicity compared to osmium. Osmium's use in electrical contacts is limited by its toxicity concerns and potential release of hazardous osmium tetroxide gas during wear or oxidation, posing significant environmental and health risks. Selecting rhodium ensures safer handling, reduced environmental hazards, and compliance with stringent safety standards in electrical contact applications.
Lifespan and Maintenance of Electrical Contacts
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and lower electrical resistance, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced maintenance for electrical contacts compared to osmium. Osmium's hardness provides durability but can lead to higher wear rates and increased maintenance needs due to oxide formation under electrical load. Rhodium-plated contacts typically require less frequent replacement and cleaning, enhancing overall system reliability and reducing operational costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Osmium provides exceptional hardness and wear resistance but is less conductive and more prone to oxidation under normal conditions. Selecting the optimal material depends on balancing conductivity needs with environmental durability, where rhodium generally emerges as the preferred choice for reliable electrical contacts.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Osmium for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com