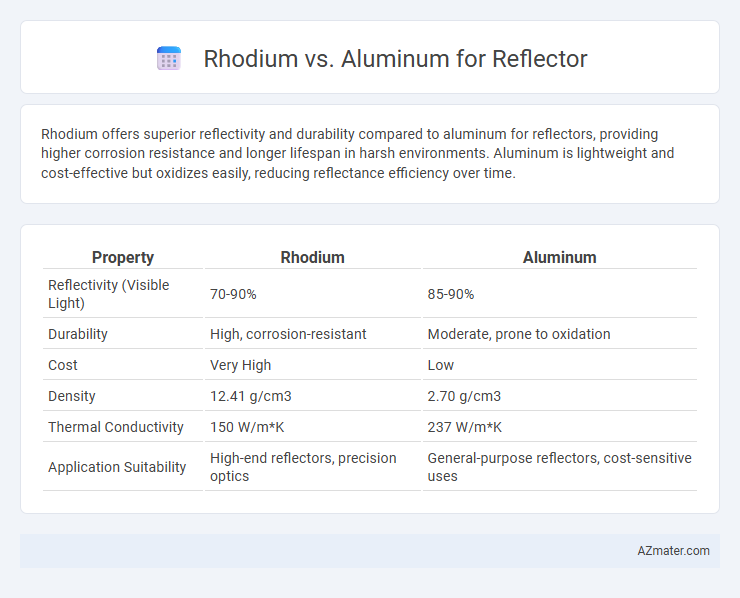
Rhodium offers superior reflectivity and durability compared to aluminum for reflectors, providing higher corrosion resistance and longer lifespan in harsh environments. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective but oxidizes easily, reducing reflectance efficiency over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity (Visible Light) | 70-90% | 85-90% |
| Durability | High, corrosion-resistant | Moderate, prone to oxidation |
| Cost | Very High | Low |
| Density | 12.41 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 150 W/m*K | 237 W/m*K |
| Application Suitability | High-end reflectors, precision optics | General-purpose reflectors, cost-sensitive uses |
Introduction to Reflector Materials
Rhodium and aluminum are prominent materials used for reflectors due to their distinct optical properties and durability. Rhodium offers superior reflectivity in the visible and ultraviolet spectrum with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance and precision applications. Aluminum, known for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness, provides good reflectivity primarily in the visible range and is widely used in general lighting and automotive reflectors.
Properties of Rhodium and Aluminum
Rhodium exhibits exceptional reflectivity in the visible and ultraviolet spectrum, with a reflectance exceeding 90%, making it highly effective for precision optical reflectors. Aluminum offers strong reflectivity across a broader range, including visible and near-infrared wavelengths, with reflectance around 85-90%, and provides excellent corrosion resistance when anodized. Rhodium's superior hardness and chemical stability outperform aluminum's softer, more reactive surface, making rhodium ideal for high-durability reflective coatings in harsh environments.
Reflectivity Comparison
Rhodium offers superior reflectivity compared to aluminum, particularly in the visible and near-UV spectrum where its reflectance can exceed 90%, making it ideal for high-precision optical applications. Aluminum provides high reflectivity in the visible range, typically around 85-90%, but its performance diminishes significantly in the UV spectrum and under harsh environmental conditions. The durability and corrosion resistance of rhodium coatings also contribute to maintaining consistent reflectivity over time, outperforming aluminum in both efficiency and longevity for reflector usage.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Rhodium offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it an ideal choice for high-performance reflectors exposed to harsh environments. Rhodium's hardness and chemical stability prevent tarnishing and oxidation, which commonly degrade aluminum reflectors over time. Aluminum, while lightweight and cost-effective, requires protective coatings to maintain performance, but these coatings can wear off, reducing long-term durability.
Cost Analysis: Rhodium vs Aluminum
Rhodium reflectors offer exceptional reflectivity and corrosion resistance but come at a significantly higher cost compared to aluminum, which remains a budget-friendly option with moderate reflectivity and durability. The price of rhodium can be up to 30 times greater per ounce than aluminum, impacting initial investment and replacement expenses in lighting or optical systems. Aluminum's lower cost and ease of fabrication make it suitable for large-scale applications, while rhodium is reserved for high-performance needs where long-term value outweighs upfront costs.
Ease of Fabrication and Application
Rhodium offers superior ease of fabrication for reflectors due to its excellent malleability and resistance to corrosion, enabling precise shaping and long-lasting performance in high-reflectance applications. Aluminum, known for its lightweight properties and cost-effectiveness, provides simpler handling and faster manufacturing processes, making it ideal for large-scale reflector production. While rhodium excels in durability and high-reflectance in harsh environments, aluminum is preferred for applications requiring budget-friendly materials with quick, efficient fabrication.
Performance in Optical Systems
Rhodium coatings exhibit superior reflectance in optical systems, particularly within the visible to near-infrared spectrum, offering reflectance values often exceeding 90%, which significantly enhances system efficiency. Aluminum, while more cost-effective and providing broad spectral reflectivity from ultraviolet to infrared ranges, typically shows lower reflectance and higher susceptibility to oxidation, diminishing long-term performance in precision optical applications. The choice between rhodium and aluminum for reflectors depends on balancing maximum reflectance and durability requirements against budget and environmental exposure conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity
Rhodium reflectors offer superior corrosion resistance and maintain high reflectivity over time, significantly reducing maintenance frequency compared to aluminum. Aluminum reflectors require regular cleaning and protective coatings to prevent oxidation and preserve performance, increasing upkeep efforts. The enhanced durability of rhodium leads to longer service life, making it a cost-effective choice for applications demanding minimal maintenance and sustained reflectance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rhodium offers superior durability and corrosion resistance in reflectors, extending product lifespan and reducing waste compared to aluminum, which is more prone to oxidation and degradation. Although rhodium mining has a higher environmental footprint due to its rarity and extraction process, its recyclability and longer lifecycle contribute to overall sustainability. Aluminum benefits from abundant availability and lower initial environmental impact, but requires energy-intensive refining and frequent replacement, increasing long-term ecological costs.
Best Use Cases for Each Material
Rhodium reflectors are ideal for high-precision optical applications requiring exceptional reflectivity and durability, such as scientific instruments, high-end lighting, and aerospace technology. Aluminum reflectors excel in general-purpose lighting, automotive headlights, and affordable household fixtures due to their lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness. Choosing rhodium supports environments with stringent corrosion resistance and long-term performance, while aluminum is preferred for large-scale and budget-conscious projects.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Aluminum for Reflector
 azmater.com
azmater.com