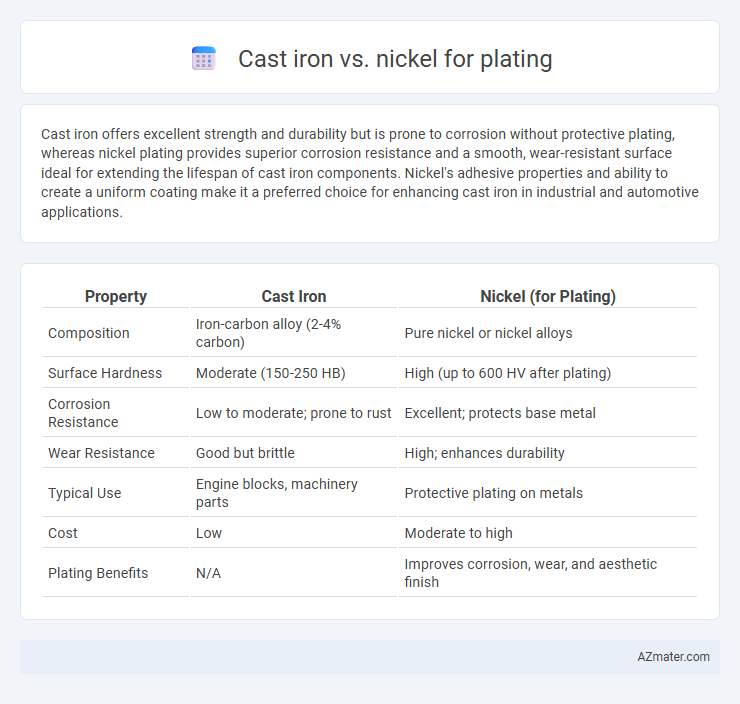
Cast iron offers excellent strength and durability but is prone to corrosion without protective plating, whereas nickel plating provides superior corrosion resistance and a smooth, wear-resistant surface ideal for extending the lifespan of cast iron components. Nickel's adhesive properties and ability to create a uniform coating make it a preferred choice for enhancing cast iron in industrial and automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cast Iron | Nickel (for Plating) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron-carbon alloy (2-4% carbon) | Pure nickel or nickel alloys |
| Surface Hardness | Moderate (150-250 HB) | High (up to 600 HV after plating) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to moderate; prone to rust | Excellent; protects base metal |
| Wear Resistance | Good but brittle | High; enhances durability |
| Typical Use | Engine blocks, machinery parts | Protective plating on metals |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
| Plating Benefits | N/A | Improves corrosion, wear, and aesthetic finish |
Introduction to Metal Plating
Metal plating enhances the surface properties of substrates like cast iron, improving corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and appearance through a thin metal coating. Cast iron, known for its hardness and brittleness, benefits from nickel plating by gaining a smooth, protective layer that resists rust and extends service life in harsh environments. Nickel plating deposits a uniform, durable film on cast iron surfaces, making it a preferred choice in automotive, industrial, and decorative applications where both functionality and aesthetic appeal are critical.
Overview of Cast Iron and Nickel
Cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy known for its excellent wear resistance, high compressive strength, and durability, commonly used in heavy-duty applications due to its hardness and brittleness. Nickel, a corrosion-resistant metal with excellent oxidation resistance and good ductility, is widely used in plating to enhance surface hardness, provide a protective barrier, and improve electrical conductivity. Nickel plating on cast iron enhances corrosion resistance, wear protection, and surface finish, making it a preferred combination in industrial coatings and machinery components.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Cast iron exhibits high carbon content and a porous surface prone to oxidation, making it susceptible to rust and corrosion without proper plating. Nickel, known for its chemical inertness and resistance to oxidation, forms a stable, non-reactive surface that protects substrates from corrosion and wear. The chemical stability and corrosion resistance of nickel plating significantly enhance the durability of cast iron components in harsh environments.
Physical Durability and Strength
Cast iron offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it highly resistant to deformation under heavy loads, while nickel plating enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance without compromising the base metal's structural integrity. Nickel plating on cast iron significantly improves wear resistance and extends lifespan by creating a tough, protective barrier against environmental factors. The combination results in a robust material suitable for high-stress applications where both physical durability and strength are critical.
Corrosion Resistance: Cast Iron vs Nickel
Nickel plating significantly enhances corrosion resistance compared to cast iron, which is prone to rust and oxidation when exposed to moisture and air. Cast iron's porous surface allows moisture penetration, leading to rapid deterioration, whereas nickel forms a dense, protective barrier that prevents oxygen and corrosive agents from reaching the base metal. The superior corrosion resistance of nickel makes it ideal for applications requiring durability in harsh environments.
Applications in Industry
Cast iron plated with nickel is widely used in automotive and heavy machinery industries due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and improved surface hardness, which extends component lifespan in harsh environments. Nickel plating on cast iron provides excellent wear resistance and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electronic connectors, industrial valves, and pump components. Industries such as aerospace and manufacturing rely on nickel-plated cast iron for parts requiring durability, resistance to abrasion, and protection against chemical exposure.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Cast iron offers a lower-cost base material with excellent durability, but it requires robust plating to prevent corrosion, making nickel plating a preferred choice due to its superior wear resistance and corrosion protection. Nickel plating provides high availability and consistent quality across industrial applications, balancing initial plating costs with long-term maintenance savings. Cost efficiency in plating choices depends on the specific use case, with nickel on cast iron delivering enhanced lifespan and reduced replacement frequency, offsetting higher upfront plating expenses.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Appeal
Cast iron plating offers a rugged surface finish with excellent durability, often characterized by a matte or slightly rough texture that enhances industrial aesthetics. Nickel plating provides a smooth, bright, and reflective surface, delivering superior corrosion resistance and a high-quality, polished appearance favored in decorative applications. The choice between cast iron and nickel plating depends on the desired balance of toughness and sleek, shiny aesthetics.
Maintenance and Longevity
Cast iron plating tends to require more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can shorten its overall longevity. Nickel plating offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, making it less prone to wear and reducing the need for regular upkeep. The enhanced maintenance efficiency and extended lifespan of nickel plating make it a preferred choice for applications demanding long-term protection.
Choosing the Right Material for Plating
Choosing between cast iron and nickel for plating depends on the intended application and desired surface properties. Cast iron offers excellent durability and wear resistance but may require additional preparation due to its porous surface, while nickel plating provides superior corrosion protection, a smooth finish, and improved hardness. Evaluating factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and aesthetic requirements ensures the selection of the most suitable material for optimal plating performance.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Nickel for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com