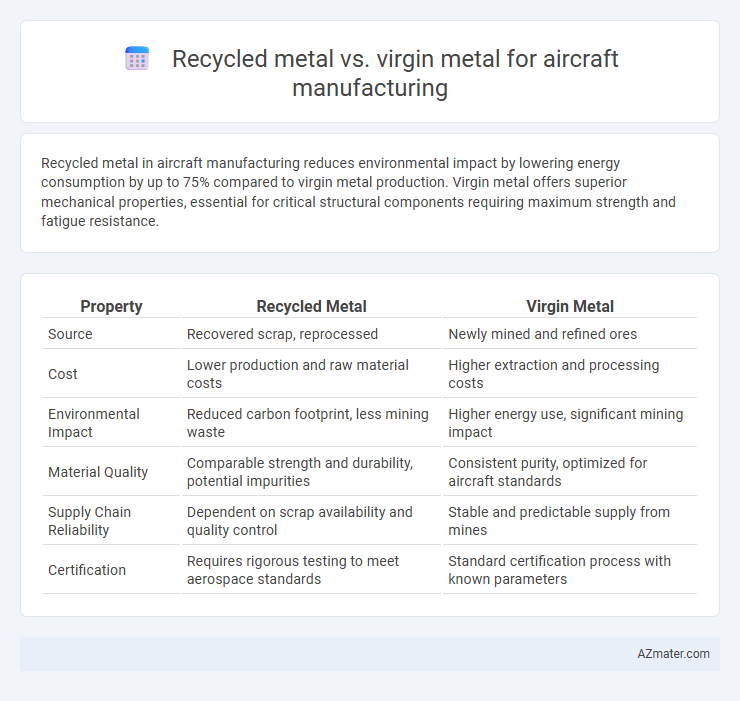
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption by up to 75% compared to virgin metal production. Virgin metal offers superior mechanical properties, essential for critical structural components requiring maximum strength and fatigue resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Metal | Virgin Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered scrap, reprocessed | Newly mined and refined ores |
| Cost | Lower production and raw material costs | Higher extraction and processing costs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint, less mining waste | Higher energy use, significant mining impact |
| Material Quality | Comparable strength and durability, potential impurities | Consistent purity, optimized for aircraft standards |
| Supply Chain Reliability | Dependent on scrap availability and quality control | Stable and predictable supply from mines |
| Certification | Requires rigorous testing to meet aerospace standards | Standard certification process with known parameters |
Introduction to Metal Use in Aircraft Manufacturing
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing offers significant environmental and economic benefits by reducing the demand for virgin metal extraction, which is energy-intensive and generates substantial carbon emissions. Virgin metal, such as aluminum and titanium, provides consistent purity and mechanical properties essential for critical structural components, ensuring high performance and safety standards. Advances in recycling technology have enabled the recovered metals to meet stringent aerospace quality certifications, making recycled metal a viable and sustainable alternative in the industry.
What is Virgin Metal?
Virgin metal refers to metal that is extracted directly from natural ore deposits through mining and refined without previous use or recycling. It offers higher purity, consistent mechanical properties, and fewer impurities compared to recycled metal, making it ideal for critical aerospace applications demanding stringent quality standards. In aircraft manufacturing, virgin metal ensures superior structural integrity and fatigue resistance, essential for safety and performance in flight.
What is Recycled Metal?
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing refers to metals recovered and reprocessed from scrap materials to create new components, reducing the need for mining virgin metals. This process involves melting down scrap aluminum, titanium, or steel, retaining essential properties while lowering environmental impacts such as energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Using recycled metal aligns with aerospace industry goals for sustainability without compromising material strength or performance critical for aircraft safety.
Material Properties: Recycled vs Virgin Metal
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing often exhibits slightly altered material properties compared to virgin metal, including variations in tensile strength and fatigue resistance due to prior processing and potential impurities. Virgin metal typically offers more consistent microstructure and mechanical properties, crucial for ensuring the highest safety and performance standards in aerospace applications. Advances in refining and alloy processing techniques have significantly improved the quality of recycled metals, making them increasingly viable without compromising structural integrity.
Environmental Impact of Using Recycled Metal
Using recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing significantly reduces energy consumption by up to 95% compared to producing virgin metal, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. Recycled metals decrease the demand for mining and raw material extraction, thereby minimizing habitat destruction and water pollution associated with these activities. Incorporating recycled aluminum and titanium in aerospace components supports sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining structural integrity and performance standards crucial for aviation safety.
Cost Comparison: Recycled vs Virgin Metal
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing offers significant cost savings compared to virgin metal, with price reductions driven by lower raw material extraction and processing expenses. Virgin metal involves higher energy consumption and refining costs, leading to increased overall production expenditures. Lifecycle analysis reveals recycled metal reduces material costs by up to 30%, making it a financially favorable choice for aerospace manufacturers seeking sustainability without compromising quality.
Performance and Safety Considerations
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing offers environmental benefits but may exhibit variations in mechanical properties compared to virgin metal, potentially affecting fatigue resistance and tensile strength. Virgin metal ensures consistent quality and performance, critical for maintaining structural integrity and meeting stringent aerospace safety standards. Careful certification and testing of recycled alloys are essential to ensure they meet the same reliability and safety benchmarks demanded in aviation applications.
Supply Chain and Availability
Recycled metal offers a more sustainable and cost-effective supply chain alternative to virgin metal in aircraft manufacturing, reducing dependency on mining and lowering environmental impact. Virgin metal availability is subject to geopolitical risks and fluctuating raw material extraction rates, often leading to supply chain delays and higher costs. Prioritizing recycled metal enhances resource efficiency and ensures a more stable supply by integrating circular economy principles within aerospace production.
Industry Trends and Innovations
Recycled metal in aircraft manufacturing is gaining traction due to sustainability goals and cost-efficiency, with the industry adopting advanced sorting and purification technologies to ensure material integrity meets aerospace standards. Innovations like improved metal alloy recovery and closed-loop recycling systems enhance the mechanical properties of recycled metals, making them competitive with virgin metals in structural applications. Industry trends emphasize integrating digital tracking and certification to guarantee traceability and compliance, fostering broader acceptance of recycled metals in aircraft production.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Aircraft Manufacturing
Recycled metal is increasingly favored in aircraft manufacturing due to its lower environmental footprint and reduced energy consumption compared to virgin metal extraction. Innovations in recycling technologies enhance the quality and reliability of recycled alloys, making them more suitable for critical aerospace applications. The future outlook for sustainable aircraft manufacturing emphasizes a circular economy approach, integrating high-performance recycled metals to meet stringent safety standards while significantly lowering carbon emissions.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Virgin metal for Aircraft manufacturing
 azmater.com
azmater.com