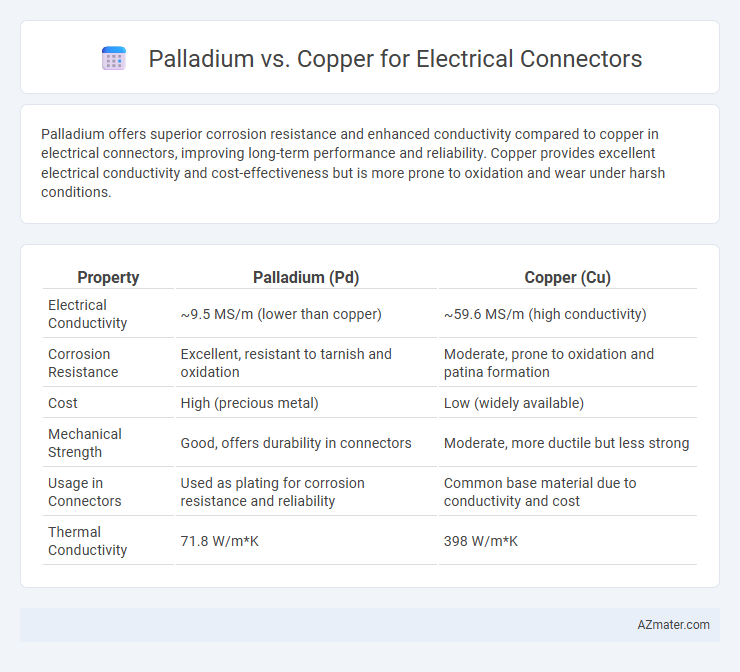
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced conductivity compared to copper in electrical connectors, improving long-term performance and reliability. Copper provides excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but is more prone to oxidation and wear under harsh conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Palladium (Pd) | Copper (Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~9.5 MS/m (lower than copper) | ~59.6 MS/m (high conductivity) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resistant to tarnish and oxidation | Moderate, prone to oxidation and patina formation |
| Cost | High (precious metal) | Low (widely available) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good, offers durability in connectors | Moderate, more ductile but less strong |
| Usage in Connectors | Used as plating for corrosion resistance and reliability | Common base material due to conductivity and cost |
| Thermal Conductivity | 71.8 W/m*K | 398 W/m*K |
Overview of Palladium and Copper in Electrical Connectors
Palladium and copper are widely used materials in electrical connectors due to their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Palladium offers superior oxidation resistance and stable performance in harsh environments, making it ideal for high-reliability applications such as aerospace and telecommunications. Copper provides outstanding electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but requires protective coatings to prevent corrosion in demanding conditions.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for long-lasting electrical connectors in harsh environments, although copper has higher intrinsic electrical conductivity with about 5.96 x 10^7 S/m versus palladium's approximately 9.5 x 10^6 S/m. Copper's excellent conductivity translates to lower electrical resistance and improved signal integrity in high-current applications, while palladium's stable conductivity under varying temperatures and oxidation conditions enhances connector reliability. The choice between palladium and copper hinges on balancing copper's superior conductivity against palladium's durability and resistance to oxidation for optimal connector performance.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, maintaining excellent electrical conductivity even in harsh environments with exposure to moisture and chemicals. Copper, while highly conductive, tends to oxidize and corrode more quickly, leading to increased electrical resistance and potential connector failure over time. The enhanced longevity of palladium-plated electrical connectors makes them ideal for critical applications requiring stable performance and minimal maintenance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Palladium exhibits superior mechanical strength and corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for electrical connectors subjected to harsh environments and repeated mechanical stress. Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity but tends to oxidize and wear faster under mechanical load, reducing connector durability over time. The enhanced hardness and resistance to deformation of palladium ensure longer-lasting connector performance in demanding applications.
Cost Analysis: Palladium vs Copper
Palladium, priced significantly higher than copper, impacts the overall cost of electrical connectors due to its rarity and market demand, typically costing several times more per kilogram. Copper offers a cost-effective alternative with excellent electrical conductivity and widespread availability, making it the preferred choice for large-scale manufacturing. While palladium's superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability may reduce long-term maintenance costs, the initial investment is substantially higher compared to copper-based connectors.
Applications in Electrical and Electronic Industries
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability connectors in aerospace, telecommunications, and medical devices. Copper, known for its high conductivity and cost-effectiveness, remains widely used in general-purpose electrical connectors and printed circuit boards across consumer electronics and automotive industries. Selecting between palladium and copper connectors depends on application-specific requirements such as durability, signal integrity, and environmental conditions.
Solderability and Manufacturing Considerations
Palladium offers superior solderability compared to copper due to its excellent oxidation resistance, ensuring consistent and reliable solder joints in electrical connectors. While copper provides excellent electrical conductivity and is cost-effective, it requires additional surface treatments like plating to prevent oxidation and maintain solderability during manufacturing. Choosing palladium reduces the need for such treatments and enhances manufacturing efficiency, but at a higher material cost and with more complex sourcing considerations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity in electrical connectors, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental waste compared to copper. Copper, while more abundant and recyclable, involves higher energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during mining and refining processes. Choosing palladium enhances connector durability and supports sustainability by lowering resource depletion and electronic waste over the product lifecycle.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity in harsh environments compared to copper, making it ideal for electrical connectors exposed to moisture, oxidation, and temperature extremes. Copper, while highly conductive, tends to oxidize and degrade faster under such conditions, requiring protective coatings to maintain performance. Palladium-plated connectors provide enhanced durability and consistent electrical performance in industrial, automotive, and marine applications where reliability is critical.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Electrical Connectors
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical connectors in harsh environments. Copper, known for its exceptional electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, suits applications requiring efficient current flow without extreme durability demands. Choosing the right material depends on balancing budget constraints with performance needs, where palladium excels in longevity and copper provides optimal conductivity at a lower price.
Infographic: Palladium vs Copper for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com