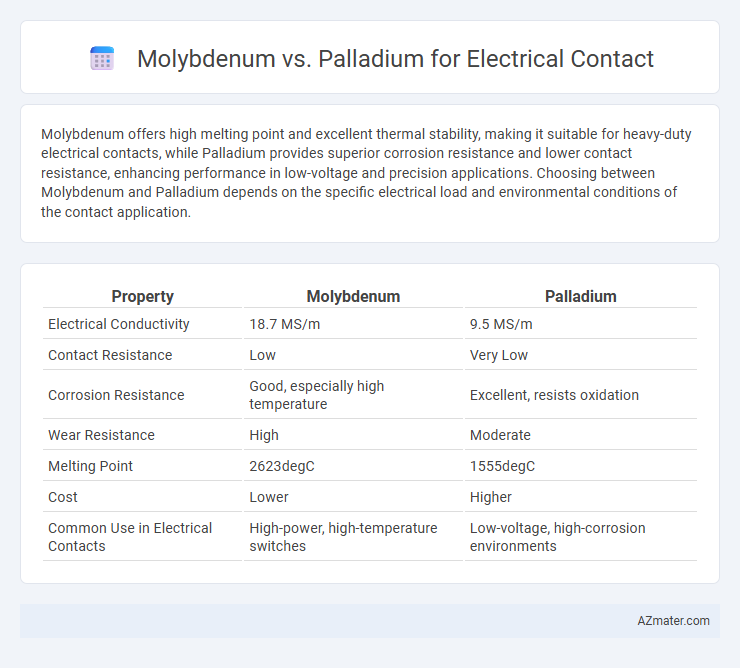
Molybdenum offers high melting point and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for heavy-duty electrical contacts, while Palladium provides superior corrosion resistance and lower contact resistance, enhancing performance in low-voltage and precision applications. Choosing between Molybdenum and Palladium depends on the specific electrical load and environmental conditions of the contact application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Palladium |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 18.7 MS/m | 9.5 MS/m |
| Contact Resistance | Low | Very Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, especially high temperature | Excellent, resists oxidation |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Melting Point | 2623degC | 1555degC |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Electrical Contacts | High-power, high-temperature switches | Low-voltage, high-corrosion environments |
Introduction to Molybdenum and Palladium in Electrical Contacts
Molybdenum exhibits excellent thermal conductivity and high melting point, making it ideal for electrical contacts requiring durability under extreme temperatures. Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and low electrical resistance, ensuring reliable conductivity in sensitive electronic applications. Both metals are crucial in electrical contact manufacturing, with molybdenum favored for mechanical strength and palladium preferred for enhanced electrical performance.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Molybdenum exhibits a high melting point of 2,623degC and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for electrical contacts in high-temperature applications, while palladium has a lower melting point of 1,555degC but superior corrosion resistance and oxidation stability. Chemically, molybdenum is less noble and more prone to surface oxidation, whereas palladium resists tarnishing and maintains conductivity in harsh environments due to its inertness. The choice between molybdenum and palladium for electrical contacts depends on balancing the need for thermal durability against corrosion resistance and electrical reliability.
Electrical Conductivity: Molybdenum vs Palladium
Molybdenum exhibits electrical conductivity around 18.7 million siemens per meter (MS/m), making it efficient in conducting electricity under high-temperature conditions. Palladium offers lower conductivity than molybdenum, approximately 9.5 MS/m, but provides excellent corrosion resistance and stability in electrical contacts. The choice between molybdenum and palladium for electrical contacts hinges on balancing the superior electrical conductivity of molybdenum against the chemical resilience of palladium.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Molybdenum exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to palladium, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1,000degC, which is crucial for high-temperature electrical contacts. Palladium, with a melting point around 1,554degC, also offers good heat resistance but tends to oxidize more rapidly at elevated temperatures, reducing its long-term reliability in thermal stress conditions. The choice between molybdenum and palladium hinges on specific application temperature ranges, with molybdenum preferred for extreme heat environments and palladium favored for moderate heat with enhanced corrosion resistance.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Molybdenum exhibits superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments due to its stable oxide layer, making it ideal for electrical contacts exposed to oxidative stress. Palladium offers excellent oxidation resistance and prevents contact degradation by forming a protective palladium oxide film, enhancing long-term conductivity. Both metals ensure durability in electrical contacts, but molybdenum is preferred for high-temperature applications, while palladium excels in humid or chemically aggressive atmospheres.
Mechanical Strength and Wear Performance
Molybdenum offers superior mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for high-stress electrical contacts subjected to frequent mechanical movements. Palladium provides good conductivity and corrosion resistance but generally exhibits lower hardness and wear performance compared to molybdenum. In applications demanding durability and long-term wear resistance, molybdenum-based contacts outperform palladium counterparts due to their enhanced mechanical robustness.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Molybdenum offers a cost-effective option for electrical contacts due to its lower raw material price and widespread mining sources compared to palladium, which commands a premium price linked to its rarity and high demand in electronics. Market availability of molybdenum is more stable, with extensive global reserves and steady production, whereas palladium supply is constrained by its limited geographic mining locations, primarily in Russia and South Africa, making it susceptible to geopolitical risks. The cost analysis favors molybdenum for budget-sensitive projects, while palladium's superior corrosion resistance and conductivity justify its higher cost in high-performance applications.
Applications in Electrical and Electronic Devices
Molybdenum offers excellent thermal conductivity and stability, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical contacts in vacuum tubes and semiconductor devices. Palladium provides superior corrosion resistance and low electrical resistance, often used in connectors, switches, and relay contacts to ensure long-term reliability. Both metals enhance performance in electronic devices, with molybdenum preferred for heat dissipation and palladium favored for preventing oxidation and maintaining consistent conductivity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Molybdenum offers a lower environmental footprint compared to palladium due to its abundance and energy-efficient extraction processes, reducing resource depletion and pollution. Palladium, while highly effective for electrical contacts because of its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, suffers from supply constraints and intensive mining practices that contribute significantly to ecological damage and carbon emissions. Choosing molybdenum supports sustainability goals by promoting resource conservation and minimizing hazardous mining impacts in electrical contact manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Molybdenum offers superior thermal stability and resistance to arc erosion, making it ideal for high-temperature and high-current electrical contacts. Palladium excels in corrosion resistance and low contact resistance, ensuring reliable performance in low-voltage, precise switching applications. Selecting the right material depends on operating conditions--molybdenum suits heavy-duty environments, while palladium is preferred for sensitive, low-current electrical contacts.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Palladium for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com