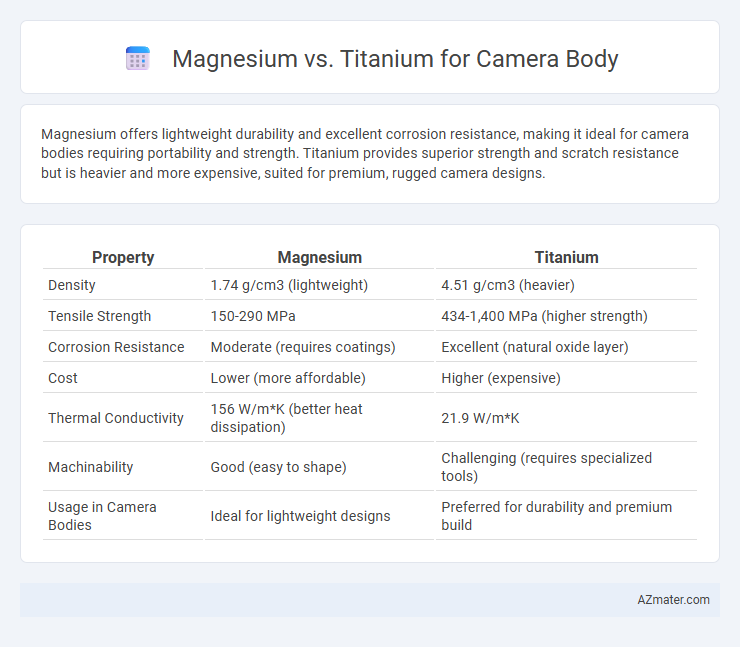
Magnesium offers lightweight durability and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for camera bodies requiring portability and strength. Titanium provides superior strength and scratch resistance but is heavier and more expensive, suited for premium, rugged camera designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnesium | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.74 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 4.51 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 150-290 MPa | 434-1,400 MPa (higher strength) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (requires coatings) | Excellent (natural oxide layer) |
| Cost | Lower (more affordable) | Higher (expensive) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 156 W/m*K (better heat dissipation) | 21.9 W/m*K |
| Machinability | Good (easy to shape) | Challenging (requires specialized tools) |
| Usage in Camera Bodies | Ideal for lightweight designs | Preferred for durability and premium build |
Introduction: Importance of Camera Body Materials
Camera bodies crafted from magnesium and titanium significantly influence durability, weight, and handling in photography equipment. Magnesium offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice for lightweight yet robust camera construction. Titanium provides superior corrosion resistance and exceptional strength, ideal for professional cameras exposed to extreme conditions.
Magnesium vs Titanium: Material Properties Overview
Magnesium offers lightweight characteristics, excellent strength-to-weight ratio, and good vibration damping, making it ideal for portable camera bodies. Titanium provides superior corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and enhanced durability, contributing to long-lasting camera performance in harsh environments. Both materials balance strength and weight, but titanium is denser and more expensive, while magnesium excels in weight reduction and cost efficiency.
Weight Comparison: Which Is Lighter?
Magnesium camera bodies typically weigh between 100 to 200 grams less than titanium counterparts, making magnesium the lighter material option for camera construction. Titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability but usually results in a heavier camera body due to its density of about 4.5 g/cm3, compared to magnesium's 1.74 g/cm3. For photographers prioritizing lightweight gear, magnesium is generally preferred, while titanium is chosen for enhanced toughness and premium build quality.
Durability and Strength Differences
Magnesium camera bodies offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, providing robust impact resistance while remaining lightweight, making them ideal for portable professional use. Titanium, though heavier, boasts superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance, resulting in an extremely durable, long-lasting camera body that withstands harsh environmental conditions. The choice between magnesium and titanium hinges on balancing lightweight portability against maximum structural resilience in demanding photography settings.
Corrosion Resistance: Performance in Challenging Environments
Magnesium and titanium camera bodies exhibit distinct corrosion resistance qualities impacting durability in harsh conditions. Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance due to its stable oxide layer, making it ideal for environments with high humidity, salt exposure, or chemical contact. Magnesium, while lightweight, is more prone to corrosion and typically requires protective coatings to withstand challenging environments effectively.
Cost and Manufacturing Implications
Magnesium and titanium both offer distinct advantages for camera bodies, with magnesium being the more cost-effective option due to its lower raw material price and easier manufacturing processes such as die casting. Titanium delivers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance but incurs higher expenses from complex machining and longer production times, impacting overall cost efficiency. Manufacturers often choose magnesium to balance durability and affordability, while titanium is reserved for premium models where performance justifies the premium price.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Dissipation
Magnesium camera bodies offer superior thermal conductivity, efficiently dissipating heat generated by the camera sensor and electronic components during prolonged use. Titanium, while more durable and corrosion-resistant, has lower thermal conductivity, which can lead to slower heat dissipation and potential thermal buildup. The enhanced heat management in magnesium bodies helps maintain optimal camera performance and reduces the risk of overheating in high-intensity shooting environments.
Impact on Camera Design and Aesthetics
Magnesium offers a lightweight and durable solution for camera bodies, allowing for more compact and ergonomic designs without sacrificing strength. Titanium, while heavier and more expensive, provides exceptional rigidity and a premium finish that enhances the camera's luxury appeal and resistance to wear. The choice between magnesium and titanium significantly influences the overall camera aesthetics, durability, and user experience in high-end camera manufacturing.
Field Performance: User Experiences
Magnesium camera bodies are favored by professionals for their lightweight design, enhancing handheld stability and reducing fatigue during extended shoots. Titanium bodies offer superior durability and corrosion resistance, often preferred in harsh environmental conditions such as underwater or extreme temperatures. Users report that while magnesium provides excellent balance and comfort in the field, titanium's ruggedness ensures long-term reliability for adventure and wildlife photography.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Camera
Magnesium camera bodies offer lightweight durability and superior shock absorption, making them ideal for photographers requiring portability and ruggedness. Titanium bodies provide exceptional strength and corrosion resistance with a premium feel but typically come at a higher cost and increased weight. Selecting between magnesium and titanium depends on balancing the need for lightweight design against budget and durability preferences in various shooting environments.
Infographic: Magnesium vs Titanium for Camera Body
 azmater.com
azmater.com