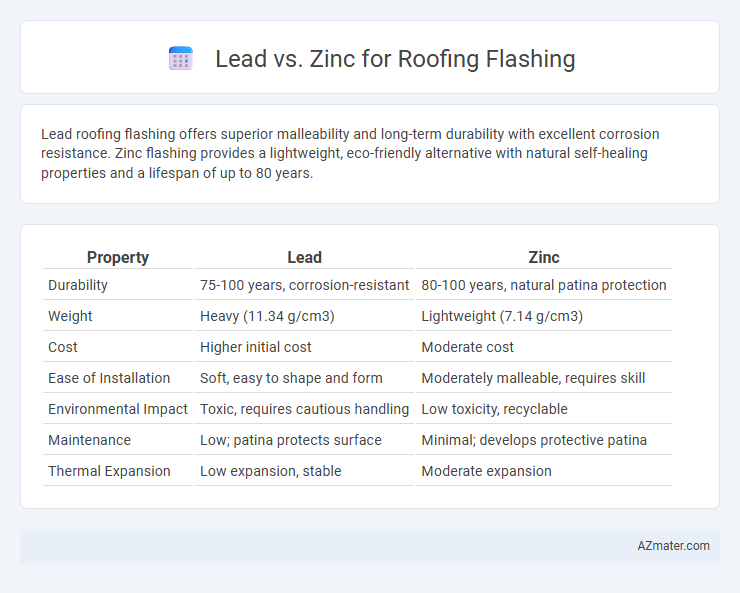
Lead roofing flashing offers superior malleability and long-term durability with excellent corrosion resistance. Zinc flashing provides a lightweight, eco-friendly alternative with natural self-healing properties and a lifespan of up to 80 years.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | 75-100 years, corrosion-resistant | 80-100 years, natural patina protection |
| Weight | Heavy (11.34 g/cm3) | Lightweight (7.14 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Moderate cost |
| Ease of Installation | Soft, easy to shape and form | Moderately malleable, requires skill |
| Environmental Impact | Toxic, requires cautious handling | Low toxicity, recyclable |
| Maintenance | Low; patina protects surface | Minimal; develops protective patina |
| Thermal Expansion | Low expansion, stable | Moderate expansion |
Introduction to Roofing Flashing Materials
Roofing flashing materials like lead and zinc play a crucial role in preventing water infiltration at joints and roof penetrations. Lead offers high durability and malleability, making it ideal for complex roof shapes, while zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance and a natural patina that enhances longevity. Both materials are favored in construction for their weatherproofing qualities, but zinc is often preferred for sustainable and low-maintenance roofing solutions.
Overview: Lead vs Zinc Flashing
Lead roofing flashing offers exceptional malleability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for complex joints and detailed sealing. Zinc flashing provides superior durability and a natural patina that enhances weatherproofing over time, with lower environmental impact and easier installation. Both materials protect roof structures effectively, but lead is preferred for flexibility while zinc is favored for longevity and sustainability.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Lead roofing flashing offers exceptional durability due to its malleability and resistance to corrosion, typically lasting over 100 years with minimal maintenance. Zinc, while also highly durable and corrosion-resistant, generally provides a lifespan of 80 to 100 years and develops a protective patina that enhances longevity. Both metals perform well under harsh weather conditions, but lead's superior flexibility and heavier weight contribute to a longer-lasting roofing solution.
Weather Resistance and Corrosion
Lead roofing flashing offers exceptional weather resistance due to its malleability and natural ability to expand and contract with temperature fluctuations, preventing cracks and leaks. Zinc roofing flashing provides superior corrosion resistance, forming a protective patina that self-heals minor damages and extends lifespan in harsh environmental conditions. Both metals excel in durability, but zinc's resistance to atmospheric pollutants makes it highly suitable for coastal or industrial areas.
Installation Process: Lead vs Zinc
Lead roofing flashing offers superior malleability, allowing for easier shaping and fitting around complex roof profiles during installation. Zinc flashing requires precise cutting and heating to create tight seals, which demands skilled labor for accurate soldering and folding. The installation of lead is generally quicker due to its softness, while zinc provides enhanced durability but may extend project timelines due to its rigidity and specialized handling needs.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Lead roofing flashing offers durability and excellent malleability but poses significant health risks due to lead's toxicity, which can contaminate soil and water during weathering or improper disposal. Zinc presents a safer alternative with lower toxicity, reduced environmental impact, and natural patination that provides long-term corrosion resistance without harmful runoff. Selecting zinc over lead minimizes environmental pollution and protects workers and inhabitants from hazardous lead exposure.
Maintenance Requirements
Lead roofing flashing offers exceptional durability with minimal maintenance due to its self-sealing properties and resistance to corrosion, often lasting over a century without significant repairs. Zinc flashing requires periodic inspection and occasional cleaning to remove patina buildup, which can protect the metal but may also trap dirt and moisture if neglected. Both materials benefit from proper installation, but lead's low upkeep and longevity make it a superior choice for maintenance-conscious roofing projects.
Cost Analysis: Lead vs Zinc
Lead roofing flashing generally has a higher upfront cost due to its density and weight, but offers excellent durability and malleability, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Zinc is typically more affordable initially and provides good corrosion resistance and longevity, making it a cost-effective option for many roofing projects. Total cost analysis should consider installation complexity, material lifespan, and maintenance requirements to determine the best value between lead and zinc flashing.
Aesthetic Differences
Lead roofing flashing offers a traditional, matte gray finish that naturally weathers to a unique patina, enhancing the visual appeal of historic or classic buildings. Zinc flashing provides a smoother, bluish-gray surface that develops a uniform, protective patina over time, blending well with contemporary architectural styles. The choice between lead and zinc can significantly influence the roof's aesthetic character, with lead favoring a rustic and aged look, while zinc delivers a sleek, modern appearance.
Best Applications for Each Material
Lead roofing flashing excels in durability and malleability, making it ideal for complex roof joints, chimneys, and valleys where precise shaping is critical. Zinc offers superior corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan, making it suitable for coastal environments and modern architectural designs with sleek, minimalistic profiles. Both materials provide excellent waterproofing, but lead is preferred for traditional or historical restorations, whereas zinc is favored for sustainable, low-maintenance roofing solutions.
Infographic: Lead vs Zinc for Roofing Flashing
 azmater.com
azmater.com