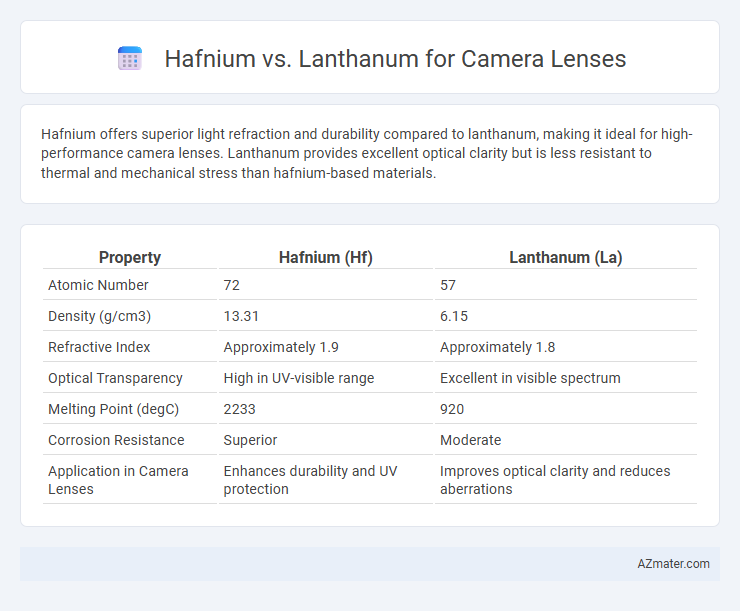
Hafnium offers superior light refraction and durability compared to lanthanum, making it ideal for high-performance camera lenses. Lanthanum provides excellent optical clarity but is less resistant to thermal and mechanical stress than hafnium-based materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Lanthanum (La) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 72 | 57 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 13.31 | 6.15 |
| Refractive Index | Approximately 1.9 | Approximately 1.8 |
| Optical Transparency | High in UV-visible range | Excellent in visible spectrum |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2233 | 920 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior | Moderate |
| Application in Camera Lenses | Enhances durability and UV protection | Improves optical clarity and reduces aberrations |
Introduction to Hafnium and Lanthanum in Camera Lenses
Hafnium and Lanthanum are key elements used in advanced camera lens manufacturing due to their unique optical properties. Hafnium oxide enhances lens durability and reduces chromatic aberration, improving image clarity, while Lanthanum glass offers high refractive index and low dispersion, enabling compact lens designs with superior sharpness. Combining these materials optimizes lens performance by balancing hardness, light transmission, and color accuracy in professional photography applications.
Chemical Properties and Structure Comparison
Hafnium and Lanthanum differ significantly in chemical properties and structure, impacting their use in camera lenses. Hafnium is a transition metal with a high atomic number (72) and exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion and high melting point (2233degC), making it ideal for durable lens coatings and precision optical components. Lanthanum, an alkaline earth metal from the lanthanide series with atomic number 57, has a larger ionic radius and lower melting point (920degC), offering unique refractive indices that enhance lens clarity but with less durability compared to hafnium-based materials.
Optical Performance: Refractive Index and Dispersion
Hafnium-based optics exhibit a higher refractive index compared to lanthanum, enhancing light bending capabilities crucial for superior image sharpness in camera lenses. Lanthanum glass, known for its low dispersion, effectively minimizes chromatic aberration, resulting in clearer color accuracy across the frame. Combining hafnium's refractive strength with lanthanum's dispersion control can optimize optical performance, balancing sharpness and color fidelity in advanced photographic lenses.
Manufacturing Processes and Material Availability
Hafnium offers superior hardness and high refractive index, enhancing lens durability and optical performance, but its complex extraction and limited availability increase manufacturing costs. Lanthanum, more abundant and easier to process, provides excellent light transmission and low dispersion, making it a cost-effective choice for camera lenses. The manufacturing process for hafnium lenses often requires advanced techniques like vacuum deposition, while lanthanum lenses can be produced using conventional glass melting methods.
Impact on Image Quality: Clarity and Sharpness
Hafnium-based camera lenses exhibit superior light transmission and significantly reduce chromatic aberration compared to lanthanum lenses, resulting in enhanced clarity and sharper image rendering. The higher refractive index of hafnium glass allows for better control over spherical aberrations, improving edge-to-edge sharpness in photographs. Lanthanum lenses, while effective, typically produce slightly softer images with more color fringing, impacting overall image quality in high-precision photography.
Durability and Resistance to Environmental Factors
Hafnium-based camera lenses offer superior durability with excellent resistance to scratches, corrosion, and high temperatures, making them ideal for challenging environmental conditions. Lanthanum lenses provide high refractive indices and excellent optical clarity but are generally less resistant to harsh elements like moisture and abrasive impacts. Choosing Hafnium enhances long-term lens performance in rugged environments, while Lanthanum prioritizes optical quality under controlled conditions.
Cost Considerations and Market Trends
Hafnium-coated camera lenses typically carry a higher price point due to the metal's rarity and advanced manufacturing processes, making them more suitable for professional-grade optics where enhanced durability and performance justify the cost. Lanthanum glass lenses, known for improved refractive properties and cost-effectiveness, have gained popularity in mid-range to high-end camera markets, balancing quality and affordability. Market trends indicate a growing demand for lanthanum-based lenses driven by consumer preference for high-quality optics with reasonable pricing, whereas hafnium lenses remain niche with limited but specialized applications.
Compatibility with Lens Coatings and Designs
Hafnium oxide offers superior compatibility with advanced camera lens coatings due to its higher refractive index and durability, enabling enhanced anti-reflective and scratch-resistant layers. Lanthanum-based glass, while effective in reducing chromatic aberration, tends to be less compatible with certain sophisticated multi-layer coatings because of its chemical properties. Lens manufacturers often prefer hafnium-infused elements for cutting-edge designs requiring maximal lens clarity and coating adherence.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Hafnium-based coatings in camera lenses offer superior durability and resistance to corrosion, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental waste. Lanthanum, while providing excellent optical clarity, often involves mining practices with higher ecological impact and potential toxicity risks during processing. Choosing hafnium-enhanced lenses supports safer manufacturing environments and contributes to sustainable product lifecycles due to its lower environmental footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hafnium and Lanthanum
Hafnium and Lanthanum both enhance camera lenses, with Hafnium offering superior durability and resistance to heat-induced distortion, making it ideal for high-performance optics. Lanthanum's high refractive index improves image sharpness and reduces chromatic aberration, beneficial for precision photography. Choosing between them depends on specific needs: Hafnium suits robust, long-lasting lenses, while Lanthanum excels in optical clarity and resolution.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Lanthanum for Camera Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com