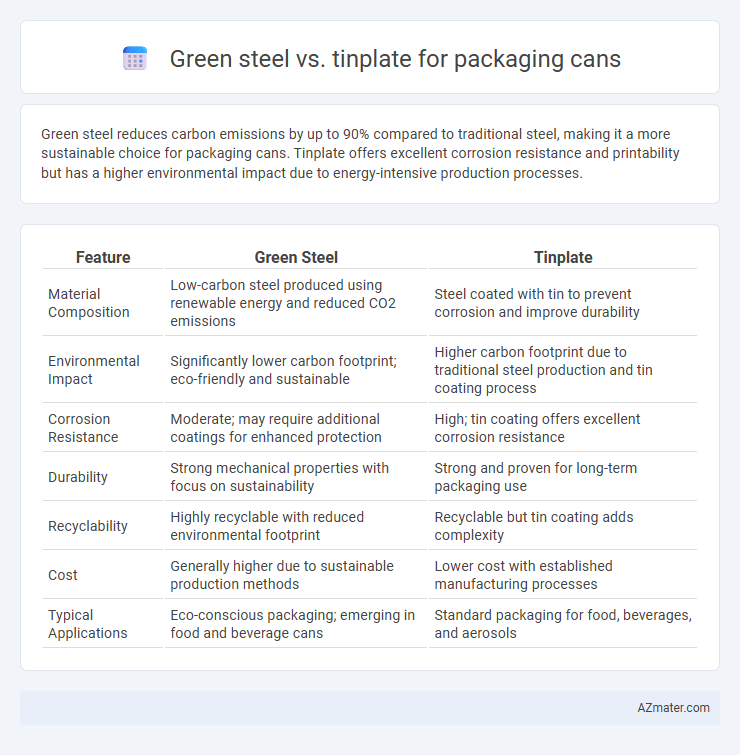
Green steel reduces carbon emissions by up to 90% compared to traditional steel, making it a more sustainable choice for packaging cans. Tinplate offers excellent corrosion resistance and printability but has a higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive production processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Steel | Tinplate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Low-carbon steel produced using renewable energy and reduced CO2 emissions | Steel coated with tin to prevent corrosion and improve durability |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lower carbon footprint; eco-friendly and sustainable | Higher carbon footprint due to traditional steel production and tin coating process |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; may require additional coatings for enhanced protection | High; tin coating offers excellent corrosion resistance |
| Durability | Strong mechanical properties with focus on sustainability | Strong and proven for long-term packaging use |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable with reduced environmental footprint | Recyclable but tin coating adds complexity |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable production methods | Lower cost with established manufacturing processes |
| Typical Applications | Eco-conscious packaging; emerging in food and beverage cans | Standard packaging for food, beverages, and aerosols |
Introduction to Sustainable Packaging Materials
Green steel, produced using low-carbon technologies such as hydrogen reduction, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional steel by significantly reducing CO2 emissions in packaging manufacturing. Tinplate, commonly used in packaging cans, combines steel with a thin tin coating to enhance corrosion resistance but remains reliant on conventional steel production processes with higher environmental impacts. Transitioning to green steel for tinplate production supports sustainable packaging by lowering the carbon footprint and aligning with circular economy principles.
What is Green Steel?
Green steel refers to steel produced through environmentally friendly methods that significantly reduce carbon emissions, primarily by using hydrogen or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy instead of traditional coal-based blast furnaces. In contrast to tinplate, which is traditional steel coated with tin for corrosion resistance in packaging cans, green steel aims to minimize the carbon footprint associated with raw material production while maintaining similar mechanical properties and durability. This sustainable approach aligns with increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions in the food and beverage industry.
What is Tinplate?
Tinplate is a thin sheet of steel coated with a layer of tin, primarily used in packaging cans for food and beverages due to its corrosion resistance and strength. Green steel refers to steel produced using environmentally sustainable methods that reduce carbon emissions, contrasting with traditional tinplate manufacturing which can have a significant environmental footprint. The choice between green steel and conventional tinplate impacts sustainability goals in the packaging industry, emphasizing the importance of eco-friendly materials without compromising durability.
Environmental Impact: Green Steel vs Tinplate
Green steel significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing hydrogen-based or electric arc furnace processes instead of traditional blast furnaces, lowering the overall environmental footprint in packaging production. Tinplate, though widely recycled, involves energy-intensive tin coating and steel manufacturing processes that contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to green steel alternatives. Transitioning to green steel in packaging cans can drastically decrease lifecycle carbon emissions and support sustainable supply chains in the metal packaging industry.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Green steel, produced using low-carbon technologies, offers enhanced strength and durability compared to traditional tinplate, making it more resistant to dents and corrosion. Its superior tensile strength ensures longer-lasting packaging, ideal for products requiring extended shelf life. While tinplate remains cost-effective, green steel provides a more sustainable option without compromising mechanical performance.
Manufacturing Processes and Energy Consumption
Green steel production utilizes hydrogen-based direct reduction and electric arc furnaces, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace methods used for tinplate manufacturing. Tinplate production involves coating steel sheets with tin, requiring energy-intensive melting and electroplating processes that increase overall energy consumption. The shift to green steel reduces reliance on fossil fuels and decreases the carbon footprint in packaging can manufacturing by optimizing energy efficiency during steel production.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Green steel, produced using environmentally sustainable methods, generally incurs higher production costs compared to conventional tinplate due to advanced technologies and lower economies of scale. Market trends reveal a growing demand for green steel packaging driven by increased consumer preference for eco-friendly products and stricter environmental regulations, influencing manufacturers to consider long-term cost benefits despite initial premiums. Cost analysis indicates that while tinplate remains cost-effective for mass production, the escalating carbon pricing and sustainability mandates are narrowing the cost gap, pushing the packaging industry toward green steel adoption.
Recyclability and End-of-Life Options
Green steel in packaging cans offers superior recyclability due to its low carbon footprint and compatibility with existing steel recycling infrastructure, enabling indefinite material recovery without loss of quality. Tinplate, a traditional packaging material, is highly recyclable but involves energy-intensive processes and potential challenges in separating tin coatings during recycling. End-of-life options for green steel promote circular economy principles by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and facilitating closed-loop recycling systems, whereas tinplate recycling, while established, contributes to higher environmental impacts and limited resource efficiency.
Industry Adoption and Case Studies
Green steel, produced using low-carbon technologies, is increasingly adopted in the packaging industry to meet sustainability goals and reduce carbon footprints. Leading companies like ArcelorMittal and SSAB have launched green steel lines specifically targeting tinplate manufacturers, demonstrating successful case studies of integrating eco-friendly materials without compromising durability or printability. Major brands in beverage and food sectors are transitioning to green steel tinplate cans, supported by lifecycle assessments confirming significant GHG emissions reductions compared to traditional tinplate.
Future Outlook for Green Packaging Solutions
Green steel offers a sustainable alternative to traditional tinplate in packaging cans by significantly reducing carbon emissions through innovative production methods like hydrogen-based direct reduction. The future outlook for green packaging solutions emphasizes the integration of green steel with recyclable materials to meet stringent environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Advancements in green steel technology and increased investment in renewable energy sources will drive widespread adoption, positioning it as a key material in achieving circular economy goals within the packaging industry.
Infographic: Green steel vs Tinplate for Packaging can
 azmater.com
azmater.com