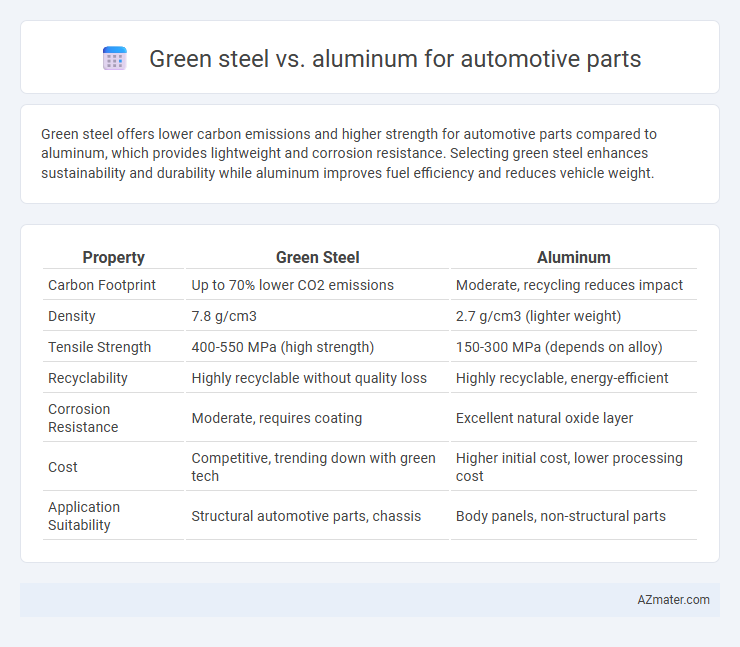
Green steel offers lower carbon emissions and higher strength for automotive parts compared to aluminum, which provides lightweight and corrosion resistance. Selecting green steel enhances sustainability and durability while aluminum improves fuel efficiency and reduces vehicle weight.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint | Up to 70% lower CO2 emissions | Moderate, recycling reduces impact |
| Density | 7.8 g/cm3 | 2.7 g/cm3 (lighter weight) |
| Tensile Strength | 400-550 MPa (high strength) | 150-300 MPa (depends on alloy) |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable without quality loss | Highly recyclable, energy-efficient |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, requires coating | Excellent natural oxide layer |
| Cost | Competitive, trending down with green tech | Higher initial cost, lower processing cost |
| Application Suitability | Structural automotive parts, chassis | Body panels, non-structural parts |
Introduction to Green Steel and Aluminum in Automotive Manufacturing
Green steel, produced using hydrogen-based reduction or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, significantly reduces carbon emissions in automotive manufacturing compared to traditional steel. Aluminum, renowned for its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio, enhances vehicle fuel efficiency and performance but involves energy-intensive extraction processes. Automakers increasingly balance green steel's sustainable production benefits against aluminum's weight savings to optimize environmental impact and vehicle efficiency.
Material Properties: Strength, Weight, and Durability
Green steel offers superior tensile strength and enhanced durability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for automotive parts requiring high load-bearing capacity. Aluminum provides significant weight reduction, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and vehicle handling, though it generally has lower strength and scratch resistance. Advanced green steel grades combine strength with corrosion resistance, balancing durability and sustainability for automotive manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Comparison
Green steel production reduces carbon emissions by up to 70% compared to traditional steel, making it a more sustainable option for automotive parts. Aluminum recycling consumes only 5% of the energy required for primary aluminum production, significantly lowering its carbon footprint. Despite aluminum's lightweight benefits contributing to fuel efficiency, green steel's lower lifecycle emissions position it as a key material for reducing the automotive industry's overall environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency in Production Processes
Green steel production significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking, using renewable energy sources and hydrogen-based reduction methods that lower energy consumption by up to 30%. Aluminum production, while less energy-intensive per ton, relies heavily on electricity, often from non-renewable sources, which can offset its energy efficiency benefits. In automotive part manufacturing, green steel offers superior energy efficiency during production due to lower thermal requirements and advancements in recycling, positioning it as a more sustainable choice for reducing the industry's overall carbon footprint.
Cost Analysis: Raw Materials and Manufacturing Expenses
Green steel offers a cost advantage over aluminum in automotive parts due to lower raw material prices and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing, driven by innovations in electric arc furnace technology and hydrogen-based steelmaking. Aluminum's higher extraction and refining costs, coupled with energy-intensive processes like electrolysis, often result in greater overall expenses despite its lightweight benefits. Manufacturers must weigh green steel's cost efficiency and sustainability against aluminum's performance characteristics when optimizing production budgets.
Recyclability and End-of-Life Management
Green steel demonstrates superior recyclability in automotive parts due to its established, energy-efficient closed-loop recycling systems that reduce carbon emissions and preserve material properties. Aluminum offers lightweight advantages but faces challenges in end-of-life management, as its recycling requires higher energy consumption and can lead to quality degradation over multiple cycles. Implementing green steel in automotive manufacturing enhances sustainability by enabling more efficient recycling processes and reducing environmental impact compared to aluminum.
Performance in Crash Safety and Vehicle Integrity
Green steel demonstrates superior crash safety performance due to its high tensile strength and excellent energy absorption during impact, enhancing occupant protection in automotive parts. Aluminum offers lightweight benefits that improve fuel efficiency but exhibits lower stiffness and energy absorption, potentially compromising vehicle integrity in severe collisions. Combining green steel with aluminum components can optimize structural durability and crashworthiness while maintaining overall vehicle weight balance.
Design Flexibility and Engineering Challenges
Green steel offers superior strength and durability, enabling automotive parts with complex geometries and higher load-bearing capacity, while aluminum provides greater design flexibility due to its lightweight and excellent formability, ideal for intricate shapes and fuel efficiency. Engineering challenges for green steel include managing higher material weight and ensuring energy-efficient production methods, whereas aluminum requires addressing issues like lower fatigue strength and susceptibility to corrosion. Balancing performance, sustainability, and manufacturability is crucial when selecting between green steel and aluminum for automotive components.
Industry Adoption and Future Trends
Green steel is gaining traction in the automotive industry due to its lower carbon footprint compared to traditional steel, driven by innovations in hydrogen-based reduction processes. Aluminum remains favored for lightweight applications and exceptional corrosion resistance, with ongoing improvements in recycling rates enhancing its sustainability profile. Future trends indicate a hybrid material approach, integrating green steel and aluminum to optimize performance, cost, and environmental impact in vehicle manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material for Automotive Parts
Selecting green steel for automotive parts offers superior strength, recyclability, and lower carbon emissions compared to aluminum, making it ideal for structural components requiring durability. Aluminum provides lightweight benefits that improve fuel efficiency and reduce vehicle weight, suitable for non-structural or weight-sensitive applications. Evaluating performance needs, environmental impact, and cost efficiency guides automakers in choosing the optimal material for sustainable vehicle design.
Infographic: Green steel vs Aluminum for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com