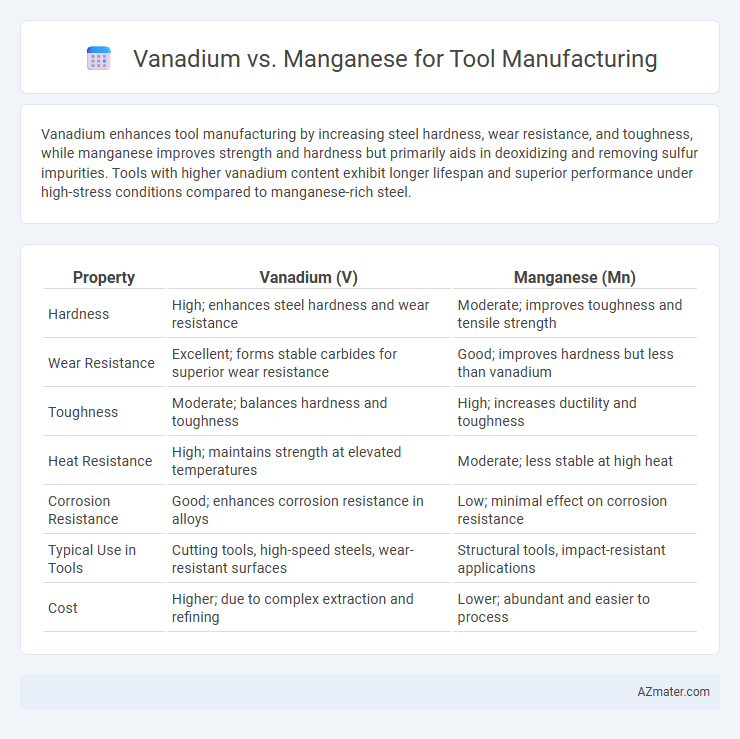
Vanadium enhances tool manufacturing by increasing steel hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, while manganese improves strength and hardness but primarily aids in deoxidizing and removing sulfur impurities. Tools with higher vanadium content exhibit longer lifespan and superior performance under high-stress conditions compared to manganese-rich steel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Vanadium (V) | Manganese (Mn) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High; enhances steel hardness and wear resistance | Moderate; improves toughness and tensile strength |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent; forms stable carbides for superior wear resistance | Good; improves hardness but less than vanadium |
| Toughness | Moderate; balances hardness and toughness | High; increases ductility and toughness |
| Heat Resistance | High; maintains strength at elevated temperatures | Moderate; less stable at high heat |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good; enhances corrosion resistance in alloys | Low; minimal effect on corrosion resistance |
| Typical Use in Tools | Cutting tools, high-speed steels, wear-resistant surfaces | Structural tools, impact-resistant applications |
| Cost | Higher; due to complex extraction and refining | Lower; abundant and easier to process |
Introduction to Vanadium and Manganese in Tool Manufacturing
Vanadium and manganese are critical alloying elements in tool manufacturing, enhancing steel's hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. Vanadium forms stable carbides that refine grain structure and improve high-temperature strength, essential for cutting and machining tools. Manganese increases steel's hardenability and tensile strength, while also acting as a deoxidizer, which improves the overall durability of tools used in heavy-duty applications.
Chemical Properties: Vanadium vs Manganese
Vanadium exhibits superior chemical stability and resistance to oxidation compared to manganese, making it ideal for enhancing tool steel hardness and durability. Manganese primarily improves strength and toughness by deoxidizing the alloy and stabilizing austenite during heat treatment. Vanadium's ability to form hard carbides significantly outperforms manganese in wear resistance, critical for high-performance cutting tools.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Vanadium enhances tool manufacturing by significantly increasing mechanical strength and wear resistance through carbide formation, resulting in superior toughness and durability. Manganese improves hardenability and impact strength but does not match vanadium's ability to refine grain structure and maintain hardness under high stress. Tools alloyed with vanadium exhibit longer service life and better performance in demanding industrial applications compared to manganese-enhanced tools.
Impact on Tool Hardness and Wear Resistance
Vanadium enhances tool hardness and wear resistance by forming stable carbides that improve edge retention and toughness in steel alloys. Manganese contributes to hardness by increasing hardenability and removing impurities, but its effect on wear resistance is less pronounced compared to vanadium. Steel with higher vanadium content typically demonstrates superior durability and longevity in cutting tools than manganese-enriched steel.
Corrosion Resistance: Vanadium vs Manganese
Vanadium enhances corrosion resistance in tool manufacturing by forming stable oxides that protect the metal surface from oxidation and wear. Manganese contributes to corrosion resistance by improving the steel's toughness and refining grain structure, but its protective oxide layer is less robust than vanadium's. Tools alloyed with vanadium typically exhibit superior durability and longevity in corrosive environments compared to manganese-containing counterparts.
Cost-Efficiency in Manufacturing Processes
Vanadium offers superior wear resistance and strength, reducing tool replacement frequency and lowering long-term manufacturing costs compared to manganese. Manganese, being less expensive initially, provides adequate toughness but may lead to faster tool degradation and increased downtime expenses. Optimizing alloy selection by balancing vanadium's durability with manganese's cost can enhance overall cost-efficiency in tool manufacturing processes.
Common Applications in Tool Production
Vanadium is widely used in tool manufacturing due to its ability to improve hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, making it ideal for cutting tools, drill bits, and high-performance industrial blades. Manganese primarily enhances the strength and toughness of steel, which is essential for impact-resistant tools such as hammers, wrenches, and heavy-duty construction equipment. Both elements are critical in alloy formulations, with vanadium favoring precision tooling and manganese suited for durability in rugged applications.
Machinability and Workability Differences
Vanadium enhances tool manufacturing by significantly improving machinability through increased hardness and wear resistance, allowing for longer tool life and better edge retention in cutting applications. Manganese contributes to workability by promoting toughness and reducing brittleness, which facilitates shaping and forming while maintaining strength. Vanadium's role is crucial for hardened tool components, whereas manganese excels in applications requiring ductility and impact resistance during manufacturing processes.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Vanadium and manganese both enhance tool manufacturing alloys, with vanadium improving wear resistance and toughness while manganese increases hardenability and strength. From an environmental perspective, vanadium extraction and processing pose concerns due to potential release of toxic compounds, necessitating strict controls, whereas manganese mining typically involves lower toxic emissions but can cause significant soil disruption. Safety considerations highlight that vanadium compounds may cause respiratory irritation and require careful handling, while manganese exposure at high levels can lead to neurological effects, emphasizing the importance of adequate protective measures in manufacturing environments.
Choosing the Right Alloy: Key Takeaways
Vanadium enhances tool steel by significantly improving hardness, wear resistance, and toughness due to its ability to form stable carbides, which is essential for cutting and high-impact applications. Manganese primarily contributes to increased strength and hardenability, while also aiding in deoxidation and sulfur fixation, making it crucial for improving overall steel durability. Selecting the right alloy depends on balancing vanadium's carbide-forming benefits with manganese's strength and toughness advantages to tailor tools for specific manufacturing requirements.
Infographic: Vanadium vs Manganese for Tool Manufacturing
 azmater.com
azmater.com