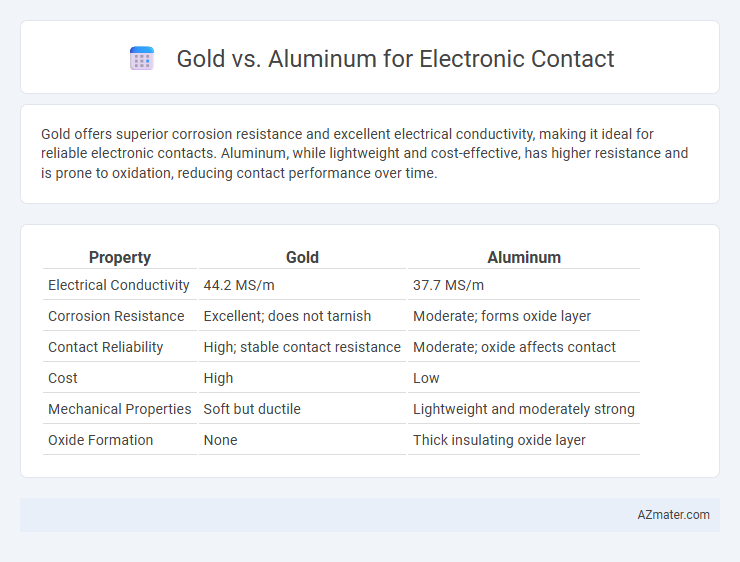
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for reliable electronic contacts. Aluminum, while lightweight and cost-effective, has higher resistance and is prone to oxidation, reducing contact performance over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gold | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 44.2 MS/m | 37.7 MS/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent; does not tarnish | Moderate; forms oxide layer |
| Contact Reliability | High; stable contact resistance | Moderate; oxide affects contact |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Mechanical Properties | Soft but ductile | Lightweight and moderately strong |
| Oxide Formation | None | Thick insulating oxide layer |
Introduction to Electronic Contact Materials
Gold and aluminum are prominent materials used for electronic contacts due to their distinct electrical and physical properties. Gold offers excellent corrosion resistance and superior conductivity, ensuring reliable signal transmission in critical applications. Aluminum provides a lightweight and cost-effective alternative with good conductivity but requires protective coatings to prevent oxidation and maintain performance.
Key Properties of Gold and Aluminum
Gold provides superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electronic contacts. Aluminum offers lightweight and cost-effective solutions but has lower conductivity and is more prone to oxidation, requiring protective coatings. The choice between gold and aluminum depends on balancing durability, conductivity, and cost in electronic contact applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Gold exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to aluminum, with a conductivity of approximately 44.2 million siemens per meter (MS/m) versus aluminum's 37.8 MS/m. This higher conductivity allows gold contacts to offer lower resistance and more reliable signal transmission in electronic components. Despite aluminum's cost-effectiveness and lighter weight, gold's stable conductivity and resistance to oxidation make it the preferred choice for critical electronic contacts.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Gold offers superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to aluminum, making it an ideal choice for electronic contacts in harsh environments. Its stable, non-reactive surface ensures consistent electrical conductivity over time, preventing performance degradation. Aluminum rapidly forms an insulating oxide layer that can impair signal quality and increase contact resistance, limiting its long-term reliability in critical electronic applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Gold exhibits superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electronic contacts requiring long-term reliability. Aluminum offers higher mechanical strength and lower weight but is prone to oxidation, which can degrade contact performance over time. The choice between gold and aluminum depends on balancing the need for durability against cost and mechanical robustness in specific electronic applications.
Cost Analysis: Gold vs Aluminum
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and reliable conductivity for electronic contacts but comes at a significantly higher material cost compared to aluminum. Aluminum provides a cost-effective alternative with lower weight and price, though it requires additional surface treatments to prevent oxidation and maintain efficient electrical performance. When analyzing total cost of ownership, gold's premium price is offset by lower maintenance and replacement rates, whereas aluminum demands frequent inspection and potential rework, influencing long-term expenses.
Solderability and Surface Compatibility
Gold offers superior solderability and excellent surface compatibility for electronic contacts due to its resistance to oxidation and corrosion, ensuring reliable and long-lasting connections. Aluminum, while lightweight and cost-effective, presents challenges in soldering because of its rapid oxide layer formation, which inhibits solder flow and adhesion without specialized surface treatments or fluxes. For high-performance electronic applications demanding durability and consistent electrical conductivity, gold remains the preferred contact material over aluminum.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Gold is favored for electronic contacts in modern electronics due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, ensuring reliable signal transmission in critical applications like smartphones, computers, and aerospace systems. Aluminum, while less conductive and more prone to oxidation, offers a lightweight and cost-effective alternative suitable for large-scale applications such as power distribution networks and certain consumer electronics. The choice between gold and aluminum contacts depends on performance requirements, with gold being preferred for high-reliability and long-term durability, and aluminum chosen for budget-conscious, weight-sensitive designs.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Gold offers exceptional corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it highly reliable for electronic contacts with extended lifecycle durability. Although gold mining has significant environmental impacts, its superior longevity reduces the frequency of replacements, thereby minimizing electronic waste and associated resource consumption. Aluminum, while abundant and lightweight, is prone to oxidation which can impair conductivity and shorten contact lifespan, potentially leading to increased material use and environmental burden due to more frequent component replacement.
Choosing the Right Material for Specific Electronic Contacts
Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability electronic contacts in critical applications such as aerospace and medical devices. Aluminum, while more cost-effective and lightweight, has lower conductivity and can form insulating oxide layers, limiting its use to less demanding or cost-sensitive contacts. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints to ensure optimal contact functionality and longevity.
Infographic: Gold vs Aluminum for Electronic Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com