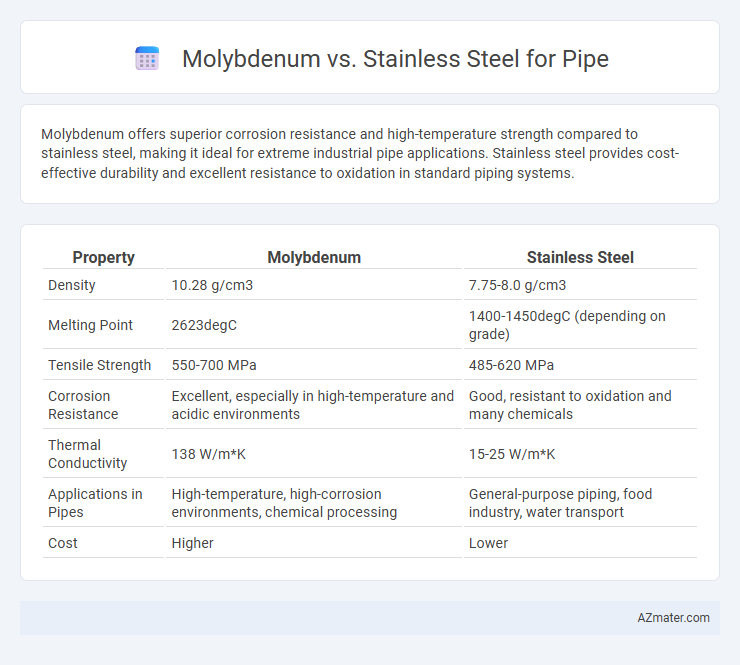
Molybdenum offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to stainless steel, making it ideal for extreme industrial pipe applications. Stainless steel provides cost-effective durability and excellent resistance to oxidation in standard piping systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 10.28 g/cm3 | 7.75-8.0 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2623degC | 1400-1450degC (depending on grade) |
| Tensile Strength | 550-700 MPa | 485-620 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, especially in high-temperature and acidic environments | Good, resistant to oxidation and many chemicals |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m*K | 15-25 W/m*K |
| Applications in Pipes | High-temperature, high-corrosion environments, chemical processing | General-purpose piping, food industry, water transport |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction: Molybdenum vs Stainless Steel for Pipe
Molybdenum-enhanced stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to standard stainless steel, making it ideal for demanding piping applications in chemical and petrochemical industries. Stainless steel, typically grades 304 or 316, provides excellent durability and cost-effectiveness for general piping needs but may lack the enhanced performance of molybdenum-alloyed variants under aggressive environmental conditions. Selecting between molybdenum and stainless steel pipes depends on the specific requirements of chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and budget constraints in industrial piping systems.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Molybdenum enhances stainless steel by improving corrosion resistance and strength, especially in aggressive environments containing chlorides and high temperatures. Stainless steel typically contains iron, chromium (10-30%), nickel (up to 35%), and varying amounts of molybdenum (0-7%), which significantly boosts pitting and crevice corrosion resistance. Pure molybdenum pipes, with a chemical composition primarily of molybdenum (99.95%), offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability but lack the toughness and weldability found in stainless steel alloys.
Mechanical Properties Overview
Molybdenum exhibits superior tensile strength and high-temperature resistance compared to stainless steel, making it ideal for demanding industrial pipe applications. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and good ductility but generally has lower yield strength and thermal stability than molybdenum alloys. The choice between molybdenum and stainless steel pipes depends on specific mechanical property requirements such as creep resistance, hardness, and operational environment temperature.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
Molybdenum enhances stainless steel's corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and acidic environments, by forming a protective oxide layer that prevents pitting and crevice corrosion. Stainless steel grades with higher molybdenum content, such as 316 and 904L, exhibit superior durability in marine, chemical processing, and high-temperature applications. Compared to standard stainless steel, molybdenum-alloyed variants significantly extend pipe lifespan by resisting localized corrosion and chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking.
Temperature and Thermal Performance
Molybdenum exhibits superior high-temperature strength and thermal stability compared to stainless steel, maintaining structural integrity in environments exceeding 1,000degC, ideal for extreme heat applications in pipelines. Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity but typically withstands temperatures up to 870degC before losing mechanical properties. Molybdenum's low thermal expansion and high melting point minimize thermal stress and deformation, making it more suitable for high-temperature pipe systems in power plants and chemical processing industries.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Molybdenum pipes exhibit higher initial material costs compared to stainless steel, driven by molybdenum's scarcity and specialized production processes. Stainless steel offers more cost-effective options with widespread availability and lower manufacturing expenses, making it a preferred choice in budget-sensitive projects. Economic considerations must weigh the long-term durability and corrosion resistance of molybdenum, which can reduce maintenance costs and extend service life, potentially offsetting its upfront price premium.
Typical Applications in Industry
Molybdenum-enhanced stainless steel pipes excel in high-temperature and corrosion-resistant applications, such as chemical processing, petrochemical industries, and power plants, due to their superior strength and resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. Stainless steel pipes without molybdenum are commonly used in plumbing, food processing, and architectural applications where moderate corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. Industrial environments requiring optimal durability in aggressive conditions frequently select molybdenum-containing stainless steel for critical piping systems.
Durability and Longevity
Molybdenum-enhanced stainless steel exhibits superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to standard stainless steel, particularly in harsh industrial environments with high temperatures and chemical exposure. The addition of molybdenum significantly improves resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, extending the pipe's service life in aggressive media. This enhanced alloy composition ensures longer longevity and reduced maintenance costs for piping systems in chemical processing, oil and gas, and marine applications.
Maintenance and Service Life
Molybdenum-enhanced stainless steel pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance and higher temperature tolerance, significantly reducing maintenance frequency compared to standard stainless steel. The molybdenum content strengthens the passive oxide layer, extending service life in aggressive environments such as chemical processing and marine applications. Stainless steel pipes without molybdenum require more frequent inspections and repairs due to increased susceptibility to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Molybdenum pipes excel in high-temperature and corrosive environments due to their superior strength and oxidation resistance, making them ideal for chemical processing or aerospace applications. Stainless steel pipes offer excellent overall durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for plumbing, food processing, and general industrial use. Selecting the right pipe material depends on specific operational conditions, budget constraints, and required longevity, with molybdenum preferred for specialized, demanding environments and stainless steel for versatile, everyday applications.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Stainless Steel for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com