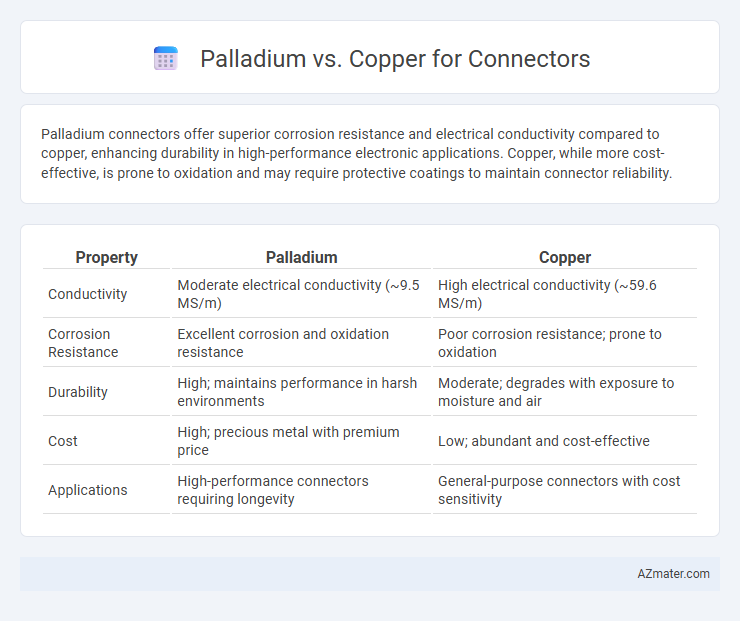
Palladium connectors offer superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to copper, enhancing durability in high-performance electronic applications. Copper, while more cost-effective, is prone to oxidation and may require protective coatings to maintain connector reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Palladium | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Moderate electrical conductivity (~9.5 MS/m) | High electrical conductivity (~59.6 MS/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance | Poor corrosion resistance; prone to oxidation |
| Durability | High; maintains performance in harsh environments | Moderate; degrades with exposure to moisture and air |
| Cost | High; precious metal with premium price | Low; abundant and cost-effective |
| Applications | High-performance connectors requiring longevity | General-purpose connectors with cost sensitivity |
Introduction to Palladium and Copper in Connectors
Palladium and copper are essential metals used in electrical connectors, each offering unique benefits. Palladium provides excellent corrosion resistance and high conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability and high-performance applications. Copper, known for its superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in connectors where durability and efficient current flow are critical.
Material Properties: Palladium vs Copper
Palladium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity compared to copper, making it ideal for connectors in harsh environments. Copper offers higher electrical conductivity and better thermal conductivity but is prone to oxidation and wear over time. The choice between palladium and copper depends on balancing durability and conductivity requirements for specific connector applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it highly suitable for high-reliability connector applications where signal integrity is critical. Copper exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among common conductive metals (approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m), surpassing palladium's conductivity (~9.5 x 10^6 S/m), which leads to lower contact resistance and improved current-carrying capability. While copper connectors provide optimal electrical performance, palladium coatings enhance durability and prevent oxidation, balancing conductivity with long-term reliability in demanding electronic environments.
Corrosion Resistance Differences
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for connectors in harsh environments where oxidation and tarnish can degrade performance. Copper connectors are prone to surface oxidation and corrosion, which can result in increased contact resistance and signal loss over time. The enhanced chemical stability of palladium ensures longer-lasting conductivity and reliability in electronic connections.
Cost Analysis: Palladium vs Copper
Copper connectors offer a cost-effective solution with significantly lower material expenses compared to palladium, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications. Palladium connectors, while pricier due to higher raw material and processing costs, provide superior corrosion resistance and longevity, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals copper's upfront affordability contrasts with palladium's long-term reliability benefits in connector performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Palladium offers superior mechanical strength compared to copper, enabling connectors to withstand higher stress and repeated mating cycles without deformation. Its excellent corrosion resistance enhances long-term durability, reducing the risk of connector failure in harsh environments. Copper, while highly conductive, tends to deform more easily under mechanical stress, which can compromise connector longevity in demanding applications.
Applications in Connector Technology
Palladium offers superior corrosion resistance and stable electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-reliability connectors in aerospace, medical devices, and automotive electronics. Copper excels in cost-effectiveness and excellent electrical conductivity, commonly used in consumer electronics and general electrical connectors where budget and performance balance is essential. The choice between palladium and copper in connector technology hinges on application-specific requirements such as environmental durability, electrical performance, and cost constraints.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Palladium connectors offer superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, reducing electronic waste compared to copper connectors, which are more prone to oxidation and degradation. Copper mining and processing contribute significantly to environmental pollution and habitat disruption, while palladium, despite being rarer, supports more sustainable usage through higher durability and recyclability. Choosing palladium connectors enhances sustainability by minimizing material replacement frequency and lowering the overall carbon footprint associated with electronic components.
Performance in High-Frequency Environments
Palladium connectors exhibit superior corrosion resistance and stable electrical conductivity, making them highly effective in high-frequency environments where signal integrity is critical. Copper connectors offer excellent electrical conductivity but are more prone to oxidation, potentially leading to signal degradation over time. In applications demanding consistent high-frequency performance, palladium's durability and resistance to signal loss often outweigh copper's initial conductivity advantages.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Connectors
Palladium connectors offer superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making them ideal for high-reliability applications in harsh environments. Copper connectors provide outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity at a more cost-effective price, suitable for general-purpose uses where durability demands are moderate. Assess factors such as environmental conditions, electrical performance requirements, and budget constraints to select the optimal material for your connector needs.
Infographic: Palladium vs Copper for Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com