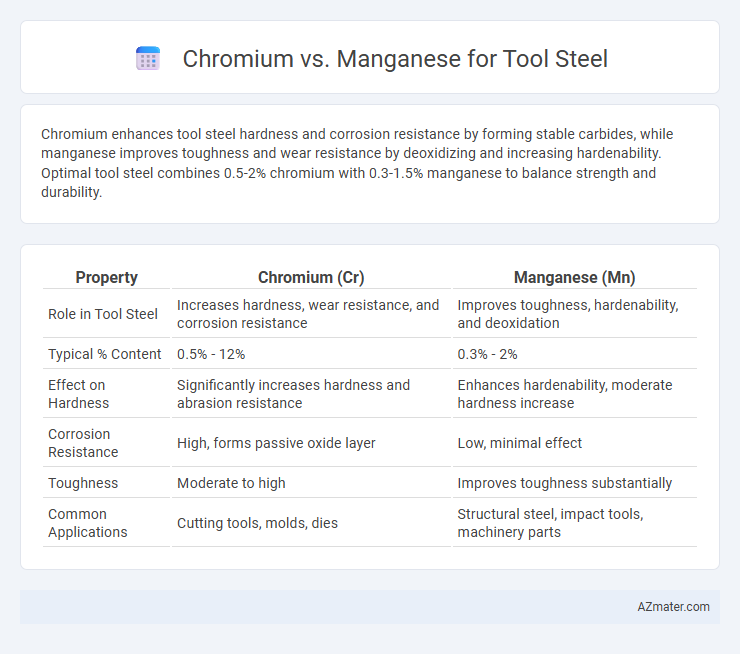
Chromium enhances tool steel hardness and corrosion resistance by forming stable carbides, while manganese improves toughness and wear resistance by deoxidizing and increasing hardenability. Optimal tool steel combines 0.5-2% chromium with 0.3-1.5% manganese to balance strength and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chromium (Cr) | Manganese (Mn) |
|---|---|---|
| Role in Tool Steel | Increases hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance | Improves toughness, hardenability, and deoxidation |
| Typical % Content | 0.5% - 12% | 0.3% - 2% |
| Effect on Hardness | Significantly increases hardness and abrasion resistance | Enhances hardenability, moderate hardness increase |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, forms passive oxide layer | Low, minimal effect |
| Toughness | Moderate to high | Improves toughness substantially |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, molds, dies | Structural steel, impact tools, machinery parts |
Introduction to Tool Steel Alloying Elements
Chromium and manganese are essential alloying elements in tool steel, significantly enhancing hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. Chromium contributes to corrosion resistance and forms hard chromium carbides that improve abrasion resistance, while manganese acts as a deoxidizer and counteracts brittleness by improving hardenability and tensile strength. The balanced combination of chromium and manganese optimizes tool steel performance for cutting, shaping, and impact applications.
Understanding Chromium’s Role in Tool Steel
Chromium significantly enhances tool steel by increasing hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, contributing to prolonged tool life in demanding applications. It forms hard carbides that improve cutting performance and toughness, essential for high-speed and impact tools. In comparison, manganese primarily boosts hardenability and deoxidation, but chromium's role is vital for superior durability and heat resistance in tool steel.
Key Benefits of Manganese in Tool Steel
Manganese in tool steel significantly enhances toughness and wear resistance by improving hardenability and reducing brittleness, essential for high-impact applications. It acts as a deoxidizer and combines with sulfur to form manganese sulfides, which improve machinability and reduce the risk of cracking during heat treatment. Compared to chromium, manganese offers superior shock resistance and helps maintain the structural integrity of tool steel under heavy-duty conditions.
Hardness and Wear Resistance: Chromium vs Manganese
Chromium significantly enhances tool steel hardness by forming hard carbides, improving wear resistance in high-stress applications. Manganese contributes to toughness and hardness through a solid solution strengthening effect but offers less wear resistance compared to chromium. The superior carbide formation of chromium results in better durability and prolonged tool life in abrasive environments.
Impact on Toughness and Ductility
Chromium enhances tool steel's toughness by forming hard carbides that improve wear resistance without severely compromising ductility. Manganese contributes to toughness by promoting a uniform microstructure and increasing hardenability, which helps reduce brittleness and maintain ductility. Balancing chromium and manganese levels is crucial to achieving optimal toughness and ductility in tool steel for impact-resistant applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Element Performs Better?
Manganese enhances the toughness and hardness of tool steel but offers limited corrosion resistance compared to chromium. Chromium significantly improves corrosion resistance by forming a passive oxide layer that protects the steel surface from rust and oxidation. In tool steel applications where corrosion resistance is critical, chromium outperforms manganese due to its superior ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Effect on Hardenability in Tool Steels
Chromium significantly increases the hardenability of tool steels by promoting the formation of chromium carbides, which enhances wear resistance and strength at elevated temperatures. Manganese improves hardenability by stabilizing austenite and refining grain size, leading to better toughness and impact resistance in tool steels. The combination of chromium and manganese creates a balanced microstructure that optimizes hardenability and performance in demanding cutting and shaping applications.
Influence on Machinability and Workability
Chromium significantly enhances tool steel's hardness and wear resistance, improving machining efficiency by maintaining edge sharpness longer than manganese. Manganese primarily increases toughness and hardenability, but excessive amounts can reduce machinability by causing increased work hardening during cutting. Optimizing chromium levels yields better workability and surface finish, while controlled manganese additions balance impact strength without severely compromising machinability.
Common Tool Steel Grades with Chromium and Manganese
Common tool steel grades such as A2 and D2 prominently feature chromium, enhancing hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, while manganese contributes to toughness and impact strength in grades like O1 and W1. Chromium concentrations typically range from 0.9% to 13%, significantly improving hardenability and edge retention, whereas manganese content varies from 0.3% to 1.4%, optimizing deoxidation and grain refinement. The combination of chromium and manganese in tool steels balances hardness and durability, making them suitable for cutting, shaping, and forming applications.
Choosing Between Chromium and Manganese for Specific Applications
Chromium enhances tool steel by improving hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools and high-stress applications. Manganese increases toughness and impact resistance, which is beneficial for tools subjected to shock loading and abrasive conditions. Selecting between chromium and manganese depends on prioritizing hardness and surface durability versus toughness and shock absorption in the intended tool steel application.
Infographic: Chromium vs Manganese for Tool Steel
 azmater.com
azmater.com