Brass fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine and electrical applications. Iron fasteners provide higher tensile strength and cost efficiency, suitable for heavy-duty structural uses.
Table of Comparison
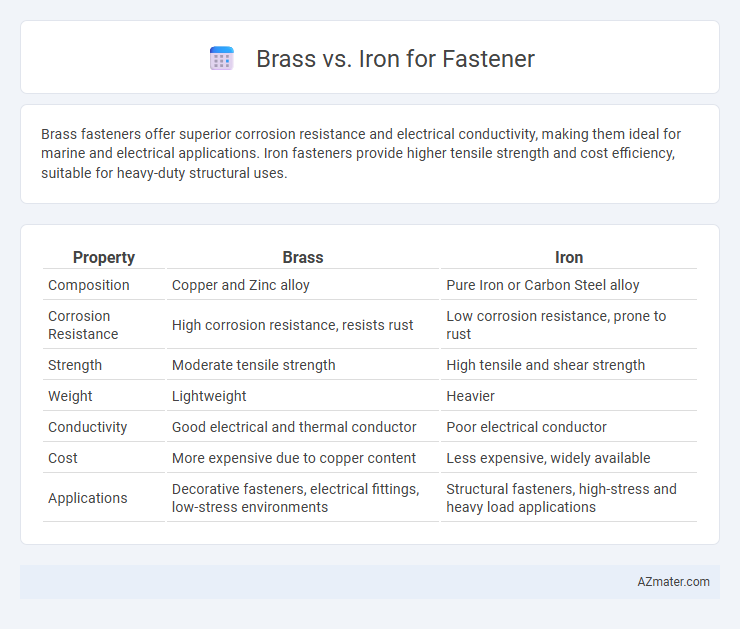
| Property | Brass | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Zinc alloy | Pure Iron or Carbon Steel alloy |
| Corrosion Resistance | High corrosion resistance, resists rust | Low corrosion resistance, prone to rust |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile and shear strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Conductivity | Good electrical and thermal conductor | Poor electrical conductor |
| Cost | More expensive due to copper content | Less expensive, widely available |
| Applications | Decorative fasteners, electrical fittings, low-stress environments | Structural fasteners, high-stress and heavy load applications |
Introduction to Brass and Iron Fasteners
Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine, electrical, and decorative applications. Iron fasteners, known for their high tensile strength and durability, are commonly used in construction and heavy-duty industrial settings. Choosing between brass and iron fasteners depends on environmental exposure, mechanical requirements, and aesthetic preferences.
Material Composition and Properties
Brass fasteners consist primarily of copper and zinc, offering excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine and electrical applications. Iron fasteners, typically made of carbon steel or wrought iron, provide higher tensile strength and durability but are prone to rust without proper coatings. The choice between brass and iron fasteners depends on the balance between corrosion resistance and mechanical strength required for the specific application.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Brass fasteners offer moderate strength with excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for decorative and marine applications where durability in harsh environments is essential. Iron fasteners, typically stronger and more impact-resistant, excel in heavy-duty construction tasks but are prone to rust without protective coatings. Selecting between brass and iron depends on balancing the need for mechanical strength against long-term durability in specific environmental conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: Brass vs Iron
Brass fasteners exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to iron fasteners due to their copper and zinc alloy composition, which naturally resists oxidation and rust in harsh environments. Iron fasteners are prone to rust and degradation when exposed to moisture and oxygen, often requiring protective coatings such as galvanization or painting to enhance durability. Brass fasteners maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appeal in marine, electrical, and outdoor applications where corrosion resistance is critical.
Cost and Availability
Brass fasteners typically cost more than iron fasteners due to the higher price of copper and zinc alloys and their more complex manufacturing process. Iron fasteners are widely available and produced in large quantities, making them generally more economical and accessible for various industrial applications. The choice between brass and iron fasteners depends on budget constraints and the specific environment, with iron being the more cost-effective and readily available option.
Aesthetic Appeal and Applications
Brass fasteners offer a distinctive golden hue and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for decorative applications such as furniture, marine hardware, and architectural detailing where visual appeal is paramount. Iron fasteners, typically steel-based, provide superior strength and durability but lack the inherent shine and aesthetic charm of brass, often requiring coatings to prevent rust in structural or industrial applications. Choosing brass enhances ornamental qualities and longevity in visible, moisture-prone environments, while iron suits heavy-duty uses requiring mechanical strength over appearance.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Brass fasteners are significantly lighter than iron, offering enhanced ease of handling and reduced overall weight in applications where weight is critical. Iron fasteners provide greater strength but are heavier, which can impact installation speed and increase fatigue during manual handling. Choosing brass over iron improves corrosion resistance and machinability while maintaining sufficient durability for lighter-duty fastening needs.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Brass fasteners exhibit excellent electrical conductivity, making them suitable for electrical applications requiring efficient current flow and corrosion resistance. Iron fasteners, with lower electrical conductivity, are less ideal for electrical uses but offer higher mechanical strength and durability. When thermal conductivity is critical, brass fasteners provide superior heat dissipation compared to iron, enhancing performance in heat-sensitive environments.
Typical Uses in Different Industries
Brass fasteners are preferred in electrical and marine industries due to their excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for electronic components and marine hardware. Iron fasteners dominate construction and automotive sectors because of their high strength and affordability, suitable for structural frameworks and machinery assembly. The choice hinges on specific industry demands, balancing durability requirements with environmental exposure.
Choosing the Right Fastener Material
Selecting the right fastener material depends on factors like corrosion resistance, strength, and application environment. Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine or electrical applications, while iron fasteners provide superior strength and durability suited for structural uses. Understanding the requirements of your project ensures optimal performance and longevity of the fasteners.
Infographic: Brass vs Iron for Fastener
 azmater.com
azmater.com