Cast iron roofing offers exceptional durability and resistance to harsh weather, while zinc provides superior corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan with low maintenance requirements. Choosing between cast iron and zinc depends on budget, climate, and desired aesthetic for roofing projects.
Table of Comparison
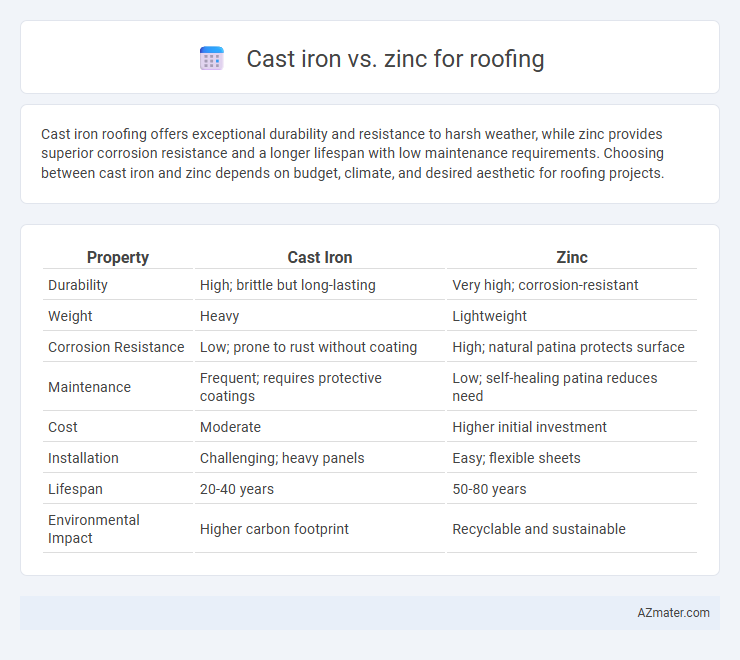
| Property | Cast Iron | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High; brittle but long-lasting | Very high; corrosion-resistant |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low; prone to rust without coating | High; natural patina protects surface |
| Maintenance | Frequent; requires protective coatings | Low; self-healing patina reduces need |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Installation | Challenging; heavy panels | Easy; flexible sheets |
| Lifespan | 20-40 years | 50-80 years |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Recyclable and sustainable |
Introduction to Cast Iron and Zinc Roofing
Cast iron roofing offers exceptional durability and resistance to fire, making it ideal for long-lasting structures. Zinc roofing provides natural corrosion resistance and develops a protective patina over time, enhancing its lifespan while requiring minimal maintenance. Both materials contribute unique aesthetic and functional benefits suited for diverse architectural styles and environmental conditions.
Material Properties: Cast Iron vs. Zinc
Cast iron roofing offers exceptional durability and high compressive strength but is prone to rust and requires protective coatings, while zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance with a natural patina that develops over time, enhancing longevity. Zinc is lighter and more malleable, allowing for easier installation and complex design adaptability compared to the brittle nature of cast iron. Thermal expansion rates differ, with zinc accommodating temperature fluctuations better, reducing risks of cracking in roofing applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cast iron roofing offers exceptional durability with a lifespan of up to 50 years, resisting impact and harsh weather conditions effectively. Zinc roofing provides superior corrosion resistance and self-healing properties, often lasting between 80 to 100 years with minimal maintenance. Both materials outperform traditional roofing options, but zinc's longevity and low maintenance make it a preferred choice for sustainable roofing solutions.
Weather Resistance and Corrosion Performance
Cast iron roofing offers exceptional weather resistance due to its dense, durable composition, effectively withstanding heavy rain, wind, and extreme temperatures. Zinc roofing excels in corrosion performance with its self-healing patina that protects against rust and environmental pollutants, ensuring long-lasting durability in coastal and industrial settings. Both materials provide strong resistance to weather elements, but zinc's superior corrosion resistance makes it ideal for harsh, moisture-prone environments.
Installation Process and Techniques
Cast iron roofing requires precise handling and heavy-duty equipment for installation due to its weight and rigidity, often involving specialized fastening methods like bolting or welding to ensure durability. Zinc roofing, being lighter and more malleable, allows for easier cutting, shaping, and fastening using techniques such as soldering or standing seam installation, which enhances weather resistance and longevity. Both materials demand skilled labor, but zinc's flexibility typically results in faster installation times and reduced structural support requirements compared to cast iron.
Cost Implications and Return on Investment
Cast iron roofing offers superior durability and longevity, often lasting over 50 years, which translates to higher upfront costs but reduced maintenance expenses and a stronger return on investment over time. Zinc roofing, being lighter and easier to install, generally has a lower initial cost and excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring moderate maintenance expenses and a reasonable ROI. Evaluating the total life cycle cost, including installation, maintenance, and potential energy savings, zinc may provide better immediate budget benefits, while cast iron delivers long-term financial value through durability and resilience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cast iron roofing offers excellent durability and recyclability, reducing long-term environmental impact through its longevity and potential for reuse in new materials. Zinc roofing features natural corrosion resistance and is highly sustainable due to its low maintenance requirements and nearly 100% recyclability, minimizing resource extraction and waste. Both metals contribute significantly to eco-friendly roofing solutions by supporting circular economy principles and lowering carbon footprints over their lifecycle.
Maintenance and Repair Needs
Cast iron roofing requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, often needing protective coatings and prompt repairs of any chips or cracks to maintain durability. Zinc roofing offers superior resistance to corrosion and typically demands less frequent maintenance, with natural patina formation acting as a protective layer that reduces repair needs. Both materials benefit from periodic inspections, but zinc's low upkeep makes it a preferred choice for long-term, low-maintenance roofing solutions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Cast iron roofing offers a classic, rustic aesthetic with its heavy, textured surface and natural patina that enhances vintage or industrial-style architecture. Zinc roofing provides superior design flexibility due to its malleability, allowing for intricate shapes, seamless seams, and modern, sleek finishes that complement contemporary or minimalist structures. Both materials enable unique visual expressions, but zinc's ability to be easily molded and combined with various coatings offers greater customization options for innovative roofing designs.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Roofing Project
Cast iron offers exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting roofing projects in harsh weather conditions, while zinc provides superior flexibility and self-healing properties that reduce maintenance needs. Zinc's lightweight nature eases installation and lessens structural load, whereas cast iron's robust strength suits applications requiring heavy-duty performance. Assessing environmental factors, budget, and project lifespan helps determine the best roofing material tailored to your specific requirements.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Zinc for Roofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com