Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for decorative and electrical applications. Titanium fasteners provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance in harsh environments, suitable for aerospace and marine uses.
Table of Comparison
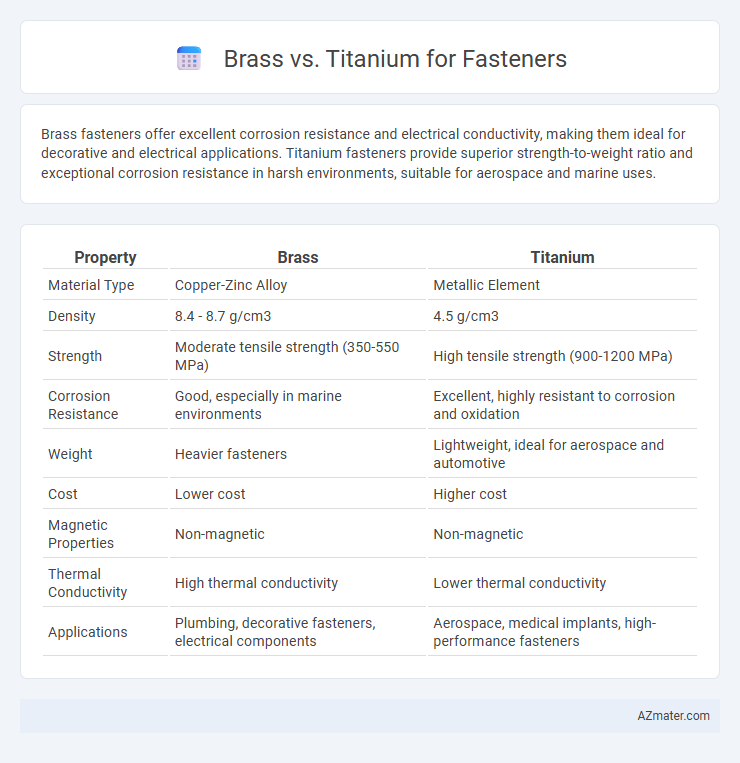
| Property | Brass | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copper-Zinc Alloy | Metallic Element |
| Density | 8.4 - 8.7 g/cm3 | 4.5 g/cm3 |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength (350-550 MPa) | High tensile strength (900-1200 MPa) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, especially in marine environments | Excellent, highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation |
| Weight | Heavier fasteners | Lightweight, ideal for aerospace and automotive |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity |
| Applications | Plumbing, decorative fasteners, electrical components | Aerospace, medical implants, high-performance fasteners |
Introduction to Brass and Titanium Fasteners
Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for decorative and electrical applications. Titanium fasteners provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional resistance to extreme environments, commonly used in aerospace and marine industries. Both materials deliver specific advantages depending on the performance requirements and environmental conditions of the fastening application.
Material Properties of Brass Fasteners
Brass fasteners are prized for their excellent corrosion resistance, non-magnetic properties, and superior electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine and electrical applications. Their moderate tensile strength combined with good ductility allows for easy machining and forming while maintaining durability in diverse environments. Compared to titanium, brass offers less strength but provides better corrosion resistance in saltwater and favorable thermal and acoustic conductivity, enhancing performance in specialized uses.
Material Properties of Titanium Fasteners
Titanium fasteners offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and high tensile strength compared to brass, making them ideal for demanding applications in aerospace and marine environments. Their superior resistance to fatigue and extreme temperatures ensures long-lasting performance under stress and harsh conditions. While brass fasteners provide good machinability and electrical conductivity, titanium fasteners excel in durability and structural integrity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium fasteners offer significantly higher tensile strength compared to brass, making them ideal for high-stress applications. Brass fasteners exhibit excellent corrosion resistance but tend to deform under heavy loads due to their lower mechanical strength. Titanium's superior durability and resistance to fatigue make it a preferred choice for aerospace and automotive industries where reliability under extreme conditions is critical.
Corrosion Resistance: Brass vs Titanium
Titanium fasteners exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to brass, especially in harsh environments like marine or chemical applications where exposure to saltwater and acidic conditions is prevalent. Brass fasteners, while resistant to corrosion in mild environments, tend to tarnish and degrade over time when exposed to aggressive elements, leading to potential weakening. The oxide layer formed naturally on titanium surfaces provides long-lasting protection, making titanium fasteners ideal for demanding conditions requiring durability and longevity.
Weight Differences Between Brass and Titanium
Brass fasteners typically weigh more than titanium fasteners due to the higher density of brass, which is approximately 8.5 g/cm3 compared to titanium's density of around 4.5 g/cm3. This significant weight difference makes titanium fasteners preferable in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace and automotive industries. Choosing titanium over brass can reduce component weight by nearly 40-50%, enhancing overall efficiency and performance.
Cost Considerations for Brass and Titanium Fasteners
Brass fasteners generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to titanium, making them a budget-friendly option for applications where moderate strength and corrosion resistance are sufficient. Titanium fasteners, while more expensive initially, provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, often resulting in lower lifecycle costs for high-performance or critical applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership includes factors such as durability, maintenance, and environmental conditions, where titanium's long-term benefits can justify the higher initial investment.
Typical Applications for Brass Fasteners
Brass fasteners are commonly used in marine, electrical, and decorative applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and attractive appearance. These fasteners are ideal for plumbing fixtures, musical instruments, and architectural hardware where non-magnetic properties and aesthetic appeal are essential. Their moderate strength and ease of machining make them suitable for light to medium load fastening in environments requiring resistance to water and chemical exposure.
Typical Applications for Titanium Fasteners
Titanium fasteners are commonly utilized in aerospace, marine, and medical industries due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. These fasteners perform exceptionally in environments exposed to saltwater, extreme temperatures, and chemical exposure, making them suitable for aircraft structures, shipbuilding, and surgical implants. Their durability and non-magnetic properties also make titanium fasteners ideal for electronic equipment and high-performance automotive applications.
Choosing the Right Fastener: Brass or Titanium
Choosing the right fastener depends on the application requirements, where brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, ideal for marine and electrical environments. Titanium fasteners provide superior strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional corrosion resistance, and high-temperature tolerance, making them suitable for aerospace and industrial uses. Consider factors such as mechanical load, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency to determine whether brass or titanium fasteners best meet the performance and durability needs of your project.
Infographic: Brass vs Titanium for Fastener
 azmater.com
azmater.com