Alloy steel pipes offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness compared to cast iron pipes, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Cast iron pipes provide excellent durability and cost-effectiveness but are more brittle and prone to cracking under stress or impact.
Table of Comparison
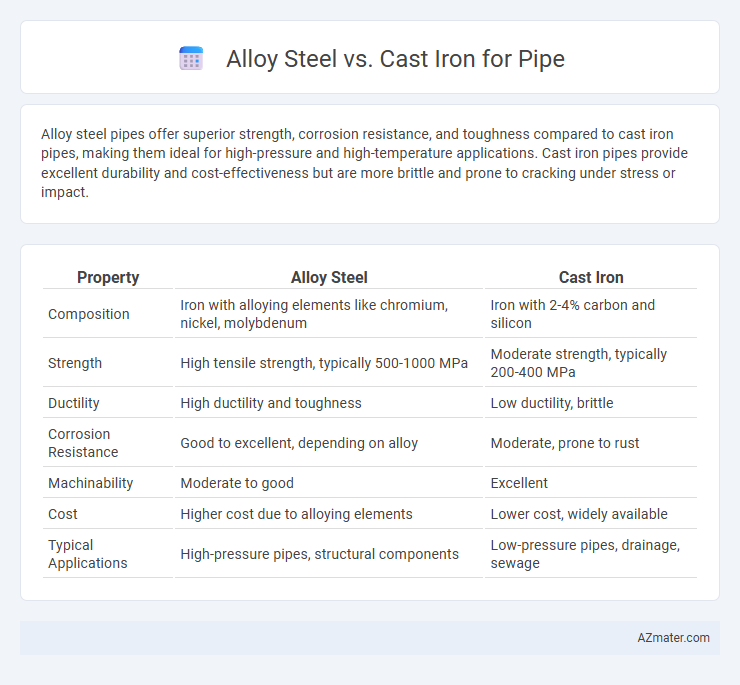
| Property | Alloy Steel | Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron with alloying elements like chromium, nickel, molybdenum | Iron with 2-4% carbon and silicon |
| Strength | High tensile strength, typically 500-1000 MPa | Moderate strength, typically 200-400 MPa |
| Ductility | High ductility and toughness | Low ductility, brittle |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good to excellent, depending on alloy | Moderate, prone to rust |
| Machinability | Moderate to good | Excellent |
| Cost | Higher cost due to alloying elements | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Applications | High-pressure pipes, structural components | Low-pressure pipes, drainage, sewage |
Introduction to Pipe Material Selection
Alloy steel pipes offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability compared to cast iron, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Cast iron pipes, known for their excellent compressive strength and cost-effectiveness, are typically used in low-pressure water and sewage systems. Selecting the appropriate pipe material depends on factors such as mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Overview of Alloy Steel and Cast Iron
Alloy steel pipes are engineered with added elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, enhancing their strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Cast iron pipes, primarily composed of iron, carbon, and silicon, offer excellent compressive strength and durability but are more brittle and susceptible to fracture under impact or tension. The choice between alloy steel and cast iron pipes depends on the specific requirements of performance, durability, and environmental conditions in industrial and infrastructure projects.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Alloy steel pipes contain a higher percentage of alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which enhance corrosion resistance and strength compared to cast iron. Cast iron primarily consists of iron, carbon (2-4%), and silicon, resulting in brittleness and lower tensile strength. The variable chemical composition of alloy steel provides superior mechanical properties and durability for high-pressure and temperature applications.
Mechanical Properties and Strength
Alloy steel pipes exhibit superior mechanical properties and higher tensile and yield strength compared to cast iron, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Cast iron pipes possess excellent compressive strength and wear resistance but tend to be brittle, limiting their flexibility and impact resistance. The enhanced ductility and toughness of alloy steel enable better performance under dynamic loads, whereas cast iron's rigidity makes it more prone to cracking under stress.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Alloy steel pipes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to cast iron due to their enhanced chemical composition, which often includes chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, providing excellent protection against rust and chemical degradation. Cast iron, while durable, is prone to corrosion over time, especially in acidic or moist environments, leading to potential structural weakening and shorter service life. The higher mechanical strength and improved resistance to wear and environmental factors make alloy steel pipes significantly more durable for demanding industrial applications.
Temperature and Pressure Handling
Alloy steel excels in handling high temperatures and pressures compared to cast iron, making it ideal for demanding pipe applications in industries like oil and gas or power generation. Its enhanced strength and toughness allow alloy steel pipes to maintain integrity under extreme thermal cycling and high-pressure conditions. Cast iron, while corrosion-resistant and cost-effective, typically fails to perform reliably above moderate temperatures and pressures due to brittleness and lower tensile strength.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Alloy steel pipes generally have higher upfront costs compared to cast iron pipes due to their superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, which reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Cast iron pipes are less expensive initially but may incur greater long-term costs because of their susceptibility to corrosion, brittleness, and shorter lifespan, leading to frequent repairs or replacements. Economic considerations favor alloy steel in projects demanding longevity and low maintenance, while cast iron might be suitable for budget-constrained applications with less critical performance requirements.
Applications in Various Industries
Alloy steel pipes exhibit exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-pressure applications in the oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation industries. Cast iron pipes, known for their rigidity and durability, are widely used in water distribution, sewage systems, and underground infrastructure projects. The choice between alloy steel and cast iron pipes depends on factors such as operating pressure, environmental conditions, and required lifespan in diverse industrial applications.
Installation, Maintenance, and Longevity
Alloy steel pipes offer superior installation flexibility thanks to their higher tensile strength and corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent fittings or replacements. Maintenance of alloy steel is generally lower due to its enhanced durability and resistance to wear, whereas cast iron pipes require regular inspections to address brittleness and potential cracking. Alloy steel also boasts greater longevity in demanding environments, outperforming cast iron which is prone to rust and degradation over time under similar conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Alloy steel pipes offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and flexibility, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Cast iron pipes excel in durability and cost-effectiveness for low-pressure water and sewage systems but are more brittle and prone to corrosion. Selecting the right pipe material depends on the specific operational demands, environmental conditions, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Alloy steel vs Cast iron for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com